Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Study Material 9th Lesson Principles of Management Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Study Material 9th Lesson Principles of Management
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the principls of management?
Answer:
Principles of Management :
Henry Fayol is known for the general principles of management formulated by him in the 20th century. Hence, he is called as ‘Father of Management’. Fayol’s principles of management are as follows :
Fayol’s principles of management are as follows :
1. Division of Labour :
- Division of labour leads to specialization which increases the efficiency of individual employees.
- Fayol recommended that work of all kinds must be subdivided and allocated to number of persons. Sub division makes each task simpler and results in greater efficiency, by repeating a small’part of work the individual acqires speed and accuracy in his performance. This principle is applicable to both technical as well as managerial work.
2. Parity of Authority and Responsibility :
- Authority refers to the right of a superior to give order to subordinate, take decision on specified matters, use resources of the organization, and guide and regulate the behavior of subordinates.
- Responsibility includes with respect to performance of functions and achieving goals in the satisfactory manner.
- The principle of parity suggests that there must be parity between authority and responsibility. Giving authority without corresponding responsibility can lead to arbitrary and unmindful use of authority.
- Similarly, if a person is given some responsibility he must also be given adequate authority. Lack of necessary authority makes the individual ineffective.
3. Discipline :
- Discipline in the context of management means obedience, proper conduct in relation to others and complying with the rules and regulations of the organization.
- Discipline is required not only on the part of workers but also on the part of management, It is facilitated if there are good supervisors at all levels, rules are clear, and penalties ae imposed with fairness.
4. Unity of Command :
- The principle states that a subordinate should receive orders and be accountable to one and only, one superior.
- No employee, therefore, should receive instructions from more than one person. The principle is necessary to avoid confusion and conflict.
5. Unity of Direction :
- According to this principle, the efforts of all the members of the organization should be directed towards common goals. A group of activities having the same objective must have one head and one plan.
- For this purpose there should be one hed and one plan for a group of activities having the same objectives.
- The principle seeks to ensure unity of action, co-ordination of strength and focusing of effort.
6. Subordination of individual to general interest:
- The interest of one employee or group of employees should not prevail over that of the company organization.
- The interest of the firm as a whole is more important than the interest of an individual or group of person.
3) Individual interest must be subordinaed to the general interest or the interest of the whole firm.
7. Remuneration of personnel :
- To maintain the loyalty and support of workers, they must receive full and fair wage for services rendered.
- Remuneration should provide maximum possible satisfaction to employees and em-ployer. They should put in their best effors to improve productivity.
8. Centralization :
- It refers to the extent to which authority is concentrated or dispersed.
- The appropriate degree of centralization will vary with different concerns.
- Under centralization managers or executives play an important role.
9. Scalar Chain :
- The scalar chain is the chain of superiors ranging from the ultimate authority to the lowest ranks.
- It shows the line of authority from the highest executive to the lowest one for the purpose of communication.
- This will help an employee to know the person whom he sould contact for advice and guidance.
10. Order :
- Order requires that there is a place for everything and everything in its place.
- Social order requires the employment of ‘the right man in the right place’.
11. Equity :
- Equity is a combination of kindliness and justice. It seeks to elicit loyalty and devo-tion from personnel.
- The managers should show kindness and justice in dealing with their subordinaes.
- The application of the principle equity leads to successful working of the firm.
12. Stability of tenure of personnel :
- Every employes must feel that he enjoys security of the job. If he knows that he has to work at one place only, he will take interest in the give his best performance.
- If there is no stability of tenue, he loses interest in the job and wits for an opportunity to quit the firm. It is said instability, of tenure is an evidence of bad running of affairs.
13. Initiative :
- Initiative involves thinking out and execution of a plan and ensuring its success. This gives zeal and energy to an organization.
- Fayol advised managers to allow employees. Show initiative as much as possible. The freedom to propose a plan and to execute it is known as initiative.
- It will enable employees to experience the keenest satisfaction from their jobs.
14. Esperit de crops :
- It implies that union is strength, which comes from the harmony of the personnel.
- It emphasizes the importance of teamwork and group endeavors,
- The management should never adopt divide and rule policy. It should encourage team spirit and team work. This ensures smooth working of the organization.
![]()
Question 2.
Management is considered to be both on art and science. Explain.
Answer:
Management is considered both an art and science, because it is systematized knowledge which Provides laws capable of universal application and has a cause and effect relationship.
Management is an art :
- The application of management skills is governed by the type of aptitudes and ability possessed by the manager, which are highly personalized blending of imagination, creativity and insight.
- This permits management being described as an art. Management cannot be compared with sciences like physics, chemistry or mathematics so far the degree of precision is concerned.
- No doubt, mangement is a science, but not as exact in its results as in the case of physics or chemistry. This is for the simple reason that management science deals with human beings who are more widely influenced by a number of material factors.
- Management as science is still in the evolutionary stage and management is practiced as yet largely as an art like the earlier period. But the growing needs of management service have evolved it as a profession.
Management is science :
- Science is a systematized body of knowledge pertaining to a specific field of study and contains general facts that explain a phenomenon. It establishes the cause and effect relationship between two or more factors and ascertains the underlying principle governing the relationship.
- Theories are being continuously formulated as an aid to a more systematic analysis of managerial behavior thus resulting in the study of management moving into the man-agement science.
- This expression stresses the constant search for evolving and verifying principles and rules as well as for further knowledge resulting.in the emergence of managerial tech-niques effective universally.
- Scientific method or attitude has been increasingly adopted by good managers towards performance of their job of managing.
- They have developed inquiring minds which first attempt to identify the problem, for hypothesis or tentative solutions, then investigate in terms of current knowledge and even controlled experiments, classify the data so obtained and develop it into alternative courses of action.
Question 3.
What are the contributions of Henry Fayol in the field of management?
Answer:
Henry Fayol is known for the general principles of management formulated by him in the 20th century. Fayol graduated in 1860 as a mining engineer. Henry Fayol, an engineer; industrial magnate and he was a successful cheif executive with a large experience in the field of general Administration and Management.
Fayol developed general theory of organization, and administration to all organizations. He wrote “to manage is to forecast and plan, to organize, to command to coordinate and to control”.
Fayol’s contribution to the science of management may be summerised as follows :
a) Classification of industrial activities.
b) Classification of managerial functions.
c) Universal principles of management.
d) Significance of management function.
e) Managerial qualities and training.
f) Macro approach to management.
g) Human aspect of management.
Henry Fayol has been rightly called “The father of the management”. He has identified 14 principles of management those are division of labour, authority and responsibility, discipline, unity of command; unify of direction; subordination; remuneration; centralisation, scalar chain, order, equity, stability of tenure; initiative; esperit-de-corps etc.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the nature of management.
Answer:
1. Science as well as an Art :
Managemen is considered both a science and an art, because it is systematized knowledge which provides laws capable fo universal application and has a cause and efffect relationship.
2. Social Responsibility :
Management has been accepted as a profession in the area of discipline and its responsibilities have increased. A manager is not only answerble to his employer but equally to the society. He is considered to be .the representative of the society also and has to care for the interests of the consumers as well.
3. Mamagement has a Distinct Entiry :
Managers at the higher level do not work at the operative level. They get the work done by others. Organisation get success in maximum output of work at minimum imput in the form of man power, materials and time. Management is a process of universal application and it is required at each and every level of organization.
4. Purposive Activity :
Management is always aimed at achieving certain specified objecives. It is a tool which helps efficient use of human and physical resources to accomplish the predetermined goals. Management has no justification to exist without objectives.
5. Management is Pervasive :
Management is relevant for all types of organizations- economic political and political. Wherever more than one person is engaged in working for a common goal, management is necessary. That is why it is asserted that management is an essential element of organized activity irrespective of the type or size of the activity.
6. Management is a Group Activity :
Management is concerned with a group activity. It involves the use of group efforts in the achieving predetermined objectives.
Question 5.
What are the objectives of management?
Answer:
In any organisation there are different objectives and management has to achieve the objectives in an effective and efficient manner. Objectives of any business entity can be classified into Organizational objectives, Social objectives and Personal or individual objectives.
i) Organizational Objectives :
- Management of a business is responsible for setting and achieving objectives for it ssuccess.
- It has to achieve a variety of objectives in all areas considering the interest of all stakeholders including shareholders, employees, customers and government.
- The main objective of any organization should be to utilize human and material resources to the maximum possible advantage i.e, to fulfil the economic objectives of a business. These are survived, profit and growth.
ii) Social Objectives :
- It involves the creation of benefit for society. As a part of society, every organization whether it is business or non-business, has a social obligation to fulfill.
- This includes using environmental friendly methods of production, giving employment opoortunities to the disadvantaged sections of society and providing basic amenities like schools and creches to employees.
iii) Peraonal Objectives :
- Organizations are made up of person who have different personalities, backgrounds, experiences and objectives.
- They all become part of the organization to satisfy their diverse needs. These vary form financial needs social needs growth and development.
- Management has to reconcile personal goals with organizational objectives for har-mony in the organization.
Question 6.
Explain the significance of Management.
Answer:
Management plays an important and crucial role in a changing and complex society, whatever is the political philosophy, or structue of a society.
- Management assembles and organizes available resources for achieving of the goals of an enterprise.
- Management helps in improving the quality of lives of the people in the society by developing the human as well as non-human resources of production.
- Management has to face and solve numerous labour problems which arise almost every day in society and industrial organizaion.
- Management has to accomplish the objectives set forth in the beginning by any industrial organization.
- Management ability is put to test when it helps organization to survive in the market under free cut-throat competition.
- Management provides stability in the society by changing and modifying the resources or production in the fast changing economic and social environment.
- Various factors of production are inter-related and interdependent each contributing to the efficiency of others. Management strikes proper balance among them by securing maximum efficiency.
- Management provides maximum utilization of scarce resources by selecting its best possible alternative use in industry from out of various uses to which it can be put.
- Management helps an organization to survive in its dynamic environment. Good management enables an enterprise to adjust to the complex and every changing external environment.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the characteristics of Management?
Answer:
- Management is the process of planning organizing, staffing, directing and controlling the enterprise resources efficeintly and effectively for achieving the goals of the organization.
- According to RF. Drucker, “Management is a multipurpose organ that manages a business and manages managers, and manages workers and work”.
CHARACTERISTICS :
The following are the important characteristics of management.
1. It is an Economic Activity :
Management is part and parcel of every economic activity of man who struggles for better living in his existing society moulded under different management aspects like planning, coordianting, controlling etc.
2. It is a creative activity :
Management is creative, purposeful, group, motivating, economy oriented and delegating activity, and above all decision-making activity.
3. It gets things done through others :
It is its purpose that management gets the things done through other people. It does not perform the work itself but helps others to do. It coordinaes individual actions into a team.
4. It coordinates efforts :
In any organization a group of people is involved in working. The management activity brings about a co-ordinated efforts of many individuals and small groups towards organisational objective.
5. It is a process :
Management is the process which managers create, direct, maintain and operate purposive organizations through systematic, Coordinative human efforts.
6. Its goal oriented :
The purpose of management is to achieve certain goals. If the objective of a comp is to maximize profit, steps may be taken to reduce the cost or production and add new line of product or replace the existing machine with automated machine to provide maximum output which results in attaining the aim of maximum profits.
7. If acts as a group :
Management refers to a group of people who together carryout various managerial activities. All the managers from the chief executive to the first line supurvisors are collectively addressed as management.
8. It is a discipline :
Management is recognized as formal discipline having an organized body of knowledge which can be learnt through instructions and teaching. All over world scholars are doing research on the principles and practices of management.
Question 8.
Explain the levels of Management?
Answer:
There are threee levels of management which are explained here under :
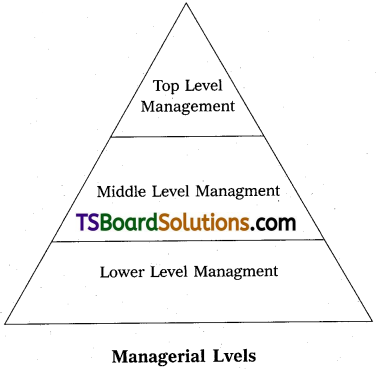
A. Top level :
1) According to of E.F.L Brech, the functions of top level, which actually are board of directors, Managing Director, Chief Executive and General Manager, who establishes policies, plans and objecives.
2) It needs more human skills, innovative decision making conceptual clarity to compare the technical skills.
3) The functions include :
i) Fixing the objectives of the enterprise and protecting the interests of the enterprises’ as its trustees;
ii) Evaluating the achievements of the enterprises
iii) Selecting the chief executive, allocating the incomes, discussing the complicated and serious matters.
B. Middle Level:
- Middle level management bridges gap between Top level management and Lower level management.
- Departmental heads of various departments are finance manager, personnel manager, production or marketing manager etc.
- Their main function is to implement the policies and programs formulated by the top management for the execution and to render valuable services for the successful operation of their deparments.
C. Lower Lelvel:
- Lower level management consist of superintendents, supervisors and foremen who are in touch with direct arrangement of workers.
- Supervisors are those having authority to exercise independent judgement in hearing, discharging, disciplining, rewarding and taking other actions of a similar nature with respect to employees. In offices they are known as supervisors and in factories as foremen.
- In the present age, supervisors have an important place in the management hierarchy and they are considered as ‘friends, guides and well wishers of labour.
Question 9.
Is management science or Art? Explain.
Answer:
Management is considered both an art and science, because it is systematized knowledge which Provides laws capable of univerwsal application and has a cause and effect relationship.
Management is an art:
- The application of management skills is governed by the type of aptitudes and ability possessed by the manager, which are highly personalized blending of imagination, creativity and insight.
- This permits management being described as an art. Management cannot be compared with sciences like physics, chemistry or mathematics so far the degree of precision is concerned.
- No doubt, mangement is a science, but not as exact in its results as in the case of physics or chemistry. This is for the simple reason that management science deals1 with human beings who are more widely influenced by a number of material factors.
- Management as science is still in the evolutionary stage and management is practiced as yet largely as an art like the earlier period. But the growing needs of management service have evolved it as a profession.
Management is science :
- Science is a systematized body of knowledge pertaining to a specific field of study and contains general facts that explain a phenomenon. It establishes the cause and effect relationship between two or more factors and ascertains the underlying principle governing the relationship.
- Theories are being continuously formulated as an aid to a more systematic analysis of managerial behavior thus resulting in the study of management moving into the management science.
- This expression stresses the constant search for evolving and verifying principles and rules as well as for further knowledge resulting in the emergence of managerial techniques effective universally.
- Scientific method or attitude has been increasingly adopted by good managers towards performance of their job of managing.
- They have developed inquiring minds which first attempt to identify the problem, for hypothesis or tentative solutions, then investigate in terms of current knowledge and even controlled experiments, classify the data, so obtained and develop it into altemative courses of action.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define Management.
Answer:
Generally mangement has been defined as “getting things done through others”.
Definitions :
- Management is a multipurpose organ that manges a business and manages managers and manages workers and work. – Peter F. Drucker.
- Management is the art of knowing what you want to do and then seeing that it is done in the best and cheapest way”. – F.W. Taylor.
- “To manage is to forecast and to plan, to organize, to*command, to co-ordinate and to control.” – Henry Fayol.
![]()
Question 2.
Name any two important dcharacteristics of management.
Answer:
The following are the important characteristics of management.
- It is an economic activity.
- It gets things done through others.
- It is a creative activity.
- It co-ordinates efforts.
- It is a process.
- It is goal oriented.
- It acts as a group.
- It is a discipline.
1) It is an economic activity :
Management is part and parcel of every economic activity of man who struggles for better living in his existing society, the fate of which is rather moulded by management under different aspects like planning, co-ordinating, controlling etc., It is the sum total of those activities.
2) It gets things done through others :
It is its purpose that management gets the things done through other people. It does not perform the work itself but helps to do. It co-ordinates individual actions into a team. In any organization a group of people is involved in working towards a common objective. Whatever the managers do they have some purpose in it. Managers motivate people to get things done through them.
3) It is a creative activity :
Management is creative activity-purposeful activity-group activity – motivating activity – economy oriented activity – delegating activity and above all, a decision – making activity.
Question 3.
What is the meant by unit of Direction.
Answer:
Unity of Direction :
- According to this principle, the efforts of all the members of the organization should be directed towards common goals. A group of activities having the same objective must have one head and one plan.
- For this purpose there should be one hed and one plan for a group of activities having the same objectives.
- The principle seeks to ensure “unity of action, co-ordination of strength and focusing of effort.
Question 4.
What are the basic features of management as a profession?
Answer:
- Profession refers to an occupation, which is supported a well-defined of knowledge that can be learnt through instruction, in which entry is restricted by examination or education and which is associated with service to others above self interest.
- The view of management is progressively changing. Managers must receive training in management and possess requisite educational qualifications.
- In the field of management does not any professional association as that of Bar Council of India for practicing lawyers, chartered accountants, cost accountants and company secretaries and so on.
- In some respects management qualify as a profession but it does not have certain features which generally are recognized as profession.
- We may say that the management is emerging as a profession backed by a number of principles, techniques and tools have developed which need proper training, education and learning.
Question 5.
Is Management Art?
Answer:
Management is an art :
The application of management skills is governed by the type of aptitudes and ability possessed by the manager, which are highly personalized blending of imagination, creativity and insight. This permits management being described as an art. Management cannot be compared with sciences like physics, chemistry or mathematics so far the degree of precision is concerned. No doubt, mangement is a science, but not as exact in its results as in the case of physics or chemistry.
This is for the simple reason that management science deals with human beings who are more widely influenced by a number of material factors. Management as science is still in the evolutionary stage and management is practiced as yet largely as an art like the earlier period. But the growing needs of management service have evolved it as a profession.
Question 6.
Is Management Profession.
Answer:
- Profession refers to an occupation, which is supported a well-defined of knowledge that can be learnt through instruction, in which entry is restricted by examination or education and which is associated with service to others above self interest.
- The view of management is progressively changing. Managers must receive training in management and possess requisite educational qualifications.
- In the field of management does not any professional association as that of Bar Council of India for practicing lawyers, chartered accountants, cost accountants and company secretaries and so on.
- In some respects management qualify as a profession but it does not have certain features which generally are recognized as profession.
- We may say that the management is emerging as a profession backed by a number of principles, techniques and tools have developed which need proper training, education and learning.
![]()
Question 7.
Is management a science?
Answer:
Management as science :
Science is a systematized body of knowledge pertaining to a specific field of study and contains general facts that explain a phenomenon. It establishes the cause and effect relationship between two or more factors and ascertains the underlying principle governing the relationship. Theories are being continuously formulated as an aid to a more systematic analysis of managerial behavior thus resulting in the study of management moving into the management science.
This expression stresses the constant search for evolving and verifying principles and rules as well as for further knowledge resulting in the emergence of managerial techniques effective universally. Scientific method or attitude has been increasingly adopted by good managers towards performance of their job of managing. They have developed inquiring minds which first attempt to identify the problem, for hypothesis or tentative solutions, then investigate in terms of current knowledge and even controlled experiments, classify the data so obtained and develop it into alternative courses of action.
Question 8.
What are the organisational objectives of Management?
Answer:
Organizational Objectives :
- Management of a business is responsible for setting and achieving objectives for it ssuccess.
- It has to achieve a variety of objectives in all areas considering the interest of all stakeholders including shareholders, employees, customers and government.
- The main objective of any organization should be to utilize human and material resources to the maximum possible advantage i.e., to fulfil the economic objectives of a business. These are survival, profit and growth.
Question 9.
What is top level management.
Answer:
Top level:
1) According to of E.F.L Brech, the functions of top level, which actually are board of directors, Managing Director, Chief Executive and General Manager, who establishes policies, plans and objecives.
2) It needs more human skills, innovative decision making conceptual clarity to compare the technical skills.
3) The functions include :
i) Fixing the objectives of the enterprise and protecting the interests of the enterprises’ as its trustees;
ii) Evaluating the achievements of the enterprises :
iii) Selecting the chief executive, allocating the incomes, discussing the complicated and serious matters.
Question 10.
Distinguish management and administration.
Answer:
Management and Administration :
Administration is considered as wider in scope in comparison with management. Administration is concerned with policy making for achieving objectives whereas management is considered as executing the policy.
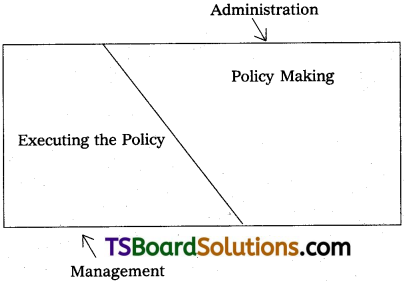
Distinction between Management and Administration :
- Administration lays down broad goals and objectives for which the industrial enterprises have been set up. Management formulates plans which would lead to the fulfillmen of the enterprise objectives.
- Administration lays down broad policies and principles for guidance. Management execute these policies into practice.
- Administration draws out the outline and framework for the execution of its policies. Management controls and supervises the activities concerned to execution of policies.
- Administration provides directon, guidance and leadership in all the activities of the enterprise. Management co-ordinates the various activities within a particular department and co-ordinates the activities of the various departments.
Question 11.
Distinguish Unity of command and unity of Direction.
Answer:
| Basis | Unity of Command | Unity of Direction |
| Meaning | One subordinate should receive orders from and should be responsible to only one superior | Each group of activities having same objectives must have one head and one plan. |
| Aim | It prevents dual subordination. | It prevents overlapping of activities. |
| Implications | It affects an individual employee | It affects the entire organization. |
![]()
Question 12.
What is parity of authority and responsibility.
Answer:
Partiy of Authority and Responsibility
- Authority refers to the right of a superior to give order to subordinage, take decision on specified matters, use resources of the organization, and guide and regulate the behaviour of subordinaes.
- Responsibility includes obligation with respect to perforance of functions and achieving goals in the satisfactory manner.
- The principle of parity suggests that there must be parity between authority and responsibility. Giving authority without corresponding responsibility can lead to arbitrary and unmindful use of authority.
- Similarly, if a person is given some responsibility he must also be given adequate authority. Lack of necessary authority makes the individual ineffective.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Scalar chain.
Answer:
- The scalar chain is the chain of superiors ranging from the ultimate authority to the lowest ranks.
- It shows the line of authority from the highest executive to the lowest one for the purpose of communication.
- This will help an employee to know the person whom he sould contact for advice and guidance.
Question 2.
Administration.
Answer:
- Administration is concerned with policy making.
- Administration is considered as wider in scope in comparision with management.
- According to Haimann, administration is overall; determination of policies, the setting of major objectives, layingout of broad programmes, major projects so forth.
Question 3.
List out the principles of management.
Answer:
Henry Fayol contributed 14 principles. He is a ‘Father of Management’ The important principles are division of labour, parity of authority and responsibility, discipline, unity of com-mand, esperit-de-corps etc.
![]()
Question 4.
Unit of command.
Answer:
- The principle states that a subordinate should receive orders and be accountable to one and only one superior.
- No employee, therefore, should receive instructions from more than one persoji. The principle is necessary to avoid confusion and conflict.
Question 5.
Esperit de corps.
Answer:
- It implies tht union is strength, which comes from the harmony of the personnel.
- It emphasizes the importance of teamwork and group endeavors.
- The management should never adopt ‘divide and rule’ policy. It should encourage team spirit and team work. This ensures smooth working of the organization.
Question 6.
Unity of Direction.
Answer:
- According to this principle, the efforts of all the members of the organization should be directed towards common goals. A group of activities having the same objective must have one head and one plan.
- For this purpose there should be one hed and one plan for a group of activities having the same objectives.
- The principle seeks to ensure “unity of action, co ordination of strength and focusing of effort.
Question 7.
Authority and responsibility.
Answer:
- Authority refers to the right of a superior to give order to subordinate, take decision on specified matters, use resources of the organization, and guide and regulate the behavior of subordinates.
- Responsibility includes with respect to performance of functions and achieving goals in the satisfactory manner.
- The principle of parity suggests that there must be parity between authority and re-sponsibility. Giving authority without corresponding responsibility can lead to arbitary and unmindful use of authority.
Question 8.
centralization.
Answer:
- It refers to the extent to which authority is concentrated or dispersed.
- The appropriate degree of centralization will vary with different concerns.
- Under centralization managers or executives play an important role.
Question 9.
Principle of Inititative.
Answer:
- The freedom to propose a plan and to execute it is known as initiative. Initiative involves thinking out and execution of a plan and ensuring its success. This gives zeal and energy to an organization.
- Fayol advised managers to allow employees.
- It will enable employees to experience the keenest satisfaction from their jobs.
![]()
Question 10.
Middle level management.
Answer:
- Middle level management bridges gap between Top level management and Lower level management.
- Departmental heads of various departments are finance manager, personnel rpanager, production or marketing manager etc.
- Their main function is to implement the policies and programs formulated by the top management for the execution and to render valuable services for the successful operation of their deparments.
Question 11.
Principle of Discipline.
Answer:
- Discipline in the context of management means obedience, proper conduct in relation to others and complying with the rules and regulations of the organization.
- Discipline is required not only on the part of workers but also on the part of management, It is facilitated if there are good supervisors at all levels, rules are clear, and penalties are imposed with fairness.