Here you will find Telangana TSBIE State Board Syllabus TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material Pdf free download, TS Intermediate 2nd Year Chemistry Textbook Solutions Questions and Answers in English Medium and Telugu Medium according to the latest exam curriculum. The chapter-wise TS Inter 2nd Year Study Material will help the students in understanding the concept behind each question in a detailed way.
Students can check the TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Syllabus & TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Important Questions for strong academic preparation. Students can use TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Notes as a quick revision before the exam.
TS Intermediate 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material Pdf Download | TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Textbook Solutions Telangana
- Chapter 1 Solid State
- Chapter 2 Solutions
- Chapter 3 Electrochemistry and Chemical Kinetics
- Chapter 4 Surface Chemistry
- Chapter 5 General Principles of Metallurgy
- Chapter 6 P-Block Elements
- Chapter 7 d and f Block Elements & Coordination Compounds
- Chapter 8 Polymers
- Chapter 9 Biomolecules
- Chapter 10 Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Chapter 11 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Chapter 12 Organic Compounds Containing C, H and O
- Chapter 13 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
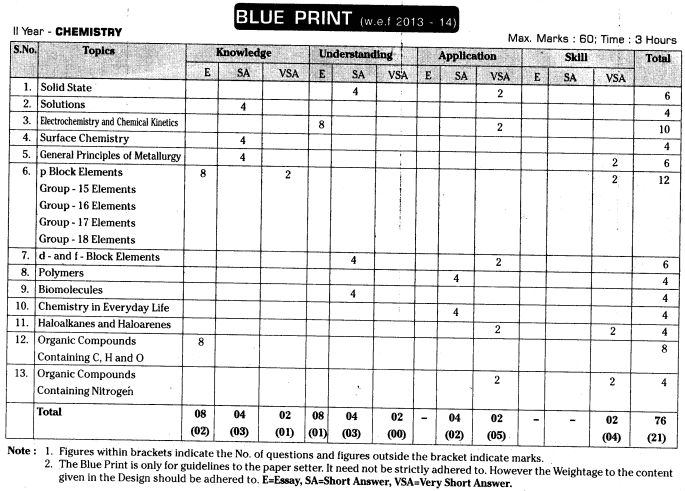
TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Weightage Blue Print 2022-2023
TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Syllabus
Telangana TS Intermediate 2nd Year Chemistry Syllabus
TELANGANA STATE BOARD OF INTERMEDIATE EDUCATION, HYDERABAD
Chemistry-II
Syllabus (w.e.f. 2013-14)
Chapter 1: SOLID STATE
1.1 General characteristics of solid state 1.2 Amorphous and crystalline solids 1.3 Classification of crystalline solids based on different binding forces (molecular, ionic, metallic and covalent solids) 1.4 Probing the structure of solids: X-ray crystallography 1.5 Crystal lattices and unit cells, Bravais lattices primitive and centred unit cells 1.6 Number of atoms in a unit cell (primitive, body centred and face centred cubic unit cell)1.7 Close packed structures: Close packing in one dimension, in two dimensions and in three dimensions- tetrahedral and octahedral voids- formula of a compound and number of voids filled- locating tetrahedral and octahedral voids 1.8 Packing efficiency in simple cubic, bcc and in hcp, ccp lattice. 1.9 Calculations involving unit cell dimensions-density of the unit cell. 1.10 Imperfections in solids-types of point defects-stoichiometric and non-stoichiometric defects 1.11 Electrical properties-conduction of electricity in metals, semiconductors and insulators- band theory of metals 1.12 Magnetic properties.
Chapter 2: SOLUTIONS
2.1 Types of solutions 2.2 Expressing concentration of solutions-mass percentage, volume percentage, mass by volume percentage, parts per million, mole fraction, molarity and molality 2.3 Solubility: Solubility of a solid in a liquid, solubility of a gas in a liquid, Henry’s law 2.4 Vapour pressure of liquid solutions: vapour pressure of liquid-liquid solutions. Raoult’s law as a special case of Henry’s law -vapour pressure of solutions of solids in liquids 2.5 Ideal and non-ideal solutions 2.6 Colligative properties and determination of molar mass-relative lowering of vapour pressure-elevation of boiling point-depression of freezing point-osmosis and osmotic pressure-reverse osmosis and water purification. 2.7 Abnormal molar masses-van’t Hoff factor.
Chapter 3: ELECTROCHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL KINETICS
ELECTROCHEMISTRY
3.1 Electrochemical cells 3.2 Galvanic cells measurement of electrode potentials 3.3 Nernst equation-equilibrium constant from Nernst equation- electrochemical cell and Gibbs energy of the cell reaction 3.4 Conductance of electrolytic solutions-measurement of the conductivity of ionic solutions-variation of conductivity and molar conductivity with concentration-strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes-applications of Kohlrausch’s law 3.5 Electrolytic cells and electrolysis: Faraday’s laws of electrolysis-products of electrolysis 3.6 Batteries: primary batteries and secondary batteries 3.7 Fuel cells 3.8 Corrosion of metals-Hydrogen economy
CHEMICAL KINETICS
3.9 Rate of a chemical reaction 3.10 Factors influencing rate of a reaction: dependence of rate on concentration- rate expression and rate constant- order of a reaction, molecularity of a reaction 3.11 Integrated rate equations-zero order reactions-first order reactions- half life of a reaction 3.12 Pseudo first order reaction 3.13 Temperature dependence of the rate of a reaction -effect of catalyst 3.14 Collision theory of chemical reaction rates.
Chapter 4: SURFACE CHEMISTRY
4.1 Adsorption and absorption: Distinction between adsorption and absorption-mechanism of adsorption-types of adsorption-characteristics of physisorption-characteristics of chemisorptions-adsorption isotherms- adsorption from solution phase-applications of adsorption 4.2 Catalysis: Catalysts, promoters and poisons-auto catalysis- homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis- adsorption theory of heterogeneous catalysis-important features of solid catalysts: (a) activity (b) selectivity-shape-selective catalysis by zeolites- enzyme catalysis-characteristics and mechanism-catalysts in industry 4.3 Colloids 4.4 Classification of colloids: Classification based on physical state of dispersed phase and dispersion medium- classification based on nature of interaction between dispersed phase and dispersion medium- classification based on type of particles of the dispersed phase- multi molecular, macromolecular and associated colloids-cleansing action of soaps-preparation of colloids-purification of colloidal solutions- properties of colloidal solutions: Tyndal effect, colour,Brownian movement-charge on colloidal particles, electrophoresis 4.5 Emulsions 4.6 Colloids Around us- application of colloids.
Chapter 5: GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF METALLURGY
5.1 Occurance of metals 5.2 Concentration of ores-levigation, magnetic separation, froth floatation, leaching 5.3 Extraction of crude metal from concentrated ore-conversion to oxide, reduction of oxide to the metal 5.4 Thermodynamic principles of metallurgy-Ellingham diagram-limitations-applications-extraction of iron, copper and zinc from their oxides 5.5 Electrochemical principles of metallurgy 5.6 Oxidation and reduction 5.7 Refining of crude metal-distillation, liquation poling, electrolysis, zone refining and vapour phase refining 5.8 Uses of aluminium, copper, zinc and iron
Chapter 6: p-BLOCK ELEMENTS
GROUP-15 ELEMENTS
6.1 Occurance- electronic configuration, atomic and ionic radii, ionisation energy, electronegativity, physical and chemical properties 6.2 Dinitrogen-preparation, properties and uses 6.3 Compounds of nitrogen-preparation and properties of ammonia 6.4 Oxides of nitrogen 6.5 Preparation and properties of nitric acid 6.6 Phosphorous-allotropic forms 6.7 Phosphine-preparation and properties 6.8 Phosphorous halides 6.9 Oxoacids of phosphorous
GROUP-16 ELEMENTS
6.10 Occurance- electronic configuration, atomic and ionic radii, ionisation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy, electronegativity, physical and chemical properties 6.11 Dioxygen-preparation, properties and uses 6.12 Simple oxides 6.13 Ozone-preparation, properties, structure and uses 6.14 Sulphur-allotropic forms 6.15 Sulphur dioxide-preparation, properties and uses 6.16 Oxoacides of sulphur 6.17 Sulphuric acid-industrial process of manufacture, properties and uses
GROUP-17 ELEMENTS
6.18 Occurance, electronic configuration, atomic and ionic radii, ionisation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy, electronegativity, physical and chemical properties 6.19 Chlorine-preparation, properties and uses 6.20 Hydrogen chloride- preparation, properties and uses 6.21 Oxoacids of halogens 6.22 Interhalogen compounds
GROUP-18 ELEMENTS
6.23 Occurance, electronic configuration, ionization enthalpy, atomic radii electron gain enthalpy, physical and chemical properties(a) Xenon-fluorine compounds-XeF2, XeF4 and XeF6 -preparation, hydrolysis and formation of fluoro anions-structures of XeF2, XeF4 and XeF6 (b) Xenon-oxygen compounds XeO3 and XeOF4 – their formation and structures
Chapter 7: d AND f BLOCK ELEMENTS &COORDINATION COMPOUNDS
d AND f BLOCK ELEMENTS
7.1 Position in the periodic table 7.2 Electronic configuration of the d-block elements 7.3 General properties of the transition elements (d-block) -physical properties, variation in atomic and ionic sizes of transition series, ionisation enthalpies, oxidation states, trends in the M2+/M and M3+/M2+ standard electrode potentials, trends in stability of higher oxidation states, chemical reactivity and EJ values, magnetic properties, formation of coloured ions, formation of complex compounds, catalytic properties, formation of interstitial compounds, alloy formation 7.4 Some important compounds of transition elements-oxides and oxoanions of metals-preparation and properties of potassium dichromate and potassium permanganate-structures of chromate, dichromate, manganate and permanganate ions 7.5 Inner transition elements(f-block)-lanthanoids- electronic configuration-atomic and ionic sizes- oxidation states- general characteristics 7.6 Actinoids-electronic configuration atomic and ionic sizes, oxidation states, general characteristics and comparision with lanthanoids 7.7 Some applications of d and f block elements.
COORDINATION COMPOUNDS
7.8 Werner’s theory of coordination compounds 7.9 Definitions of some terms used in coordination compounds 7.10 Nomenclature of coordination compounds-IUPAC nomenclature 7.11 Isomerism in coordination compounds-(a)Stereo isomerism-Geometrical and optical isomerism (b)Structural isomerism-linkage, coordination, ionisation and solvate isomerism 7.12 Bonding in coordination compounds. (a)Valence bond theory -magnetic properties of coordination compounds-limitations of valence bond theory (b) Crystal field theory (i) Crystal field splitting in octahedral and tetrahedral coordination entities (ii) Colour in coordination compounds-limitations of crystal field theory 7.13 Bonding in metal carbonyls 7.14 Stability of coordination compounds 7.15 Importance and applications of coordination compounds.
Chapter 8: POLYMERS
8.1 Classification of Polymers -Classification based on source, structure, mode of polymerization, molecular forces and growth polymerization 8.2 Types of polymerization reactions-addition polymerization or chain growth polymerization-ionic polymerization, free radical mechanism-preparation of addition polymers-polythene, teflon and poly acrylonitrile-condensation polymerization or step growth polymerization-polyamides-preparation of Nylon 6,6 and nylon 6-poly esters-terylene-bakelite, melamine, formaldehyde polymer- copolymerization-Rubber-natural rubber-vulcanisation of rubber-Synthetic rubbers-preparation of neoprene and buna-N 8.3 Molecular mass of polymers-number average and weight average molecular masses-poly dispersity index (PDI) 8.4 Biodegradable polymers-PHBV, Nylon 2-nylon 6 8.5 Polymers of commercial importance-poly propene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride(PVC), urea-formaldehyde resin, glyptal, bakelite- their monomers, structures and uses.
Chapter 9: BIOMOLECULES
9.1 Carbohydrates – Classification of carbohydrates-Monosaccharides: preparation of glucose from sucrose and starch- Properties and structure of glucose- D,L and (+), (-) configurations of glucose- Structure of fructose Disaccharides: Sucrose- preparation, structure-Invert sugar- Structures of maltose and lactose-Polysaccharides: Structures of starch cellulose and glycogen- Importance of carbohydrates 9.2 Aminoacids: Natural aminoacids-classification of amino acids -structures and D and L forms-Zwitter ions Proteins: Structures, classification, fibrous and globular-primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures of proteins- Denaturation of proteins 9.3 Enzymes: Enzymes, mechanism of enzyme action 9.4 Vitamins: Explanation-names- classification of vitamins – sources of vitamins-deficiency diseases of different types of vitamins 9.5. Nucleic acids: chemical composition of nucleic acids, structures of nucleic acids, DNA finger printing biological functions of nucleic acids 9.6 Hormones: Definition, different types of hormones, their production, biological activity, diseases due to their abnormal activities.
Chapter 10: CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
10.1 Drugs and their classification: (a) Classification of drugs on the basis of pharmacological effect (b) Classification of drugs on the basis of drug action (c) Classification of drugs on the basis of chemical structure (d) Classification of drugs on the basis of molecular targets 10.2 Drug-Target interaction-Enzymes as drug targets(a) Catalytic action of enzymes (b) Drug-enzyme interaction Receptors as drug targets10.3 Therapeutic action of different classes of drugs: antacids, antihistamines, neurologically active drugs: tranquilizers, analgesics-non-narcotic, narcotic analgesics, antimicrobials-antibiotics, antiseptics and disinfectants- antifertility drugs 10.4 Chemicals in food-artificial sweetening agents, food preservatives, antioxidants in food 10.5 Cleansing agents-soaps and synthetic detergents.
Chapter 11: HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
11.1 Classification and nomenclature 11.2 Nature of C-X bond 11.3 Methods of preparation: Alkyl halides and aryl halides-from alcohols, from hydrocarbons (a) by free radical halogenation -(b) by electrophilic substitution (c) by replacement of diazonium group(Sand-Meyer reaction) (d) by the addition of hydrogen halides and halogens to alkenes-by halogen exchange(Finkelstein reaction) 11.4 Physical properties-melting and boiling points, density and solubility 11.5 Chemical reactions: Reactions of haloalkanes (i)Nucleophilic substitution reactions (a) SN2 mechanism (b) SN1 mechanism (c) stereochemical aspects of nucleophilic substitution reactions – optical activity (ii) Elimination reactions (iii) Reaction with metals-Reactions of haloarenes: (i) Nucleophilic substitution (ii)Electrophilic substitution and (iii) Reaction with metals 11.6 Polyhalogen compounds: Uses and environmental effects of dichloro methane, trichloromethane, triiodomethane, tetrachloro methane, freons and DDT.
Chapter 12: ORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING C, H AND O
(Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids) ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS
12.1 Alcohols, phenols and ethers –classification 12.2 Nomenclature: (a) Alcohols, (b)phenols and (c)ethers 12.3 Structures of hydroxy and ether functional groups 12.4 Methods of preparation: Alcohols from alkenes and carbonyl compounds- Phenols from haloarenes, benzene sulphonic acid, diazonium salts, cumene 12.5 Physical propertics of alcohols and phenols 12.6 Chemical reactions of alcohols and phenols (i) Reactions involving cleavage of O-H bond-Acidity of alcohols and phenols, esterification (ii) Reactions involving cleavage of C-O bond-reactions with HX, PX3, dehydration and oxidation (iii) Reactions of phenols-electrophilic aromatic substitution, Kolbe’s reaction, Reimer – Tiemann reaction, reaction with zinc dust, oxidation 12.7 Commercially important alcohols (methanol, ethanol) 12.8 Ethers-Methods of preparation: By dehydration of alcohols, Williamson synthesis- Physical properties-Chemical reactions: Cleavage of C-O bond and electrophilic substitution of aromatic ethers.
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
12.9 Nomenclature and structure of carbonyl group 12.10 Preparation of aldehydes and ketones-(1) by oxidation of alcohols (2) by dehydrogenation of alcohols (3) from hydrocarbons -Preparation of aldehydes (1) from acyl chlorides (2) from nitriles and esters (3) from hydrocarbons-Preparation of ketones (1) from acyl chlorides (2) from nitriles (3) from benzene or substituted benzenes 12.11 Physical properties of aldehydes and ketones 12.12 Chemical reactions of aldehydes and ketones-nucleophilic addition, reduction, oxidation, reactions due to -Hydrogen and other reactions (Cannizzaroreaction, electrophilic substitution reaction) 12.13 Uses of aldehydes and ketones.
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
12.14 Nomenclature and structure of carboxyl group 12.15 Methods of preparation of carboxylic acids- (1)from primary alcohols and aldehydes (2) from alkylbenzenes (3) from nitriles and amides (4) from Grignard reagents (5) from acyl halides and anhydrides (6) from esters 12.16 Physical properties 12.17 Chemical reactions: (i) Reactions involving cleavage of OH bond-acidity, reactions with metals and alkalies (ii) Reactions involving cleavage of C-OH bond-formation of anhydride, reactions with PCl5, PCl3, SOCl2, esterification and reaction with ammonia (iii) Reactions involving -COOH group-reduction, decarboxylation (iv) Substitution reactions in the hydrocarbon part – halogenation and ring substitution 12.18 Uses of carboxylic acids.
Chapter 13: ORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGEN
I. AMINES
13.1 Structure of amines 13.2 Classification 13.3 Nomenclature 13.4 Preparation of amines: reduction of nitro compounds, ammonolysis of alkyl halides, reduction of nitriles, reduction of amides, Gabriel phthalimide synthesis and Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction. 13.5 Physical properties13.6 Chemical reactions: basic character of amines, alkylation, acylation, carbyl amine reaction, reaction with nitrous acid, reaction with aryl sulphonyl chloride, electrophilic substitution of aromatic amines-bromination, nitration and sulphonation.
II. DIAZONIUM SALTS
13.7 Methods of preparation of diazonium salts (by diazotization) 13.8 Physical properties 13.9 Chemical reactions: Reactionsinvolvin.
III. CYANIDES AND ISOCYANIDES
13.11 Structure and nomenclature of cyanides and isocyanides 13.12 Preparation, physical properties and chemical reactions of cyanides and isocyanides.
We hope this TS Intermediate 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material Pdf Download in English Medium and Telugu Medium will be useful for students to attain the right approach for precisely answering the textbook questions. If there is any trouble in grasping the concepts related to TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Textbook Solutions Telangana, drop your questions in the comment and we will get back to you with a solution in time.