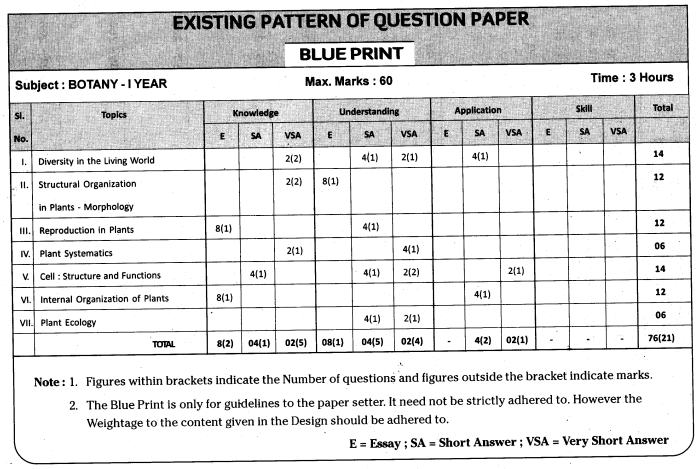
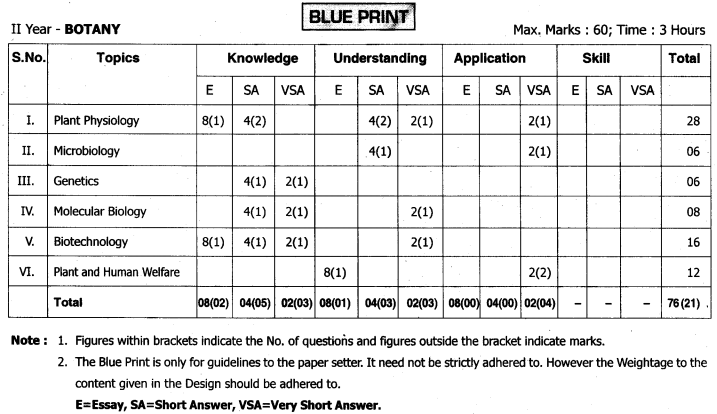
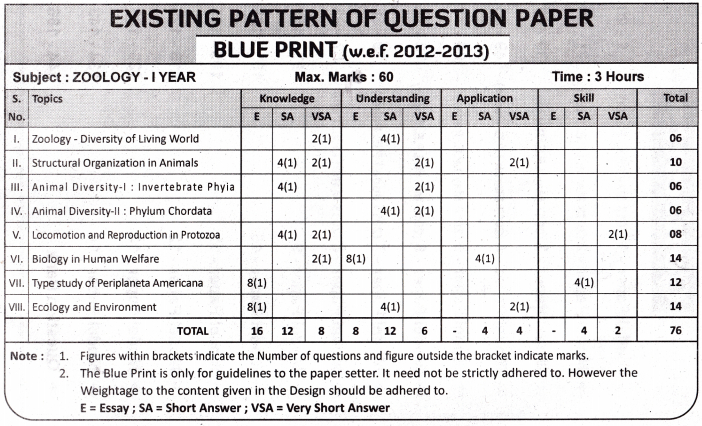
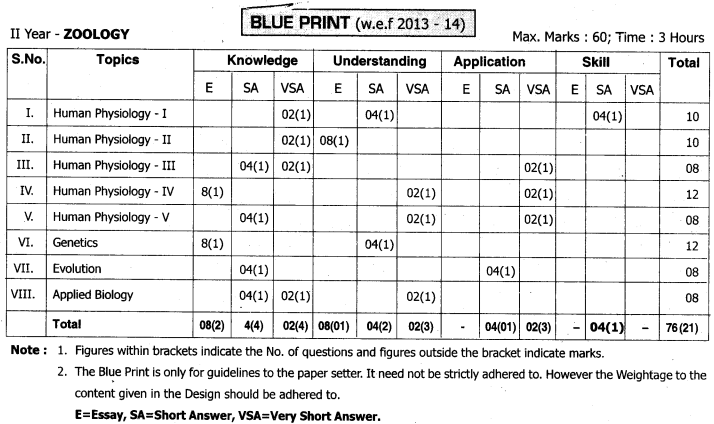
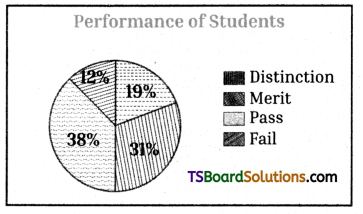
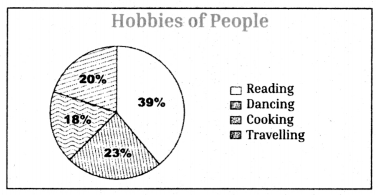
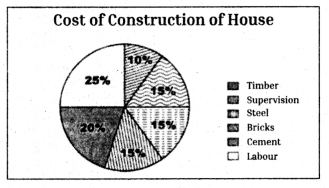
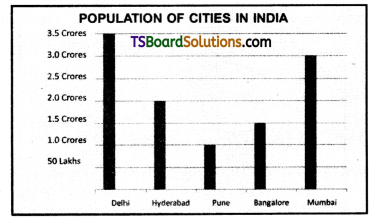
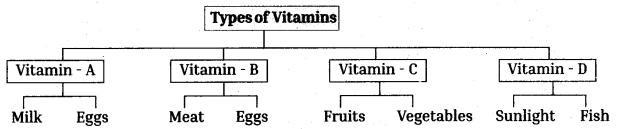
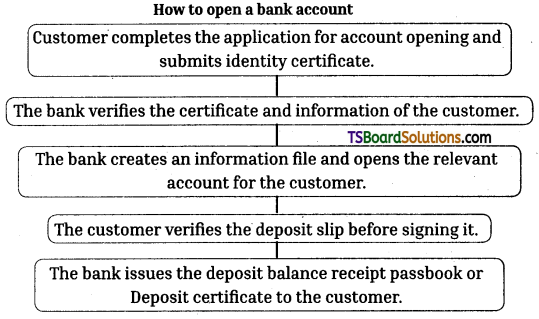
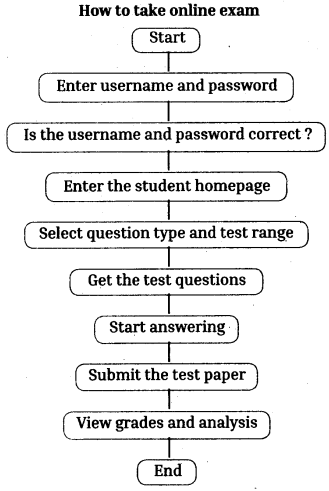
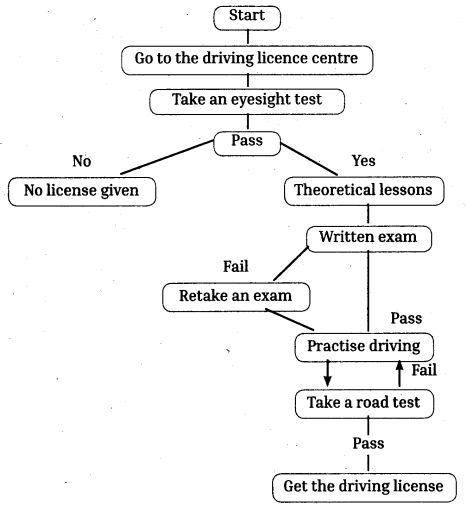
Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 1st Year English Study Material Reading Comprehension Unseen Passages Exercise Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 1st Year English Reading Comprehension Unseen Passages
Q.No. 7 (4 out of 6 Questions: 4 × 1 = 4 Marks)
EXERCISES
Read the following passages and answer the questions given after them.
I. INTRODUCING READING COMPREHENSION
1. Complementing Comprehension
Comprehension is a very comprehensive concept. It covers many aspects. Knowing the mere meaning of the text is but a small part of comprehension. Comprehension includes
(a) decoding the meaning, (b) relating it to what one knows, (c) thinking about it appropriately, (d) responding positively, (e) applying it to real life and (f) remembering it and retrieving it when needed. In that inclusive sense, comprehension forms the very base of any learning- languages, humanities, sciences and most importantly, life’s lessons. Treating comprehension as an examination-linked task is to limit our own progress. Enlightenment, enrichment and enjoyment go hand in hand as one steadily progresses in acquiring comprehension skills !
Questions :
i) Why is comprehension considered comprehensive ?
ii) What is meant by comprehension ?
iii) Write down two important aspects of true comprehension.
iv) What is at the very base of any learning ?
v) According to the passage, what is the most important subject to learn ?
vi) What is comprehension in the opinion of some persons that hampers one’s progress in learning ?
vii) What is the result of steady progress in one’s comprehension skills ?
viii) Write the expression used in the passage to mean together/in coordination.
Answers:
i) as it covers many aspects.
ii) knowing the meaning of the text
iii) decoding the meaning, remembering it, recollecting it when needed
iv) comprehension
v) life’s lessons
vi) an examination-linked task
vii) Enlightenment, enrichment and enjoyment go hand in hand.
viii) go hand in hand

2. Opportunities Unlimited
I notice the methodapplied to about six of the wealthiest men in England in a book of interviews published by an able and well-known journalist.
[This is a single sentence with twenty-six words. It is taken from G K Chesterton’s The Worship of the Wealthy]
Questions :
i) Who does the word Irefer to in the passage ?
ii) What did the narrator notice ?
iii) Where did the narrator notice it ?
iv) To whom was that method applied ?
v) Where did those six wealthy persons hail from ?
vi) Which is the book mentioned here ?
vii)Who published that book ?
viii) What is the specialty of that publisher ?
ix) What kind of people find place in the passage ?
x) Write the synonym of popular
xi) Write the other formsof the word able
xii) Can we also calla reporter a journalist ?
xiii) Can you write two or more such words used in that field as journalist?
Answers:
i) if the speaker
ii) the method applied to
iii) in a book of interviews
iv) to about six of the wealthiest men in England.
v) from England
vi) a book of interviews
vii) a well-known journalist
viii) an able and well-known person
ix) wealthy, famous persons
x) famous/well-known
xi) ably, ability, capable, unable, inability
xii) No, we cannot.
xiii) editor, composer, staffer, reporter, desk

II. GOLDEN TELANGANA SHINING
3. Innovation in Irritation-Kaleswaram
Kaleswaram, the brainchild of Sri K. Chandrashekhar Rao, is considered the world’s
largest multipurpose, multistage lift irrigation project. The other two such projects in the world (one in the USA – Colorado; and the other in Egypt – Great Manmade River) took three decades for their completion. But Kaleswaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) was inaugurated in just three years (on 21 June 2019) after starting work on it in 2016.
With three barrages, 20 lifts and 20 reservoirs, it aims at lifting water to 500 meters height and carrying it to over 500 KMs spanning 13 districts with a canal network crossing 1800 KMs. Built on the Godavari at Kaleswaram in Jayashankar Bhupalpalli district, the project mainly aims to use the till now unused Pranahitha waters near its confluence with the Godavari. The project presently lifts 2TMC (Thousand million cubic feet) water per day. Plans are a foot to increase the capacity to 3TMC a day. It aims at irrigating 37 lakh acres besides meeting the drinking water needs of Hyderabad and other villages, developing water transport and promoting fisheries and tourism.
Questions :
i ) Why is Kaleswaram called a multipurpose project ?
ii) Support the statement that KLIP is a multistage project.
iii) What is the difference between KLIP and the other such projects in the world ?
iv) Name the river that provides water to KLIP
v) To what height is water lifted from the beginning to the final point ?
vi) What is the irrigation potential of KLIP in acres ?
vii) Expand TMC.
viii) Give the location of KLIP
Answers:
i) as it irrigates, supplies drinking water, develops water transport, promotes fisheries and tourism.
ii) as it consists of three barrages, twenty lifts and twenty reservoirs.
iii) KLIP was inaugurated in three years after the work started on it while the two other such projects took three decades for their completion.
iv) the Pranahitha and the Godavari
v) 500 meters high
vi) 37 lakh acres
vii) Thousand million cubic feet
viii) Kaleswaram in Jayashankar Bhupalpalli district

4. Loving Warriors
Love is gravity, for it makes some attached to others (including animals). Pradeep Nair and Santhosi-made for each other Hyderabad couple-belong to that rarest category, attached to others. These Heroes of Hyderabad have so far rescued seventy thousand distressed animals! They foster disabled animals too. Initiated indirectly into this mission by their parents, they started their love saga 14 years ago. With registration in 2019, their 25+ active, skilled team is now officially Animal Warriors Conservation Society.
They coordinate with other NGOs, Fire, Forest and Zoo officials in wildlife conservation and activities like lake cleaning and manza cleaning. Despite resources crunch, they go ahead with their mission. Sensitive souls, intelligent minds and skilled hands are their invaluable resources. Their determined will has moved our IT Minister, KT Rama Rao into the rarest gesture of extending a furtd of rupees 10 Lakh. Crying wildlife appeals to all to strengthen their caring hands by sharing their mission of animal protection, wildlife conservation and awareness promotion.
Questions :
i) When we read about Pradeep Nair and Santhosi we think of the great saying, Love is gravity. Explain in a sentence how.
ii) Who prompted them to love animals ?
iii) What are the three goals that constitute their mission ?
iv) Who do they coordinate with in their wildlife conservation ?
v) Name the organization that got an official status in 2019.
vi) What moved the IT Minister to show the rarest gesture ?
vii) What is the appeal of crying wildlife ?
viii) Pick out the synonym of preservation from the passage.
Answers:
i) as they are attached to others, including animals
ii) their parents
iii) wildlife conservation, lake cleaning and manza cleaning
iv) with other NGOs, Fire, Forest and Zoo officials vf Animal Warriors Conservation Society
vi) their determined will
vii) to strengthen their caring hands by sharing their mission,
viii) conservation
5. Swatch Badi – Clean Telanoana – Second Only to One ?
The second Swatch Badi (the first one in India being in Bengaluru) was recently inaugurated by the Finance Minister T. Harish Rao in Siddipeta. Here, the faculty will teach how to collect garbage, segregate dry, wet and harmful garbage, take care of public health, avoid plastic and produce compost from garbage at homes. Dr. Prashanti from Bengaluru will supervise the activities at this learning centre. Children or elders, anyone can enroll here 7 for the course. Focus is on educating school-children, DWCRA [Development of Women and Children in Rural Areas] women and leaders. Teaching here is carried on in the digital form, actual demos and power point presentations. Compost generated thus can be used as manure. Spreading the concept all around is the need of the hour !
Questions :
i) Where does the first Swatch Badi in India function ?
ii) Swatch Badi in Siddipeta is the first of that kind in Telangana. Say true or false.
iii) Name the three types of garbage mentioned in the passage.
iv) Who looks after the functioning of this school ?
v) Who can join this school ?
vi) Mention the three teaching methods used here.
vii) How can the compost produced here be used ?
viii) Is it enough for Telangana to have this one school ?
Support your answer with a sentence from the passage.
Answers:
i) in Bengaluru
ii) true
iii) dry, wet and harmful
iv) Dr. Prashanthi from Bengaluru
v) Children or elders (anyone)
vi) digital form, actual demos and power point presentations
vii) as manure
viii) No. Spreading the concept all around is the need of the hour !

6. Initiative an INCH-Inspiration in TONS
An iota of initiative can ignite inspiration in tons, capable of moving mountains at a rapid pace. Sounds incredible ? See it happen in our golden Telangana right now. Miracles become common when the initiative comes from a man with integrity, good intentions and unconditional love for others. Other worth emulating traits of his sterling personality are : (a) simple living and high thinking; (b) love for truth; (c) discipline;
(d) practising before preaching; (e) democratic to the core and (f) working for common cause. His quest for truth is visible in his forty-year oldSatyanveshana Mandali.
His belief that individual progress and social progress are inseparable has prompted him to work for the development of a model town involving hundreds of committed persons from all walks of life, including spiritual areas. He is Surendra Babu Putta, 71. and the fortunate town witnessing his impact is Kodada, the Gateway of Telangana. His very lifestyle offers innumerable lessons on integrated personality development to the interested. Think, think, think-this is his mantra.
Questions :
i) How is the value of initiative highlighted in the passage ?
ii) Does the initiative from any kind of person have the same impact ?
iii) The initiative from what kind of persons can make miracles the order of the day ?
iv) Name three traits of the lead character’s personality.
v) Is it usual to have all such positive traits in persons around us ?
vi) What is the objective of the forty-year old organization mentioned in the passage ?
vii) Name the person impacting and the place being impacted.
viii) What kind of lessons can we learn from his way of living ?
Answers:
i) An iota of initiative can ignite inspiration in tons, capable of moving mountains at a rapid pace.
ii) No.
iii) from persons with integrity, good intentions and unconditional love for others.
iv) a) simple living and high thinking; b) love for truth and c) discipline
v) No, not usual
vi) Satyanveshana Mandali pursues the objective of quest for truth.
vii) Surendra Babu Putta; Kodada, the Gateway of Telangana
viii) lessons in integrated personality development

7. Save Girl Child ! n Save Mankind !
Gender bias is a global problem. Its intensity in India is intriguing for reasons both obscure and obvious. Yet, at times we see brilliant rays of hope emanating from unexpected quarters. An instance of this is an inspiring move initiated at Haridaspur village of Kondapur Mandal, Sangareddy district by the Sarpanch, Shafi to save girl children and to encourage their education. Proving that good manners too are infectious, the movement started spreading fast, for and wide. In just a year of its beginning, a handful of villages have already started following the example.
Inspired by this movement, Yeddumailaram village (Kandi Mandal) has set a record by opening Sukanya Samruddhi Yojana (SSY) accounts for 72 girl children on a single day. Opening such accounts, planting trees, honouring the mothers of girl children, encouraging girl education etc., are the main moves in this direction. Public representatives, doctors, press and officials have been actively encouraging such persons. Pride of place is credited to Intermediate Education as its personnel, particularly a Principal, have been playing an active role for long by promoting crucial awareness and raising funds, even from NRIs ! May their tribe multiply !
Questions :
i) What is the issue that is regarded as universal in this passage ?
ii) Is India in a better position in this connection than other countries ?
iii) How has Haridaspur set an example in eliminating gender bias ?
iv) What makes the narrator say that good manners are infectious ?
v) List the main moves initiated in the Save Girl Child Campaign.
vi) What kind of role is being played by the personnel from Intermediate Education ?
vii) Write the part of speech of the word personnel.
viii) Give the synonym for the word essential from the passage.
Answers:
i) gender bias
ii) No, it is not in a better position.
iii) by saving girl children, encouraging their education, honouring mothers of girl children etc.
iv) as this movement started to spread fast, far and wide
v) opening SSY accounts, planting trees, honouring mothers of girl children and encouraging girl education
vi) an active role in promoting crucial awareness and raising funds
vii) noun
viii) crucial

8. WOMEN at CENTRE-WELFARE in PROGRESS
A woman is a full circle. Within her is the power to create, nurture and transform, goes a glorious compliment, highlighting woman’s power. Then, if many women are at the helm of a village, can you imagine the degree of transformation ? A lively example is unfolding itself at Madhavaram village of Suryapet district. With the initiative from the sons of the soil like Sri Koti Reddy, Superintendent of Police, Ram Sudheer, School Assistant (Teacher), the entire village Panchayat was unanimously occupied by an all-women team.
Besides, women’s committees were formed for each important village development activity like education, health, drinking water and sanitation. Ms Vijayalakshmi, Sarpanch and Ms Janakamma, Vice-Sarpanch were all smiles when asked about their achievements in a short span of time. The long list includes a library, purified water, a gymnasium, English Medium Sections in ZP School, greenery etc. Their honesty in admitting that their move towards prohibition of liquor still awaits results stuns everyone. The village serves as a model, showcasing women’s power.
Questions ;
i) Frailty, thy name is woman, says Shakespeare. But, what does this passage say in this regard ? (Frailty means weakness-)
ii) Mention the unique feature of Madhavaram’s present panchayat.
iii) What do other all-women committees have for their function ?
iv) Why were the Sarpanch and Vice-Sarpanch all smiles ?
v) Which particular area still awaits satisfactory progress ?
vi) What does the village seek to showcase ?
vii) Who initiated the village development activities ?
viii) Write the expression from the passage used to mean jn the charge of-
Answers:
i) power, thy name is woman.
ii) It is occupied by an all-women team.
iii) education, health, drinking water, sanitation, etc.
iv) as they recorded many achievements in a short span of time
v) the prohibition of liquor
vi) women’s power
vii) Sri Koti Reddy, SP and Sri Ram Sudheer, teacher
viii) at the helm
III. LESSONS FROM ROOTS
9. Mistakes can Make Miracles
Mistakes at times can turn out to be a blessing in disguise. One such error led to the establishment of the Nobel Prize, the most coveted award in the world. When Ludwig (Alfred’s brother) died in 1888, a French newspaper erroneously confused the deceased’s identity with that of Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite that brought him enormous money. As a result, it published a scathing obituary entitled The Merchant of Death is Dead. Alfred thus had the rarest opportunity of reading his own death report (obituary). His troubled conscience said to himself, “Is this how posterity is going to remember me ? No, I must do something. The huge fortune I made must go to promote peace in this world. “What followed is history. Nobel prizes in Peace, Literature, Physics, Chemistry and Biology/Medicine were thus born !
Questions :
i) What was the error that led to the establishment of the Nobel Prize ?
ii) How did the French paper describe Alfred Nobel ?
iii) Who died in 1888 ?
iv) What was the rarest opportunity Alfred Nobel had ?
v) How did Nobel try to change his image ?
vi) Write the word used in the passage to mean death report.
vii) Give the antonym, from the passage, of appreciative.
viii) What is the difference, in terms of grammar, between the words death and dead ?
Answers:
i) confused the deceased’s identity with that of Alfred Nobel
ii) as the Merchant of Death
iii) Ludwig Nobel, Alfred’s brother
iv) to read his own death report
v) by trying to promote peace in the world and by establishing the Nobel Prize.
vi) obituary
vii) scathing
viii) death-noun; dead – adjective

10. Forget and Forgive-Live Life
Man gets and forgets : God gives and forgives; thus goes a saying. Once, a godlike four-year-old child showed the way. The girl was at the dining table, listening intently to her father admonishing her. When he took a long pause, she asked politely, “Dad, if you have finished, may I say something ?” Even while being scolded, she maintained her poise. Her patient listening and her poise teach us life’s lessons as well, or even better than the scriptures do. Think of any adult in that situation and the probable response. Can anyone be anywhere near that girl in her attitude ? We all like to be liked, no doubt. But can we order fond feelings from others ? Patience, forgiveness, love etc are some valuable qualities that help us live in peace, be liked and more importantly, help us give and yet forgive others-a sure way to spread true happiness all around.
Questions :
i) What are the attributes of man, according to the saying ?
ii) What was the girl doing while her father was scolding her ?
iii) What qualities in that girl teach us life’s lessons ?
iv) According to the passage, there are many adults like that girl. Say true or false
v) Does the writer say that fond feelings can be ordered from others ?
vi) Write is the sure way for spreading happiness all around ?
vii) Write the synonym of the word scolding.
viii) Write the antonym of the word inattentively.
Answers:
i) Man gets and forgets.
ii) She was at, the dining table, listening to her father intently.
iii) her poise and patient listening
iv) false
v) No, they cannot be ordered from others.
vi) to have patience, love, forgiveness etc., that help us live in peace, be liked and give and yet forgive.
vii) admonishing
viii) intently
IV. WOMAN EMPOWERMENT
11. A .Queen’s Wisdom
Layla, the wise queen once ruled Arabia. Her wisdom illuminated the land like the Sun. In beauty and wealth she had peers none. All the seven regions under her control enjoyed peace and prosperity, courtesy, her able and wise rule. Yet, people were not content. They used to say some unpleasant things against the queen. When the Chief Advisor wanted to know the reason for this, the queen smiled and said, “I can do almost everything I wish. I can order the frontiers to be closed; the gates of the palace to be locked and so on. But one thing I cannot do : make the people shut their mouths. It matters not what false things people say; what counts more is to continue to do which I consider to be true!”
Questions :
i) What is queen Layla famous for ?
ii) How was it that all those seven regions enjoyed peace and prosperity ?
iii) What did the Chief Advisor want to know ?
iv) What was the one thing that the queen was unable to do ?
v) Was the queen worried as she couldn’t do that ?
vi) Why was the queen not bothered by the unpleasant things people said ?
vii) What really matters most, according to the queen ?
viii) Give the antonym of the word adversity.
Answers:
i) for her wisdom, beauty, wealth
ii) due to her able and wise rule
iii) the reason for people saying some unpleasant things against the queen despite her able and wise rule
iv) to make the people shut their mouths
v) no, not worried
vi) because she knew well that what false things people say mattered not much
vii) to continue to do which she considered to be true
viii) prosperity

12. Charity Boundless
Live only to serve, to serve food seemed to be the motto that guided Ms. Dokka Seetamma all through her life. Popular as Apara Annapoorna, Ms Dokka Seetamma was born in October 1841 at Mandapeta of East Godavari District. Her father, Mr Bhavani Sankaram offered food to anyone who came to them hungry. Seetamma’s mother died when she was just six. And Seetamma had to shoulder her mother’s responsibility of serving food to the needy. Thus started habit of cooking and serving food lasted for four-plus decades. Even after her marriage to Dokka Joganna and her moving to Lankala Gannavaram, she didn’t do anything else except cooking and serving food. King Edward VII honoured her for her philanthropy by placing her photograph at a function. An aqueduct on the Godavari was named after her. And her statue finds a place in Vivekananda Park in Kakinada.
Questions :
i) What is the motto that guided Ms. Dokka Seetamma all through her life ?
ii) Where was Ms. Seetamma born ?
iii) Why did she start serving food since the time she was six ?
iv) How long did she continue in her mission of serving food ?
v) List the honours she enjoyed.
vi) What is her other popular name ?
vii) Write the idiom used in the passage to mean to take up the work,
viii) Write the part of speech of the word philanthropy.
Answers:
i) “Live only to serve, to serve food.
ii) at Mandapeta of East Godavari district
iii) as her mother died when she was six
iv) to more than four decades
v) King Edward VII placing her photograph at a function, an aqueduct on the Godavari after her name, her statue in Vivekananda Park in Kakinada
vi) Apara Annapoorna
vii) shoulder the responsibility
viii) philanthropy-noun
V. VARIETY IN CREATIVITY
13. A Modern Marvel Taking Shape on Out Soil at Sangareddy
Can you conceive of a construction without cement and steel ? Unimaginable ? But, a modern marvel-a 32 foot high Sri Chakra shaped temple is taking shape on a sprawling one and a half acre site with just natural elements like lime, jaggery, jute, gum, myrobalan fruit (karakkaya) paste, Indian bael (Maredu/Bilwa) juice, sand and stone (15 lakh pieces, some weighing 5 tons each). With Lord Shiva as the presiding deity, this Sri Kailasa Prastara Mahameru (human body) Panchamukha Umamaheswara Devasthanam, at Phasalvadi village, near Sangareddy, is being devised, planned and executed by jyothirvaasthu Vidyapeetham.
Modelled after ancient temples like Konark, Hampi, this 20 crore rupee mammoth miracle is expected to have a life of 6,000 years, says Maheswara Siddhanthi, the man behind this project. Hundreds of expert engineers, skilled sculptors, eminent architects and famous artisans have been toiling since day one i.e., 14 June 2017 and are determined to complete it at the earliest. With concepts from epics as its fountain of inspiration, this temple looks certain to flourish as a spiritual centre with unique architectural features !
Questions :
i) Mention the unique feature of this temple in terms of construction materials used.
ii) Which organization is executing the work of this temple ?
iii) Where is this temple located ?
iv) Without using cement and steel, can the structure last long ? Support your answer with a sentence from the passage.
v) Name the temples that were studied to design this temple.
vi) Who is supervising this major project ?
vii) Write the synonym of the word famous.
viii) When did the actual construction work start on this project ?
Answers:
i) Without using steel and cement, it uses only natural elements like lime, jaggery, jute, gum.
ii) Jyothirvaasthu Vidyapeetam
iii) Phasalvadi village, near Sangareddy
iv) Yes. It is expected to have a life of 6,000 years.
v) Konark, Hampi temples
vi) Maheswara Siddhanthi
vii) eminent
viii) on 14 June 2017

14. No Stops Barred
‘Go’ is the single-worded, shortest sentence. What could, then, be the longest sentence ? How many words ? Try guessing. The longest sentence has four lakh plus words. Yes, It’s a thousand-page novel titled Ducks, Newburyport, conceived and composed by Lucy Ellman. This thousand page novel won this year’s (2020) 10,000 pound Goldsmith’s Prize, for breaking the mould and extending the novel’s form. “It’s a massive achievement,”
exclaimed a judge. “This gripping, hypnotic novel remakes the novel ” extolled another judge. The ambitious form of the novel initially invited rejections till Galley Beggar finally published it. The novel is in the form of an internal monologue of a mother in Ohio as she bakes pies in her kitchen. According to the writer, this one long run-on sentence book makes its readers float around to sink or swim, engulfed in one woman’s thought.
Questions :
i) How many words are there in the longest sentence ?
ii) Who -composed that sentence and in’Which form ?
iii) What do.es, that sentence,deal with (its content) ?
iv) How was that longest sentence honoured in the year of publication ?
v) Reproduce the comments on the book by two judges.
vi) Why was the book initially rejected by the publishers ?
vii) “This one long run-on sentence book makes its readers .” What does it make its readers ?
viii) Why was this book chosen for Goldsmith’s Prize ?
Answers:
i) four lakh plus words
ii) Lucy Ellman, in the form of a novel
iii) It deals with the thoughts of a mother in Ohio as she bakes pies in her kitchen.
iv) honoured with 2020 Goldsmith’s Prize with 10,000 pound cash
v) i) It’s a massive achievement
ii This gripping, hypnotic novel remakes the novel….
vi) because of its ambitious form
vii) float around to sink or swim, engulfed in one woman’s thought
viii) for breaking the mould and extending the novel’s form

VI. PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT
15. Rags-to-writer n the Saga of Laxman Rao
India’s Capital is a home to a famous Chaiwala. A darling of the press, feted by numerous organizations and no stranger to the highest echelons of political affair, Laxman Rao led a storied life. It wasn’t his brews but his books that catapulted him into fame, and even into Teen Murthi House, where Indira Gandhi hosted him in 1984. Now the writer of twenty-five Hindi books-novels and plays-he has received awards from NGOs and literary associations and been covered more than one hundred times in print and digital media. All the while, until Delhi went into lockdown, you could still walk up to a tea stall on Vishnu Digamber Marg and treat yourself to a cup of tea from this celebrated author!
Questions :
i) Where does this famous Chaiwala, Laxman Rao, live ?
ii) What does the expression ‘no stranger to the highest echelons of political office’ mean?
iii) What catapulted Laxman Rao into fame ?
iv) Mention the medium that made Laxman Rao familiar to many.
v) What quality of Laxman Rao strikes you the most as you treat yourself with a cup of tea he made and sold to you ?
vi) Write the word used in the passage to mean much talked or written about
vii) What is the word used in the passage to mean a number of
viii) Write the synonym of honoured
Answers:
i) in Delhi
ii) known to (not stranger) many persons in highest positions (echelons levels of authority)
iii) his books
iv) Yes,.he is known to many. His books made him popular. Media gave wide publicity to his books.
v) his status as a celebrated author
vi) storied
vii) numerous
viii) feted

16. Determined to live and Write
Deprivation has driven the determined Manoranjan Byapari to dare even destiny with his pointed questions. Born as a poor, neglected and hard-working labourer with hunger as his twin brother, Manoranjan Byapari turned out to be an award-winning writer. With nearly twenty books in Bengali to his credit, including his latest work, Chandal Jibon (Bengali Title-semi autobiographical)-most of them translated into English and other languages-he received many awards-notable among them being West Bengal Sahitya Academy’s and The Hindu Award for non-fiction.
“I write because I cannot kill,” said Byapari once, adding, “The indomitable will to live keeps me alive even today despite odds like discrimination in dozens I face every day.” He started learning the letters of the alphabet when he was in prison, for no fault of his. Once riding Byapari’s rickshaw and noticing his innate talent to narrate, Maha Swetha Devi invited Byapari to write for her magazine, Bartikal. Thus, a great writer was bom, rather accidentally ! And now he is elected as an MLA from the Balagarh constituency (West Bengal) in May, 2021.
Questions :
i) What drove Manoranjan Byapari to challenge even destiny ?
ii) How has this hard-working poor labourer become popular ?
iii) Name his latest work.
iv) Mention some important honour he received.
v) Why does he write, according to himself ?
vi) Manoranjan Byapari had formal education like an ordinary boy. Say true to false.
vii) What keeps him alive despite odds in dozens he faces even today ?
viii) How did Maha Swetha Devi help the writer in Byapari take birth ?
Answers:
i) deprivation
ii) as a celebrated writer, through his award-winning books
iii) Chandal Jibon (Bengali title-semi autobiographical)
iv) West Bengal Sahitya Academy Award, The Hindu Award for non-fiction
v) “I write because I cannot kill.”
vi) false
vii) the indomitable will to live
viii) by inviting him to write for her magazine, Bartikal

17. Worshipping Heroes
Here are two unique novels – Pharaoh and the King and The Victorian-that made two heroes fans of their writer. The heroes are Chiranjeevi and Hrithik Roshan. And their writer is Dasari Venkata Vishwanath. But the reason ? Their writer is a visually challenged, Telugu Medium student who started writing his first English novel when he was just 11 (2004). Nystagmus or photophobia is the disease that disables him from focusing his sight on any object for more than a second.
Born into a farmer’s family of Gokavaram in East Godavari district, the boy was inspired by JK Rowling. Helped by his English teacher Buchibapayya and younger sister Sija, Venkat worked hard for seven years to complete his first novel in 2011, which was launched by Chiranjeevi. After that, another five years of dedicated work and the second masterpiece was out in 2016. Venkat dedicated it to his favourite hero Hrithik Roshan. That made the hero Venkat’s fan and he invited Venkat to his birthday party as a special guest. Thus, he won the hearts of two heroes, besides those of millions of readers the world over.
Questions :
i) What is unique about the two novels, according to the passage ?
ii) Who are the heroes who turned fans of that writer ?
iii) How does the disease, Nystagmus impact Venkata Vishwanath ?
iv) Name the three persons who helped, directly or indirectly, Venkata Vishwanath in writing his first novel ?
v) How long did Venkata Vishwanath take to write those two novels ?
vi) What made Hrithik Roshan a fan of Venkata Vishwanath ?
vii) How did Hrithik Roshan a fan of Venkata Vishwanath ?
viii) Visual challenges or Telugu Medium background failed to stop Venkata Vishwanath from daring to dream and succeeding. Say true or false-
Answers:
i) that made two heroes fans of their writer
ii) Chiranjeevi and Hrithik Roshan
iii) disables him from focusing his sight on any object for more than a second.
iv) JK Rowling, his English teacher Buchibapayya and his younger sister Sija
v) twelve (7 + 5) years
vi) Venkat dedicating his second novel, The Victorian, to Hrithik Roshan
vii) by inviting Venkat to his birthday party as a special guest
viii) true

VII. WIT AND HUMOUR
18. Strange Lawyer
A lawyer named Strange died, and his friend asked the tombstone maker to inscribe on his tombstone, Here lies Strange, an honest man and a lawyer. The inscriber insisted that such an inscription would be confusing, for passersby would tend to think that three men were buried under the stone. However, he suggested an alternative. He would inscribe, Here lies a man who was both an honest man and a lawyer. That way, whenever anyone walked by the tombstone and read it, they would be certain to remark, That’s strange !
Questions :
i) What was initially planned to be inscribed on the tombstone of Strange, the lawyer ?
ii) How would that inscription confuse the passersby, according to the inscriber ?
iii) Who suggested the alternative inscription ?
iv) Did the new inscription carry the name of the dead lawyer ?
v) How would the passersby know the name of the dead man, without it being on the tombstone ?
vi) What is strange (note the smalls) according to the passage ?
vii) Write the Parts of Speech of the words inscribe, inscription, inscriber.
viii) Write the word used in the passage that means misleading.
Answers:
i) “Here lies Strange, an honest man and a lawyer.”
ii) Passersby would tend to think that three men were buried under the stone.
iii) the inscriber
iv) No
v) by looking at the new inscription, “Here lies a man who was both an honest man and a lawyer”, passersby would surely remark, ‘That’s strange!”
vi) A lawyer being an honest man is strange, according to the passage.
vii) inscribe-verb; inscription-noun (refers to an action); inscriber-noun (refers to a person)
viii) confusing

19. Albert Einstein : Humour. Humanity. Humility
Albert Einstein, the Nobel laureate, was a simple man to whom success, fame and wealth meant nothing. On being appointed the Dean of a University and asked to give his requirements, his demand was for a wastepaper basket. To the stunned person, his cool , v response was, “I commit mistakes, you know.”Humility underlined his simplicity. His simplicity extended to his love for children; he believed that the hope of the world lies in viV- children. His excellent sense of humour helped him to brighten every situation. Asked for a mathematical formula for success in life, he gave, “A = X + Y + Z”, where A = success, X = work and Y = play”. “What is Z ?” was the question. “Keeping your mouth shut,” was Einstein’s response! Everybody talks about him but nobody understands him because he is more of a phenomenon and not just a man.
Questions :
i) What mattered little to Albert Einstein ?
ii) Why did Einstein ask for just a wastepaper basket as a Dean ?
iii) Which quality made his simplicity conspicious ?
iv) What was his belief about children ?
v) How did Einstein’ sense of humour help him ?
vi) What is Einstein’s formula for success in life ?
vii) Why don’t people understand Einstein ?
viii) Give thenoun form ofsimple as found in the passage.
Answers:
i) success, fame and wealth
ii) because he would commit mistakes
iii) humility
iv) “.World’s hope lies in children”.
v) to brighten every situation
vi) A = X + Y + Z (A → success; X → work; Y → play; Z → shut up your mouth)
vii) because he is more of a phenomenon than a man
viii) simplicity

VIII. HEALTH SCENARIO
20. Prime Minister Modi on YOGA
Yoga is an invaluable gift of ancient Indian tradition it embodies unity of mind and body; thought and action; restraint and fulfillment; harmony between man and nature, and a holistic approach to health and well-being. Yoga is not about exercise but to discover the sense of oneness with ourselves, the world and Nature. By changing our lifestyle and creating consciousness, it can help us to deal with climate change. Let us work towards adopting the international Yoga Day.
Questions :
i) Whose gift is Yoga according to the passage ?
ii) Yoga brings about unity between ………….. and ……………. and …………….. ; ……………… and ……………… , …………… Fill in the blanks.
iii) What does Yoga help us to discover ?
iv) How can Yoga help us to deal with climate change ?
v) Is Yoga about physical exercise alone ?
vi) Give the antonym of modern.
vii) Give the verb(present) form of thought(n/v.pt).
viii) Find the word from the passage that means agreement
Answers:
i) ancient Indian tradition
ii) mind, body; thought, action; restraint, fulfillment
iii) the sense of oneness with ourselves, the world and Nature
iv) by changing our lifestyle and creating consciousness
v) No.
vi) ancient
vii) think
viii) harmony
21. Keen Going n COV1D – 19 Taught Lessons !
Nagaland is an excellent example of how communities rise to the occasion. How ? The COVID -19 induced lockdown had convinced them about the importance of self – reliance. As their wage – earning jobs were lost, they resumed farming. And they say they have learnt a lot. With smiles on their faces they say it is a personal rediscovery, going back to nature, cultivating their own food. Food is at the core of our community life they add with pride. And, they have been expanding their farming. Love thy neighbour the community’s philosophy. As the lockdown pushed some into poverty, people have supported those in need. Even Churches began serving meals to the underprivileged. Discovering in difficulties, opportunities to live and let live, that too, joyfully is what the Nagas do and show !
Questions :
i) What did Naga communities understand after Covid induced lockdown ?
ii) What did they resume and why ?
iii) What have they felt about resuming farming ?
iv) What is their community’s philosophy ?
v) How have they practised that philosophy ?
vi) What are the Nagas doing and showing all others ?
vii) Write thesynonym , from the passage, ofcentre .
viii) According to the passage, COVID-19 helped more than it harmed them. Saytrue or false .
Answers:
i) the importance of self-reliance
ii) resumed farming as they lost their wage-earning jobs
iii) They have felt it is a personal rediscovery, going back to nature and cultivating their own • food.
iv) “Love thy neighbour.”
v) by supporting those in need
vi) discovering in difficulties, opportunities to live and let live
vii) core
viii) true

22. Virus Vs Fear
There is NO virus in this world more dangerous than Fear. Understand this fear; otherwise, you will become a dead body before your body dies. It has nothing to do with the virus. The scary atmosphere you feel in these moments is collective madness… It has happened a thousand times and will continue to happen. You usually keep your feat at bay, but in the moment of collective madness, your consciousness can be completely lost. You won’t even know when you lost control of your fear.
Then fear can make you do anything. In such a situation, you can also take your own life or the lives of others. Attention, be mindful. Don’t watch news that triggers fear. Stop talking about the epidemic, repeating the same thing is like self-hypnosis. Fear is a kind of self-hypnosis. This idea will cause chemical changes in the body. During an epidemic, the energy around the world becomes irrational. This way, you can fall into a black hole anytime. Meditation then becomes a protective aura into which no negative energy can penetrate.
Questions :
i) What, according to the narrator, is more dangerous than the virus ?
ii) What happens if one doesn’t understand this fear ?
iii) Does this happen every time ?
iv) What is lost when collective madness prevails in us ?
v) What is the warning given by the narrator ?
vi) It is ADVISABLE to discuss the EPIDEMIC ?
vii) What happens when one gets this idea (fear) ?
viii) How can we remove our negative tendency ?
Answers:
i) Fear is more dangerous than virus.
ii) One will become a dead body before one’s body dies.
iii) Yes, it happens every time.
iv) our consciousness
v) The warning is : Don’t watch news that triggers fear. Stop talking about the epidemic.
vi) No, not advisable
vii) The idea will cause chemical changes in the body.
viii) through meditation

IX. SCIENTIFIC CULTURE
23. On Srinivasa Ramanujam
Mathematics in Indiainevitably makes one think of one extraordinary figure of recent times. This is Srinivasa Ramanujam.Born into a poor Brahmin family in South India, having no opportunities for a proper education, he became a clerk in the Madras Port Trust. But he was bubbling with some irrepressible quality of instinctive genius and played about with numbers and equations in his spare time. By a lucky chance he attracted the attention of a mathematician who sent some of his amateur work to Cambridge in England.
People there were impressed and a scholarship was arranged for him. So he left his clerk’s job and went to Cambridge and during a very brief period there did work of profound value and amazing originality. The Royal Society of England went rather out of their way and made him a Fellow, but he died two years later, probably of tuberculosis, at the age of thirty three. Professor Julian Huxley has, I believe, referred to him as the greatest mathematician of the century. [ From The Discovery on India]
Questions :
i) What makes one think highly of Srinivasa Ramanujam ?
ii) Why did Ramanujam become a clerk ?
iii) What was Ramanujam doing whenever he found some free time ?
iv) What helped Ramanujam to go to Cambridge ?
v) What did people at Cambridge do for Ramanujam ?
vi) Describe the work Ramanujam did at Cambridge.
vii) ffow did the Royal Society of England honour Ramanujam ?
viii) What is the compliment Professor Julian Huxley extended tc Ramanujam ?
Answers:
i) Mathematics makes one think of Ramanujam.
ii) because of their poverty and as a result of it, having no opportunities for proper education
iii) played about with numbers and equations
iv) a rnathematician sending his work to Cambridge
v) They arranged a scholarship for him.
vi) work of profound value and amazing originality
vii) honoured Ramanujam by making him a Fellow of the Society
viii) that Ramanujam is the greatest mathematician of the century

24. The Best Award to a TEACHER
Nobel Laureate Sir Chandrashekhar Venkata Raman was among the first three recipients (the other two being Chakravarthi Rajagopala Chary and Dr Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan) of the title Bharat Ratna, the highest civilian award in India in 1954. The then President, Rajendra Prasad, wrote personally to Raman inviting him to be the personal guest in the Rashtrapathi Bhavan, when Raman came to Delhi for the award ceremony. Raman wrote a polite letter regretting his inability to attend the investiture ceremony. He had a noble reason. He had to be by the side of his Ph.D. student as the scholar was trying hard to finalize his Ph.D. thesis before the deadline. “Can there be a better award to a teacher than being by the side of a needy student ?” seems to be Raman’s message to us all!
Questions :
i) Name the highest civilian honour in India.
ii) When was that award conferred on Sir C.V. Raman ?
iii) Who were the other two recipients of the award, along with Sir C.V. Raman ?
iv) What was Rajendra Prasad’s offer to Raman ?
v) Why didn’t Raman attend the award ceremony ?
vi) What appears to be Raman’s message, by not attending the ceremony ?
vii) What is the word used in the passage to mean formal presentation ?
viii) Find the synonym of the word appears from the passage.
Answers:
i) The Bharat Ratna
ii) in 1954
iii) Chakravarthi Rajagopala Chary and Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan
iv) an invitation to Raman to be his personal guest in Rashtrapathi Bhavan
v) As Raman wanted to be by the side of his Ph.D student, as the scholar was busy finalising his Ph.D thesis
vi) “Can there be a better award to a teacher than being by the side of a needy student ?”
vii) investiture
viii) seems

25. On Tagore and Gandhi
Tagore and Gandhi have undoubtedly been the two outstanding and dominating figures of India in the first half of the twentieth century. It is instructive to compare and contrast them. No two persons could be so different from each other in their make-up or temperaments. Tagore, the aristocratic artist, turned democrat with proletarian sympathies, represented essentially the cultural tradition of India, the tradition of accepting life in the fullness thereof and going through it with song and dance.
Gandhi, more a man of the people, almost the embodiment of the Indian peasant, represented the other ancient tradition of India, that of renunciation and asceticism. And yet Tagore was primarily the man of thought, Gandhi of concentrated and ceaseless activity. Both, in their different ways, had a world outlook, and both were at the same time wholly Indian. They seemed to present different but harmonious aspects of India and to complement each other. [From The Discovery on India]
Questions :
i) How is it useful to compare and contrast Gandhiji and Tagore ?
ii) What is common to both-Tagore and Gandhiji ?
iii) Tagore was primarily the man of thought. As opposed to Tagore in this respect, how was Gandhiji ?
iv) What did Tagore essentially represent ?
v) Gandhiji represented ancient tradition. Which aspect of it did Gandhiji represent ?
vi) Did the differences in their make-up or temperaments (of Gandhiji and Tagore) lead to any friction between their relations ?
vii) ” …………… and to complement each other …………..” complement means …………….. Fill in the blank.
a) congratulations
b) appreciation
c) complete
d) appreciate
viii) Write from the passage the antonym of the word dictator.
Answers:
i) It is instructive to compare and contrast Gandhiji and Tagore.
ii) Both of them were two outstanding and dominating figures of India and both had a world outlook and both were wholly Indian.
iii) Gandhiji was a man of concentrated and ceaseless activity.
iv) the cultural tradition of India
v) of renunciation and asceticism
vi) No, they didn’t lead to any friction
vii) (c) complete
viii) democrat

X. SOCIAL MILIEU
26. GHOTUL – a Model Tribal School
The best known of these indigenous institutions is the Ghotul in Bastar, where older Muria Gond children educate youngsters through a work-play continuum and a sophisticated etiquette of passing on knowledge orally. Children learn countless skills while sharing myths, riddles, songs, dances and ethics based on values of sharing rather than competition. Similar Institutions such as Dhumkuria and Dangribasa exist in Jharkhand and Odisha.
Questions :
i) Where is Ghotul, the tribal school ?
ii) Who are the teachers in that school ?
iii) What is the main mode of teaching there ?
iv) What sophisticated procedure is followed there ?
v) Are there any other institutions of this type ? If so, where are they ?
vi) What are the names of the institutions of this type ?
vii) What does the passage discuss ?
viii) Write the word used in the passage that means a set of customs, practices followed to be polite.
Answers:
i) in Bastar
ii) Older children teach.
iii) passing on knowledge orally
iv) a sophisticated etiquette of passing on knowledge orally
v) Yes, there are, in Jharkhand and Odisha.
vi) Dhumkuria and Dangribasa
vii) The passage discusses indigenous institutions and their teaching methods.
viii) etiquette

27. The Secret Under Ground
Nature is the best teacher. Redwood trees share a secret. They are the largest trees on the planet. Some of them are even of thousands of years old. But, interestingly, their roots do not grow deep. Yet, they endure massive wind storms, devastating earthquakes etc., for centuries. How is it possible ? The secret of redwood trees lies under the ground. Their roots reach outward seeking the roots of other redwood trees. When they meet, they intertwine, making a permanent bond with one another. This way, all the redwood trees support one another. Unity is strength. Thus, they give humanity a crucial lesson : when you receive, you make a living; but when you give, you make a life !
Questions :
i) Regarding size, what is unique about redwood trees ?
ii) How long do redwood trees live ?
iii) What is the interesting feature of redwood trees ?
iv) What is the secret of redwood trees lying under the ground ?
v) How do all redwood trees support one another ?
vi) What is the crucial lesson redwood trees teach humanity ?
vii) Write the antonym, from the passage, of shallow.
viii) Give the synonym, from the passage, of destructive.
Answers:
i) Redwood trees are the largest trees on the planet.
ii) for thousands of years
iii) Their roots do not grow deep.
iv) Their roots reach outward seeking the roots of other redwood trees.
v) When the roots meet, they intertwine, making a permanent bond with one another. Thus all redwood trees support one another.
vi) Unity is strength. When you receive, you make a living; when you give, you make a life.
vii) deep
viii) devastating

28. Everything Relative
Can zero and infinity be the same? This question may seem misleadingly simple. Your instant answer could be No’. But ‘Yes’ is the right answer. That doesn’t mean No’ is wrong. How? Compare the diameter of the earth with the distance between the sun and the arth. Earth’s diameter appears to be almost zero. Now, compare the same with that of a grain. It seems to be infinite. This proves that everything is relative and nothing is abstract. Now, consider, ‘What is riches ?M If your income is more than your wants, you are RICH! More wants, less income ? That is poverty. Want to be rich? Can’t earn more ? Cut down wants, become rich. How logic can comfort one sounds lovely!
Questions :
i) What is the question that seems misleadingly simple?
ii) What would be your instant answer to that question?
iii) What proves your answer-be a yes or no-to be right or wrong?
iv) What is the definition of riches, according to the passage?
y) How can one grow rich even without being able to earn more?
vi) How does logic, even only at times, help one?
vii) Name the planet(s) mentioned in the passage.
viii) The whole passage proves one single point; What is that?
Answers:
i) Can zero and infinity be the same ?
ii) ‘No’
iii) comparison
iv) having income more than wants
v) by cutting down wants
vi) by comforting them
vii) the earth
viii) Everything is relative and nothing is abstract
29. Small is Beautiful
Be it a big task or tough problem, make it into smaller units and see its impact! Break down an unthought desire into its components and allow the child to decide. The Mac Donald’s Happy Meal comes with a burger, a drink, some fries and a small toy. My kid wanted it at age five. I could buy it but broke down the decision for her-“you don’t like fries, the burger is not the kind you really like, and the drink on its own costs far less. Are we
buying because they are selling or we really like the deal ? If we do so, sure, let us get it”. At age five, she walked from the deal. And from many others after that. [Revision Test – I]
Questions :
i) Break down an unthought desire into components. How would this help one ?
ii) What does the Happy Meal include ?
iii) Who asked for the Happy Meal and when ?
iv) The narrator could buy it. Yet he/she didn’t. What did he/she do ?
v) What should be the deciding factor to buy something, according to the narrator ?
vi) The five-year-old kid did not cry when her desire was not fulfilled. Why ?
vii) The passage extends a valuable piece of advice to parents. Say true or false.
viii) “…………… the drink on its own ………………” Write the part of speech of drink.
Answers:
i) that helps one in taking proper decisions
ii) It includes a burger, a drink, some fries and a small toy.
iii) The narrator’s kid wanted it at age five.
iv) The narrator broke down the decision for her.
v) Whether we really like the deal should be the deciding factor.
vi) The broken down decision helped the girl understand that the deal was not what she really liked.
vii) true
viii) ‘drink’-noun

30. Kumbh Mela
In my own city of Allahabad or in Haridwar, I would go to the great bathing festivals, the Kumbh Mela, and see hundreds of thousands of people come, as their forebears had come for thousands of years from all over India, to bathe in the Ganges. I would remember descriptions of these festivals written thirteen hundred years ago by Chinese pilgrims and others, and even then these meals were ancient and lost in unknown antiquity. What was the tremendous faith, I wondered, that had drawn our people for untold generations to this famous river of India ? [Revision Test – II]
Questions :
i) What is the phrase used in the passage to mean Kumbh Mela ?
ii) Kumbh Mela is a modem event, Say true of false.
iii) When did Chinese pilgrims write about this festival ?
iv) Can we say when exactly the festival began ?
v) What draws people to this famous river festival for so many years ?
vi) Write the word used in the passage to mean festival, fair.
vii) Write the synonym (from the passage) of ancestors.
viii) Write the noun form of describe.
Answers:
i) the great bathing festivals
ii) false
iii) thirteen hundred years ago
iv) No.
v) The tremendous faith
vi) ‘mela’
vii) forebears
viii) description-noun

31. Where Shawdow Stays Stable !
Shadows keep changing positions and size, if the distance between the source of light and the object changes ! But at Chaya Someswara Temple at Panagal, dear Nalgonda, the shadow (Chaya, hence the name of the temple) of pillars stays constant on the lingam at any time, despite changes in the above said distance. The pillars of ardhamandapa and open spaces near the central shrine were designed and placed in such a way by the then architects as to produce this effect of stable shadow on the lingam all through the day.
A miracle one must see to believe ! Believed to have been built in the 11 century AD, the construction credits go to Kanduru Chodas. This thrikutalayam has three shrines dedicated to Lord Shiva, Vishnu and Surya. A common hall, mandapam, keeps these three shrines as one complex. Many intricately carved pillars, around this mandapam depict scenes from the Ramayana, the Mahabharatha and the Puranas ! [Revision Test – III]
Questions :
i) Describe the nature of shadows.
ii) Give an example of exception to this nature of shadows.
iii) Why is the temple called Chaya Someswara Temple ?
iv) What makes the temple also known as thrikutalayam ?
v) Who is believed to have built this unique temple ?
vi) Where does the shadow fall all through the day ?
vii) Is it the shadow of a single object ? Support your answer with a sentence from the passage.
viii) What do the pillars depict ?
Answers:
i) Shadows keep changing positions and sizes if the distance between the source of light and the object changes.
ii) the shadow of pillars at Chaya Someswara Temple at Panagal, near Nalgonda.
iii) ‘Chaya’ in Telugu, means shadow. As he shadow here stays stable all through the day on the Lingam, the temple is called Chaya Someswara Temple.
iv) as there are three shrines
v) Kanduru Chodas
vi) on the Linga?n
vii) No. “The pillars of… produce this effect of stable shadow.”
viii) scenes from the Ramayana, the Mahabharatha and the Puranas

32. Maitri-lndeed a Friend in Need
The world is in a word, says Wordsmith. Words packed with positive vibrations can light up the dark world of narrowminded, selfish and loveless millions, says Ms Jalandhara, a writer, guide, mentor and most importantly, healer ! An incarnation of simplicity and modesty, Ms Jalandhara was born into the family of Gali Bala Sundara Rao (GBS), a godlike doctor and multifaceted personality. And she was married to Mr Chandra Mohan, a versatile, multi-lingual cine star.
Yet she shines like a star, uneclipsed between the two mighty personalities. With innumerable creative works-stories, novels etc.,-to her credit, shlfe seeks to promote peace in minds and homes with a missionary zeal. Unconditional and universal love is her panacea. Cite your problems to Maitri, a question-answer feature both online and offline, and prompt comes the solution in the form of thought-provoking counselling. Homes flourishing with smiles following her advice are innumerable all over the globe ! The true symbol of empowering woman! [Revision Test – IV]
Questions :
i) How can the dark world of millions be filled up with light ?
ii) What are the two traits highlighted here in the lead character’s personality ?
iii) Name the two prominent personalities mentioned here associated with her.
iv What is her mission ?
v) How does she seek to promote peace in minds and homes ?
vi) What is her panacea ?
vii) What does the central character stand for as a symbol ?
viii) Write the word used in the passage to mean cure-for-all.
Answers:
i) Words packed with positive vibrations can light up the dark world of millions.
ii) simplicity and modesty
iii) Gali Bala Sundara Rao, her father and Mr. Chandra Mohan, her husband.
iv) to promote peace in minds and homes
v) through her thought provoking counselling
vi) unconditional and universal love
vii) as a symbol of empowering woman
viii) panacea

33. Innocence Unbeatable
Do you think you can confuse innocent kids easily ? Find out for yourself. Once a curious boy asked his mother, Mommy, why is your hair turning grey ? The mother tried to use this occasion to teach her child a lesson in behaviour. So, she said, “It is because of you, dear. Every bad action of yours will turn one hair grey.” Instantly came the retort from the inncoent boy, “Now I know why grandmother has only grey hair on her head.” Can you see who taught whom a lesson in manners ? [Revision Test – V]
Questions :
i) What is the message given in the passage ?
ii) What quality of the boy made him ask his mother a question ?
iii) How did the mother want to use this occasion ?
iv) Why would her hair turn grey, according to the mother ?
v) Was the mother true in saying that reason for her grey hair ?
vi) Did the boy take time to answer his mother ? Support your answer with a phrase from the passage.
vii) Write the word used in the passage to mean a witty, sharp reply.
viii) Find the antonym in the passage of experienced.
Answers:
i) One cannot confuse innocent kids easily.
ii) his curiosity
iii) to teach her child a lesson in behaviour
iv) Every bad action of her son would turn one of her hairs grey.
v) No, she wasn’t true.
vi) No, instantly came the innocent retort from the boy.
vii) ‘retort’
viii) ‘innocent’

34. Beauty lies in …. …… …….
“A thing of beauty is a joy forever, says Keats. But what is real beauty ? A big question. Yet, people crave for beauty. And man’s (or woman’s) craze for beauty supports big business. Cosmetics cost a lot. Here is a list of priceless cosmetics. On being asked, a wise woman gives the list from the core of her heart. I use truth for my lips; prayer for my voice; kindness and compassion for my eyes; love for my heart; charity for my hands and finally, uprightness for my figure ! How long – lasting the cosmetic are ! How valuable they are ! Priceless possessions ! [Model Question Paper]
Questions :
i) What does Keats say about beauty ?
ii) What does the beauty business thrive on ?
iii) What list does the wise woman give us ?
iv) Where can one get the cosmetics the wise woman uses ?
v) What does that wise woman use to make her eyes look beautiful ?
vi) Describe the cosmetics the wise woman uses ?
Answers:
i) A thing of beauty is a joy forever.
ii) cosmetics
iii) the list of priceless (long-lasting) cosmetics
iv) in one’s heart
v) kind and compassion
vi) truth, prayer, kindness and compassion, love, charity and uprightness