Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Study Material 2nd Lesson Stock Exchange Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Study Material 2nd Lesson Stock Exchange
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is stock exchange? Explain its functions.
Answer:
Introduction :
Stock exchange is an organized secondary market, where the listed secu-rities are bought and sold by the investors.
Definition :
“Stock exchange is an association, organization or body of individuals, whether incorporated or not, established for the purpose of assisting, regulating and controlling business in buying, selling and dealing in securities”. – The Securities Contracts Act 1956
“Security exchanges are market places where securities that have been listed thereon may be bought and sold either for investment or speculation”. – “Pyle”
Functions of Stock Exchange :
1) Provides infrastructure for trading :
In the stock exchange, instantaneously trading gets executed. It draws investment by providing ready and continuous market for securities.
2) Provides information regarding prices :
It gives sensible information through reliable sources and publishers to investors about the prices of securities. The proposed investor knows the quotation and the investor knows the price of his holdings.
3) Protects investors wealth :
It protect the interests and wealth of investors through the enforcement of its rules and regulations.
4) Clearing House :
Without clearing house one will find lot of trades mismatched. It act on behalf of both buyer and seller and helps in trading of securities.
5) Provides liquidity :
The holder of securities can easily encash the securities by selling them to the buyer whenever he wants.
6) Helps to raise new capital :
The requirement of additional capital of an existing company can be raised by issuing the rights shares, through stock exchange.
7) Acts as a Barometer :
An efficient stock exchange acts as a Barometer of business conditions in the country.
8) Increases credit worthiness of company :
A company which got its shares to be listed in the stock exchange enjoys good reputation.
9) Minimises the dangers of speculation :
By following rules and regulations of the Acts, it minimises the dangers of speculative dealings and price manipulations.
10) Facilitates speculation :
Stock exchange facilitates speculation thereby businessman can speculate and earn profits from fluctuations in security prices.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain he significance of stock exchange.
Answer:
Introduction :
The stock exchange is a market for the purchase and sale of second hand securities. It is the central place where industrial and financial securities are brought and sold. It is the place where a buyer of a security can find a seller or a seller can find a buyer.
Significance of Stock Exchange :
The importance and need of stock exchange can be identified through its benefits to the investors, company and society.
A) To the Investors :
- Helps the investor in finding an opportunity to invest surplus funds in a reputed company.
- Reduces the risk of investro by providing continuous information market with correct evaluation of securities.
- Investors can change their investments to different companies according to their gaining.
- Continuously available for the conversion of securities thereby providing liquidity to the securities.
- Safeguards the interests of investors by the strict enforcement of rules and regulations.
- The holdlers of securities can use them as collateral securities for procuring loans.
- Investors able to know the activities of company and its credit worthiness.
- Investors earn not only good returns but they know the security prices from time to time and this promotes saving, investing and risk-taking among them.
B) To the company :
- The stock exchange provieds an opportunity to the companies to raise capital by sale of shares. So, the rapid progress of companies is largely facilitated by stock exchanges. The listing facilities provided by the stock exchange make the securities .attractive. The listing of securities gives an impression that the company is sound.
- A listed company generally enjoys better reputation and credit.
- As a listed company furnishes its financial statements, it wins the faith of investor and proves itself to be sound company.
- Stock exchange promotes the primary market for new issues as it engages ready and continuous market of securities.
- A well-organised stock exchange minimises price fluctuations and maintains steadiness of prices of securities.
- It will have wider market for its scurities.
- It can have maximum funds for expansion and modernisation sthrough ‘Rights Issue’.
C) To the society :
- By pooling up all the interested investors towards investment, it contributes to the economic developed of the nation.
- It provides opportunities to utilize the scarce financial resources to its maximum.
- It enables the government to establish successful companies for the progress of nation. A good company can keep up its status by trading its securities in stock exchange.
- It develops savings habit among the public and these savings are turned into capital for the growth of industries.
- The stock exchange acts as a mirror of society’s economy.
Question 3.
What is the procedure of listing securities?
Answer:
Introduction :
A company with minimum issued capital of ₹ 3 crores of which at least ₹ 1.8 crore (60%) is offered to the public can apply for listing in the prescribed preforma along with the following documents.
- Copies of Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association, Prospectus, Directors Reports, Balance sheets and agreements with underwriters and brokers etc.
- Specimen copies of shares and debentures certificates, letters of allotments, acceptance renunciation etc.
- Particulars regarding capital structure.
- A statement showing the distribution of shares.
- Particulars of dividends and bonus declared and or paid during the last 10 years.
- Particulars of shares of debentures for which permission to deal is applied for.
- Brief report on company’s activities since its incorporation,
- Listing agreement with required initial and annual listing fee.
A new company may not able to submit some of the above documents and it will not be an objecion for enlisting.
After submission of application along with the above documents by the company, the stock exchange scrutinizes the application, if stock exchange is statisfied with the particulars field, it may inform the company to execute a listing agreement. The agreement contains the obligations and restrictions which listing entail.
The central iisting authority has been set up in the year 2003 by’SBI for ensuring unifrom and standard practices for listing the securities in all India stock exchanges. It will have a check on the operators in small stock exchanges that have lenient listing norms.
![]()
Question 4.
What is SEBI? What are its functions and powers?
Answer:
SEBI means securities and Exchanges Board of India. SEBI come into existence through the SEBI Act, 1992 by the Indian Parliament and was given statutory powers, to overcome the undesivable practices in the stock exchange. In the year 1995, SEBI was given additional statutory powers by Government of India through an amendment to SEBI Actg 1992.
SEBI is managed by its members which consists of
a) The chairman who is nominated by Government of India.
b) Two members i.e. officers from Union Finance Ministry.
c) One member from the RBI.
d) The remaining 5 members (nominatged by Union Government of India.
Functtions of SEBI:
SEBI has three functions rolled into one body i.e.,
- quasi legislative
- quasi judicial and
- quasi executive
It drafts regulations in its legislative capacity (quasi legislative), it conducts investigation and enforcement action in its executive function (quasi judicial) and it passes rulings and orders in its judicial capacity (quasi executive). These functions may be summarised as :
- Educate investors and imparting training to the intermediaries of securities.
- Controls the working of stock exchanges.
- Register and regulate the working of intermediaries such as stock brokers, merchant bankers, underwriters etc. ,
- Regulate working of collective investment schemes including mutual funds.
- Conducts audits and inspections
- Restrocts insider trading of securities.
Powers :
For the discharging of its functions efficienctly, SEBI is vested with the following powers.
- to approve and amend the by-laws of stock exchange.
- to inspec the books of accounts of financial intermediaries.
- to inspect the books of accounts and call for periodical returns from recognised stock exchanges.
- to mandate the companies to list their shares in one or more stock exchanges.
Question 5.
Explain the various types of stock exchange speculators.
Answer:
A) Stock Exchange Speculators :
Persons who make profits by trading securities for short term purpose are known as stock exchange speculators. They accept high risk and do not take or give delivery of securities. The difference between buying and selling is their profit.
Types of speculators :
Depending upon the nature of speculation, the speculators may be called as bulls, bears, stag and lameduck.
1. Bull :
- A bull is a speculator who expects a rise in the price of certain security in future. He buys that security to sell it at the expected higher price.
- A bull in general throws its vicitm upwards. As the speculator expects a rise in the price of securities, his tendency is compared to that of bull.
- In technical terms he is said to be “on the long side of the market.” He is also known as tejiwala.
2. Bear :
- He is also known as mondiwala. A bear is a speculator, who expecs a fall in the price of certain securities and agrees to sell the securities at a fixed date in future, which he may or may not possess.
- If the price of that security falls before the date of sale, he purchases the security at a lower rate and sells it for higher rate as agreed earlier.
- The different between the purchase price and selling price is the profit earned by him.
- A bear usually presses its victim down to the ground. As the pessimistic tendency of the speculator, he expects a fall in price of security and therefore, he is named after bear.
3. Stag :
- A stag is a cautious speculator. He neither buys nor sells the shares. He, applies for the shares of a new company for face value and he expects they are sold at a premium i.e., more than its face valued.
- The difference between the price paid by him and the selling price is his profit.
4. Lameduck :
- When the expectations of bear does not become true and the price of security does not fall, he cannnot fulfil his commitment, and he is said to be lameduck.
- Bear may agree to sell certain security on a certain date and may not be able to deliver the security as it may not be available in the market.
- On the agreed date if the other party does not agree to oblige him, he suffers like a lameduck.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the features of BSE and NSE.
Answer:
The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) is formerly known as “Native Stock and Share Bro-kers Association”, which was established in the year 1877. The aim of association was to support and protect the character and status of brokers, to promote fair practices and to discourage malpractices.
Features of BSE :
- It has online trading system introduced in 1995, which is called BOLT(BSE online trading). This helps in active trading and safeguards market integrity.
- It provides other services like risk management, clearing, settlement, market, data and education to capital market participants.
- It provides a trading platform for equities of small and medium enterprises.
- It conforms international standards.
- It provides on efficient and transparent market for trading in equity, debt instruments and mutual funds.
- It has global reach helping customers around the world.
The National Stock Exchange (NSE) was incorporated in November, 1992. It is a “country wide screen based online trading system” and has international standards.
Features of NSE :
- It is a computerized national wide stock exchange where NSE members all over India are linked via statellite and cable system.
- The automated quotation system makes it convenient to the brokers to buy and sell electronically and need not shout in the trading ring about prices.
- It deals with the wholesale debt market like government securities, units by UTI etc.
- Price data will be broadcasted by the Press Trust of India (RT.I)
- It improves the settlement system, arid minimizes the risk therein. NSE has setup a subsidiary national securities clearing corporation, which guarantees the settlement of trade executed.
- It operates dealings in the corporate equity and debt instruments.
Question 7.
Who is a stock broker? Explain the role played by him in the financial market?
Answer:
Stock Broker – Meaning :
- A Stock Broker is a professional who executes buy and sell orders for stocks and other securities on behalf of clients.
- A stock broker may also be known as a registered representative, investment adviser or simply, Broker.
- Stock Brokers are usually associated with a brokerage firm and handle transactions for retail and institutional customers alike Stock Brokers often receive commissions for their services.
Role played by stock brokers in financial markets :
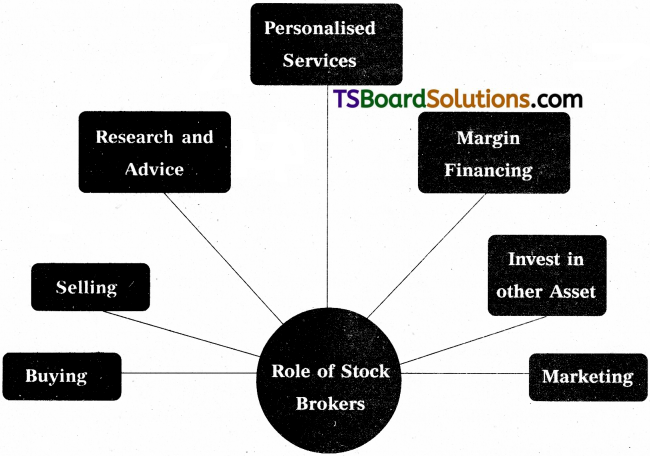
I. Buying :
- One of the most basic reponsibilities of a Stock Broker is to buy stock on behalf of his client; he may do this in different ways, depending on the type of account the client has.
- In a discretionary account, he Stock Broker buys stock for a client based on some prearranged guidelines.
- An advisory account, however, the stockbroker only advises a client on what stock to buy, while in an execution account, the Stock Broker only buys stock that the client hs specifically indicated.
2. Selling :
- The other responsibility a Stock Broker has is selling stock on behalf of a client.
- The Stock Broker can only sell stocks of a client based on the account that a client signed up for.
- If a client has an execution only account, the Stock Broker can only sell a client’s stock when asked to do so. If a client has an advisory account, a Stock Broker can only advise the client to sell his stocks, while if a client has a discretionary account, a Stock Broker has some leeway on selling the stocks based on a prearranged guideline.
3. Research and Adivce :
- Most of the broking house have set up in-house research team that scans companies and stocks as well as analyze the macro-economic scenario that impactgs the stock market.
- With the inputs from the research team, brokerage house puts buy or sell recommendation on stocks.
- Brokers also conduct investor education programmes to help improve their clients’ knowledge about investing in the markets.
4. Personalized Service :
- Most Broking Houses assign a relationship manager to interact with the client who would act as an advisor.
- Relationship managers advise their clients about when to make transactions and guide them about what to look for in the market dealings.
- They monitor client’s portfolio and provide timely advices to them.
5. Margin Financing :
- Stock exchanges monitor the extent to which brokers are lending in line with their net worth. As a result, many large Broking Houses provide financing facilities to clients who are looking to take leverage positions.
- Clients are allowed to take a position in the market after paying the margin amount. In most cases, investors are allowed to trade with a 50% margin.
6. Invest in other Asset Class :
A part from investing in stocks, Brokers also help the investors to invest in other assets classes like commodities, gold exchange traded fuds (ETFs) and mutual fund products. They also help their clients in investment in initial public offerings (IPO) of companies.
7. Marketing :
A Stock Broker finds prospective clients and builds a customer base. He may do this by writing articles in newspapers and magazines, hosting radio and television or taking time to clal prospective clients. A Stock Broker can also receive new clients through referrals from other individuals and organizations or by.attending social events where he can market his services.
![]()
Question 8.
Discuss the need for services of stock broker in the financial market.
Answer:
For a common man, it’s not possible to buy the stocks directly from the exchange. They need middlemen to execute the trade; such middlemen are known as ‘Stock Brokers’.
The Stock Broker services are needed to facilitate the buying and selling of stocks at the stock markets, on behalf of irivesors. A part from facilitating the buying selling of stocks from the stock market, Stock Brokers also offer a gamut of services to their clients such as :
1. To Provide Advisory Services :
Stock Market Brokers possess expertise related to the working of stock market, performance of stocks, market trends, and so on. Besides, they have access to the data base and research findings of Brokerage Firms that they are associated with. Hence, they can provide excellent investment advice to their clients.
2. To Offer Limited Banking Services :
Stock Market Brokers are authorized to provide limited banking services such as interest-bearing accounts, electronic deposits, and withdrawals. The clients can avail such banking-related services from the stock brokers by paying them a nominal brokerage charge.
3. To Support Other Investment Services :
A part from stokes, many stock brokers also deal in other securities such as mutual funds, bonds, exchange tradded funds, futures, options and commodity trading. They also provide investment advice related to all these products, to their clients.
4. To maintain Email Support Services :
Replying of email within a few hours during business time is considered reasonable in this matter. It’s depending on the severity of the incident.
5. To communicate through Phone/Toll Free Numbers :
Broker can provide excellent customer care through phone and toll free number.
6. To Offer Live Chat Support :
As far as live chat goes, the response should be immediae but is only possible during working days and for certain time.
7. To Leave a Message on their Website :
This can also help a clien in getting assisted fast and directed to the specific representative.
8. To Educate through Discussion forums :
This is a new and popular concept these days wher you can ask questions directly to the Broker related to any particular topic or issue.
9. To Offer Knowledge Base and. Video Tutorials :
Quick presentation of recurring issue in the knowledge base is one of the effective ways for he online community. Training and features about the tools are best to demonstrate in video tutorials to reduce traffic on ohter support features.
Thus, the services of stock broker are quite essential in trading the stock of joint stock companies.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you know about NSE?
Answer:
The National Stock Exchange (NSE) was incorporated in November, 1992. It is a “country wide screen based online trading system” and has international standards.
Features of NSE :
- It is a computerized national wide stock exchange where NSE members all over India are linked via satellite and cable system.
- The automated quotation system makes it convenient to the brokers to buy and sell electronically and need not shout in the trading ring about prices.
- It deals with the wholesale debt market like government securities, units by UTI etc.
- Price data will be broadcasted by the Press Trust of India (P.T.I)
- It improves the settlement system and minimizes the risk therein. NSE has setup a subsidiary national securities clearing corporation, which guarantees the settlement of trade executed.
- It operates dealings in the corporate equity and debt instruments. .
Question 2.
What is BSE?
Answer:
The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) is formerly known as “Native Stock and Share Brokers Association”, which was established in the year 1877. The aim of association was to support and protect the character and status of brokers, to promote fair practices and to discourage malpractices.
Features of BSE :
- It has on-line trading system introduced in 1995, which is called BOLT(BSE on line trading). This helps in active trading and safeguards market integrity.
- It provides other services like risk management, clearing, settlement, market, data and education to capital market participants.
- It provides a trading platform for equities of small and medium enterprises.
- It conforms international standards.
- It provides on efficient and transparent market for trading in equity, debt instruments and mutual funds.
- It has global reach helping customers around the world.
![]()
Question 3.
What do you mean by Bulls and Bears?
Answer:
Bull :
A Bull or Tejawalla is an operator who expects a rise in prices of securities in the future. In anticipation of price rise he makes purchases of shares and debentures with the intention to sell at higher prices in future. He being a speculator has no intention of taking delivery of securities but deals only in difference of prices. Such a speculator is called ‘Bull’ because of resemblance of his behaviour with bulb A bull tends to throw his victims up in the air. Similarly, a bull speculator tries to raise the prices of securities by placing big purchase orders.
Bears :
Bear or Mandiwala speculator expects prices to fall in future and sells securities at present with a view to purchase them at lower prices in future. A bear does not have securities at present but sells them at higher prices in anticipation that he will supply them by purchasing at lower prices in future. If the prices move down as per expectations of the bear, he will earn profits out of these transactions. A bear does not take the delivery of securities but takes the * difference if prices fall down, In case the prices are not falling as expected by the bears then they may start speculator rumours to pressurise price downwards, it is known as ‘bear said’.
Question 4.
What are the aims of listing securities?
Answer:
Listing of securities means the inclusion of securities in the official list of stock exchange for the purpose of trading.
Aims of listing the securities :
- To have control over the dealings of securities and to have proper supervision.
- To decentralise the economic power.
- To safe guard the interests *}# promoters.
- To protect the interests of investors and shareholders.
Question 5.
What is Demutualisation?
Answer:
The concept of demutualisation of stock exchange had originated in India, where two exchanges called OTCEI in 1990 and NSE in 1992 adopted a pure demutualisation structure from their birth. Demutualised stock exchanges are generally ‘for profit’ and tax paying entities.
In a demutualised stock exchange, three separate sets of people own the exchange, manage it and use its services, The owners usually appoint Board of Directors to manage the exchange, by professionals. The brokers or members are totally different from ownership and management. The ownership rights are freely transferable. Trading rights are acquired surrendered transparently.
Under this organisation structure, membership cards do not exist. Demutualisation of exchanges means segregating the ownership from management. This move was necessitated by the fact that brokers in the management of the stock exchange were misusing their position for personal gains.
Question 6.
What are the top ten stock broking firms in India?
Answer:
| Name of Stock Broker | Number of Active Clients | % Share |
| 1. Zerodha Broking Limited | 15,98,948 | 14.28 |
| 2. ICICI Securities Limited | 10,81,960 | 9.66 |
| 3. HDFC Securities Ltd. | 7,26,197 | 6.48 |
| 4. RKSV Securities India Private Limited | 6,75,551 | 6.03 |
| 5. ANGEL Broking Limited | 6,29,260 | 5.62 |
| 6. Kotak Securities Ltd. | 5,83,482 | 5.21 |
| 7. Sharekhan Ltd. | 5,47,950 | 4.89 |
| 8. Paisa Capital Limied | 4,89,661 | 4.37 |
| 9. Motial Oswal Financial Services Limited | 3,85,535 | 3.44 |
| 10. Axis securities Limited | 2,71,990 | 2.45 |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Stock Exchange.
Answer:
It is an association, organization or body of Individuals, whether incorporated or not, established for the purpose of assisting, regulating, and controlling business in buying, selling and dealing in securities.
![]()
Question 2.
Listing of securites.
Answer:
The inclusion of securities in the official list of stock exchange for the purpose of trading.
Question 3.
Lameduck.
Answer:
He is a speculator when the expectations of Bear does not become true and the price of security does not fall, he cannot fulfil his commitment, and he is said to be lameduck.
Question 4.
Stag.
Answer:
A stag is a cautious speculator. He applies for the shares of a new company at face value and he expects they are sold at a premium.
Question 5.
Jobber.
Answer:
He is a speculator who deals with securities independently and purchases and sells the securities in his own name.
Question 6.
Stock Broker.
Answer:
Broker is a link between a Jobber and general public who deals with a large variety of securities and works for commission. He contracts the Jabbr to buyer sell the securities an behalf of the general public. ’
Question 7.
SEBI.
Answer:
Securities and Exchanges Board of India(SEBI) helps to over come the undesirable practices in the stock exchange. It is controller of capital issues. Its head quarters is located in Mumbai.
Question 8.
Permitted securities.
Answer:
A stock exchange sometimes permits trading in certain securities, which are not listed at the stock exchange but are actively traded in other stock exchanges. Such securities are known as permitted securities.
![]()
Question 9.
Stock Exchange Speculators.
Answer:
The persons who make profits by trading securities for shorterm purpose, are known as stock exchange speculators.
Question 10.
Stock Exchange operators.
Answer:
- Stock Exchange operators are the participants in stock exchange market.
- Business transactions in a stock exchange are allowed only by a member of the exchange.
- There are two categories of members who transact, the business on stock exchange. They are A) Jobbers B) Broker.