Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Study Material 3rd Lesson Banking Services Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Study Material 3rd Lesson Banking Services
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define banking and explain its functions.
Answer:
Banking is derived rom French word “Bance” means a “Bench”. A bank is regarded as an institution which attracts deposits for the purpose of lending to business (or) other.
According to Banking Regulation Act 1949, Banking is defined as “accepting for the pur-! pose of lending or investment of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise and withdrawable by cheque, draft, order or otherwise.
Function of Banking :
Banking functions are divided into two categories.
A) Primary functions
B) Secondary functions
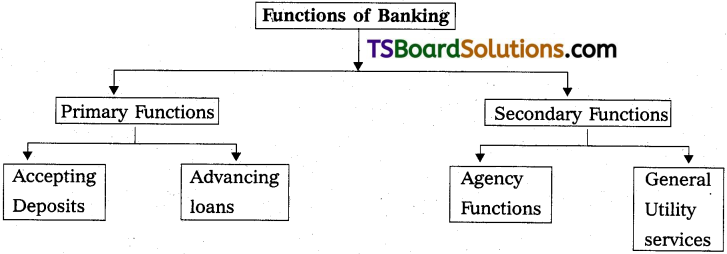
A) Primary functions :
The primary functions of Banks are divided into
I. Acceptance of deposits and
II. Advancing Loans
I. Acceptance deposits :
Accepting deposit is the primary functions of a commercial bank. The bank accept deposits from the customers in the forms such as fixed deposits, current deposits savings deposits and recurring deposits accounts.
II. Advancing Loans :
The second primary function of a commercial Bank is to make loans and advances to all types of persons particularly to business men, and entrepreneurs. Loans are made against personal security, gold and silver, stocks of goods and other assets.
Banks offers loans in the form of overdraft, cash credit, term loans, consumer credit money at call, retail loans etc.
B) Secondary Functions :
Secondary functions of a bank includes
I. Agency Services and
II. General utility services .
I. Agency Services :
Banks perform certain agency functions / services on the behalf of their customers.
The various agency services rendered by banks are as follows.
- Collection and payment of credit instruments like cheques, bills of exchange, promissory note. etc.
- Purchase and sale of securities on behalf of their customers.
- Collection of dividends on shares and credit to their accounts.
- To work as correspondent, representative of their customers.
- Banks also prepare income tax returns for their customers and help them to get refund of Income Tax.
II. General Utility Services :
In addition to agency services, banks provides many general utility services which are given belows.
- Bank provides locker facility.
- Bank issue traveller’s cheques to help their customers to travel without fear of theft or loss of money.
- Banks issue letters of credit to their customers certifying their credit worthiness.
- Banks accept and collect foreign bills of exchange on behalf of their customers.
- Banks underwrite the shares and debentures issued by the Govement, public or privage companies.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the various types of deposit accounts in bank.
Answer:
Banks generally accept four types of deposits viz., Current Deposits, Savings Deposits, Fixed Deposits and Recurring Deposits.
a) Current Deposits :
- These deposits are also known as demand deposits. These deposits can be withdrawn at any time.
- These deposits are kept by businessmen and industrialists who receive and make large payments through banks.
- Generally, no interest is allowed on current deposits.
b) Savings Deposits :
- This is meant mainly for professional men and middle-class people to help them deposit their small savings.
- There is a restriction on the amount that can be withdrawn at a particular time or during a week.
- Interest is allowed on the credit balance of this account. The rate of interest is less than that on fixed deposit. The present rate of interest offered by SBI is 2.75% p.a.
c) Fixed Deposits :
- These deposits are also known as time deposits. Thews deposits cannnot be with-drawn before the expiry of he period for which they are deposited.
- Fixed deposits are liked by depositors both for their safety and as well as for their interest.
- The present rates of interest offered by SBI ranges between 4.5% and 6.10% p.a.
d) Recurring Deposits :
- This type of deposit allows the account holder to deposit a fixed amount once a month for a certain period.
- The total deposit along with interest is payable on maturity.
- The present rates of interest offered by SBI ranges between 5,8% and 6.25% p.a.
Question 3.
Discuss the different forma of lending by a banker.
Answer:
Types of Deposits :
Bank lending can be classified into
I. Cash credit.
II. Loans (Demand loans & Term loans),
III. Overdraft.
IV. Purchasing and Discounting of bills.
I. Cash credit :
Bank agrees to lend money to the borrower upto a certain limit. The amount so agreed upon will be credited to the account of the borrower. The borrower draws the money as and when he needs and interest will be charged only on the amount actually drawn by the borrower.
II. Loans :
Loan is a specified amount sanctioned by a bank to the customer. It is granted for a fixed period. Loans are classified into A) Demand Loan B) Term Loan.
A) Demand Loan :
Demand loan is a loan which is repayable on demand. In other words, these are repayable at short notice.
B) Term Loan :
Medium and long term loans are called ‘Term Loans”. Term loans are granted for more than one year.
III. Overdraft :
The account holder is allowed to draw an amount in excess of the balance held in the account. OD facility provides on current accounts only.
IV. Purchasing and Discounting of Bills :
Bills are negotiable instruments, banker purchasing the bills. If the discounted bill is dishonoured on the due date, the banker can recover the amount from the customer who had discounted thebill.
Question 4.
How the banks in India are classified? Explain.
Answer:
Classification of Banks :
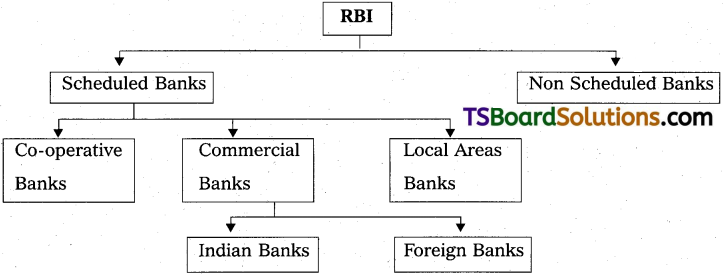
All the banks in India are governed by RBI and classified as scheduled and non scheduled banks .
A) Scheduled Bank :
1) Scheduled Banks ae banks which are included in the Second Schedule of the Banking Regulation Act, 1965. According to this schedule, a scheduled Bank :
i) Must have paid-up capital and reserve of not less than Rs. 5,00,000.
ii) Must also satisfy the RBI that its affairs arer not conducted in a manner detrimental to the interests of is depositors.
2) scheduled banks include all commercial banks like nationalised, foreign, development, co-operative and regional rural banks. There are 202 scheduled banks as on 8th October 2018)
Scheduled banks types :
1) State Co-operative Banks :
These are co-operatives owned and managed by the State.
2) Commercial Banks :
These are business entities whose main business is accepting deposits and exending loans. Their main objective is profit maximization and adding shareholder value.
Commercial Banks further sub-divided as :
1) Indian Banks :
These banks are companies registered in India under the Companies Act, 1956. Their place of origin is in India.
2) Foreign Banks :
These are banks that were registered outside India and had originated in a foreign country.
A) Non Scheduled Banks :
- These are banks which are not included in the Second Schedule of the Banking Regulation Act, 1965. It means they do not satisfy the conditions laid down by that schedule.
- These banks are not allowed to borrow money from RBI for regular banking purposes. Periodic returns need not be submitted wih RBI and cannnot become memeber of clearing house.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the features of Internet Banking.
Answer:
- It could reach out to customer spread across the countries. It removes geographical barriers.
- Traditional risks in bank transactions are eliminated.
- It enables the customers to pay electricity bills, insurance premiums etc.
- Internet is a public domain which is not subject to control of any single authority or group.
- Railway tickets air tickets are booked through E – system.
- It facilitates payment of direct taxes online.
- It enables Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) i.e., inter-bank funds transfer.
- It should continuously update their technology, as when a new technology is developed.
- New technology is developed for future period.
- It leads to establishment of an efficient and effective cost and control system.
Question 6.
Explain the primary functions of Banks.
Answer:
1) Primary functions of Banks are divided into two types.
A) Accepting Deposits and
B) Advancing loans
A) Accepting deposits:
Accepting deposits is the primary function of a commercial Bank. Banks accept deposita from the customers in the form of Fixed Deposits, current deposits, savings deposits and Recurring Deposits accounts.
a) Current Deposits :
- These deposits are also known as demand deposits. These deposits can be withdrawn at any time.
- These deposits are kept by businessmen and industrialists who receive and make large payments through banks.
- Generally, no interest is allowed on current deposits.
b) Savings Deposits :
- This is meant mainly for professional men and middle-class people to help them deposit their small savings.
- There is a restriction on the amount that can be withdrawn at a particular time or during a week.
- Interest is allowed on the credit balance of this account. The rate of interest is less than that on fixed deposit. This system greatly encourages the habit of thrift or savings. The present rate of interest offered by SBI is 2.75% p.a.
c) Fixed Deposits :
- These deposits are also known as time deposits. These deposits cannnot be with-drawn before the expiry of he period for which they are deposited.
- Fixed deposits are liked by depositors both for their safety and as well as for their interest which is higher.
- The present rates of interest offered by SBI ranges between 4.5% and 6.10% p.a.
d) Recurring Deposits :
- This type of deposit allows the account holder to deposit a fixed amount once a month for a certain period.
- The total deposit along with interest is payable on maturity.
- The present rates of interest offered by SBI ranges between 5.8% and 6.25% p.a.
B) Advancing Loans :
The second primary fucntion of commercial bank is to make loans and advances to businessmen, and entrepreneurs. Loans are made against personal security, gold and silver, stocks of goods and other assets.
Bank tendering can be classified into
I. Cash credit.
II. Loans (Demand loans & Term loans).
III. Overdraft.
IV. Purchasing and Discounting of bills.
I. Cash credit :
Bank agrees to tend money to the borrower upto a certain limit. The amount so agreed upon will be credited to the account of the borrower. The borrower draws the money as and when he needs and interest will be charged only on the amount actually drawn by the borrower.
II. Loans i Loan is a specified amount sanctioned by a bank to the customer. It is granted for a fixed period. Loans are classified into
A) Demand Loan
B) Term Loan.
A) Demand Loan:
Demand loan is a loan which is repayable on demand. In other words, these are repayable at short notice.
B) Term Loan :
Medium and long term loans are called “Term Loans”. Term loans are granted for more than one year.
III. Overdraft :
The account holder is allowed to draw an amount in excess of the balance held in the account. OD facility provides on current accounts only.
IV. Purchasing and Discounting of Bills :
Bills are negotiable instruments, banker purchasing the bills. If the discounted bill is dishonoured on the due date, the banker can recover the amount from the customer who had discounted the bill.
![]()
Question 7.
Discuss the secondary functions of banks.
Answer:
Secondary Functions :
Secondary functions of a bank include A) Agency services and B) General utility services
A. Agency Services :
Banks also perform cerain agency functions for and on behalf of heir customers. The various agency services rendered by banks are as follows:
1. Collection and Payment of Credit Instruments :
Banks collect and pay various credit instrumets like cheqes, bills of exchange, promissory notes etc., on behalf of their customers.
2. Purchase and Sale of securities :
Banks purchase and sell various securities like shares, stocks, bonds, debentures on behalf of their customers.
3. Collection of Dividends on Shares :
Banks collect dividends and interet on shares and debentures of their customers and credit them to their accounts.
4. Acts as Correspondent :
Sometimes banks act as representative and correspondents of their customers. They get passports, traveller’ stickets and even secure air and sea passages for their customers.
5. Income-tax Consultancy :
Banks may also employ income tax experts to prepare income tax returns for their customers and to help them to get refund of income tax.
6. Execution of Standing Orders :
Banks execute the standing instructions of their cus-tomers for making various periodic payments. They pay subscriptions, rents, insurance premium etc., on behalf of their customers.
7. Acts as Trustee and Executor :
Banks preserve the “will’s of their customers and execute them after their death.
B. General Utility Services :
In addition to agency services, the modern banks provide many general utility services for the community given as under :
1. Locker facility :
Bank provides locker facility to their customers. The customers can keep their valuables, such as gold and silver ornaments, imporant documents; shares and de-bentures in these lockers for safe custody.
2. Traveller’s Cheques and Credit Cards :
Banks issue travller’s cheques to help their customers to travel without the fear of theft or loss of money.
3. Letter of Credit :
Letters of credit are issued by the banks to their customers certifying their credit worthiness. Letters of credit are very useful in foreign trade.
4. Collection of Statistics :
Banks collect statistics giving important information relating to trade, commerce, industries, money and banking. They also publish valuable journals and bulletins containing articles on economic and financial maters.
5. Acting Referee :
Banks may act as referees with respect to the financial standing, business reputation and respecability of customers.
6. Underwriting Securities :
Banks underwrite the shares and debentures issued by the Government, public or private companies.
7. Gift Cheques :
Some banks issue cheques of various denominations to be used on auspicious occasions.
8. Accepting Bills of Exchange on Behalf of Customers :
Sometimes, banks accept bills of exchange, internal as well as foreign, on behalf of their customers. It enables customers to import goods.
Question 8.
Explain the different types of bank payments.
Answer:
Different types of bank payments are given below
1. Cheque :
1) A cheque is document which orders a bank to apy a particular amount of money from a person’s account to another individual or company’s account in whose name the cheque has been made or issued.
2) The cheque is utilized to make safe, secure and convenient paymens. It serves as a secure option since hard cash is not involved during the transfer process; hence the fear of loss or theft is minimized.
2. National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) :
- Naional Elecronic Fund Transfer (NEFT) is a country-wide electronic fund transfer system for sending money from one bank account to another in a safe and hassle-free manner.
- All NEFT settlements are made in a batch-wise format. Money can be sent using this system to all NEFT-enabled banks in India on an individual basis.
3. Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) :
- ‘RTGS’ or Real Time Gross Settlement is a fund transfer method through which money is sent in ‘real time’ basis without any delays.
- RTGS is typically meant for larger value transactions and the minimum amount that can be sent via this mode is Rs. 2 lakh.
- Money can be sent using RTGS through net banking. To inititate such a transaction, it is important to collect some details from the payee such as account number, bank name, IFSC code, and account holder name.
4. Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) :
- Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) is a real-time electronic fund transfer method through which money is credited immediately to the payee/beneficiary account.
- IMPS transfers can be done at any time on a 24/7 basis and on all 365 days in a year, including on Sundays and other bank holidays.
- Through IMPS, interbank transfers can be inititate through multiple channels such as mobile banking, internet banking, SMS, ATMs, etc.
- The IMPS services are managed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) and cone under the purview of the Reserve Bank of India.
5. Payment Wallets :
- A waller is a small software program used for online purchase transactions. E-wallet is a type of electronic card which is used for transactions made online through a computer or a smartphone.
- In E-wallet needs to be linked with the individual’s bank account to make paymets. E-wallet is a type of pre-paid account in which a user can store his money for any future online transaction. An E-wallet is protected with a password.
- Some of the popular Mobile Wallet companies in India are : PayTM, Google Pay, BHIM Axis Pay, PhonePey, Mobikwik, SBI’s Yono, Citi MasterPass, ICICI Pockets, HDFC PayZapp, Amazon Pay, etc.
Question 9.
What are the various types of Retail loans? Explain.
Answer:
Retail Loans :
1. Meaning :
Retail Loans are the loans acquired to buy an asset or property. Retail loans are offered by financial institutions in wide variety of forms. They are Home Loan, Car Loan, Education Loan, Personal Loan and Credit Card.
2. Types :
a) Home Loans :
- Housing being one of the fundamental needs of life. Housing Loans are provided by the financial institutions for the purpose of construction or purchase of a new home.
- National, Housing Bank (NHB) was set up with the support of RBI for coordinating and development of housing finance schemes. Housing Loans are provided by LIC, SBI, UTI and other financial Institutions.
- The Central Government has taken steps towards “Housing for All”, in this connection it has startd The Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY). This scheme covers housing for weaker sections and middle-imcome section people.
b) Car Loans
- Car Loan or Vehicle loan is the f ;nity provided by the banks to the customers allowing them to pay the value of the car in instalments.
- The payment of instalments includes interst amount determined by the abnk officials from time to time.
- These loans are granted to the salaried employees and self-employed individuals after providing necessary documents.
c) Education Loan :
- Education loan is a student friendly designed loan. These loans are given to the students who are unable to continue higher education in India and abroad due to lack of cash.
- These loans aim at providing financial support to meritorious students for pursuing higher education, such as Graduation, Post-Graduation, Professional Courses.
- Financial support is granted to the extent of Rs. 10 lakhs for studies in India and Rs. 25 lakhs for studies in abroad respectively.
d) Perosnal Loans :
- Personal loan is an unsecured loan granted by the banks to meet personal needs.
- Personal loans can also be granted for the purpose fo house repairs, renovations,wedding, on the basis of loan eligibility with a minimal document on the prevailing rages of interest.
- Personal loans are provided with a term between 1 to 3 years repayment period.
e) Credit Card :
- Credit Card is a magnetic Strip Card issued by the bank authorizing the customer to purchase the items now and pay the amount with in the prescribed period.
- Credit cards can be domestic cards and International cards. These cards are issued to individual customers and business firms operating an acccount in the banks.
- Credit Cards are generally issued based upon the individual’s credit worthiness.
![]()
Question 10.
What is E-Banking? What are its advantages and limitations.
Answer:
E-Banking :
E-Banking is a system 6f banking which is carried out with the use of elec-tronic tolls and facilitated through electronic delivery channels.
Advantages of E-Banking :
- Round the clock services will be available to the customer for all 7 days a week i.e, 24 x 7.
- Fastness and flexibility in the transactions.
- Lower operating cost for banks.
- A higher degree of personalization.
- Increased speed and accuracy of information exchange.
- Bank account can be easily accessed from anywhere and at any time.
- Leads of greater customer satisfaction.
- Internet banking help banks in reducing the workload of their branches, such as generation of statement, balance enquiry etc.
- NRI’S can monitor their bank accounts in the bank in India from wherever they are stationed. They can operate their accounts in anywhere in the world.
Disadvantages or limitations of E-Banking :
- Problems may crop up regarding security and reliability.
- Imparting training to banking staff is a big challenge.
- Non – availability of internet connection with highspeed band width in the rural areas.
- High illiteracy rate in India, is a hindrance to E-banking..
- Resistance to paperless transaction by the customer, as they may prefer evidence for their transactions on paper.
- The technology is advancing, our legal environment is not in a position to keep pace with the technology.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is Cash Credit?
Answer:
- Under cash credit the bank gives loans to the borrowers against certain security.
- The entire loan is not given at one particular time. He will be allowed to withdraw small sums of money according to his requiremetns through cheques, but he can not exceed the credit limit allowed to him.
- The borrower is required to pay interest only on the amount of credit availed by him.
Question 2.
What is fixed deposit?
Answer:
- These deposits are also know as time deposits.
- These deposits can not be withdrawn before the expiry of the period for which they are deposited.
- Fixed deposits are liked by depositors both for their safety and as well as for interest which is higher.
- In India, they are accepted between seven days to five years.
- The present rates of interest offered by SBI ranges between 4.5% and 6.10% p.a.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Credit Card?
Answer:
Credit Card :
- Credit Card is a magnetic Strip’ Card issued by the bank authorizing the customer to purchase the items now and pay the amount with in the prescribed period.
- Credit cards can be domestic cards and International cards. These cards are issued to individual customers and business firms operating an acccount in the banks.
- Credit Cards are generally issued based upon the individual’s credit worthiness.
Question 4.
What is any where banking?
Answer:
- The banking services to the customer of a bank have undergone a change with the further advancement of technology.
- A customer can operate his account from any branch of his bank situated in India. This is called “Core Banking’.
- The various services provided under anywhere banking are
A) Telebanking
B) Internet Banking
C) Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS)
D) Electronic Clearance Service (ECS)
E) Mobile banking
F) E-cheque and
G) National Electronic Fund Transfer (NEFT)
Question 5.
What do you know abot ATM service in Banking?
Answer:
Automatic Teller Machine (ATM) :
- ATM is one of the methods of electronic fund transfer. It have removed the time limitations of customer services.
- ATM is an unattended or unmanned device usually located on or off the bank premises.
- The operation mechanism begins when the card is inserted into ATM, the terminal reads and transmits the tape data to processor, which activates the account.
- It works for 24 hours a day, 7 days a week (24 x 7).
- ATM’s were used only for withdrawal, electronic transfer of funds etc. But now they are used for recharging cell phones, bill payments etc.
Question 6.
What services are offered by banker under Internet Banking?
Answer:
- Internet Banking is one of the popular modes of E-Banking.
- It enables to obtain general purpose information by a customer through banks websites, Electronic Fund Transfer (EFT), Electronic payment such as E-cheque, E-Card based payments.
- The various internet banking services ae given below :
a) Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS),
b) Electronic Clearance Service (ECS)
c) Natinal Electronic Fund Transfer (NEFT)
d) Mobile Banking
e) E-cheque.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Money at call.
Answer:
Money at Call:
Bank also grant loans for a very short period, generally not exceeding 7 days to the borrowers, usually dealers or brokers in stock exchange markets against collateral securities like stock or equity shares, debentures, etc., offered by them. Such advances are repayable immediately at short notice. Hence, They are described as money at call or call money.
![]()
Question 2.
Recurring Deposit.
Answer:
- This type of deposit allows the account holder to deposit a fixed amount once a month for a certain period.
- The total deposit along with interest is payable on maturity.
- The present rates of interest offered by SBI ranges between 5.8% and 6.25% p.a.
Question 3.
Cash credit.
Answer:
- It is an arrangement between a bank and its customer where by the bank agrees to lend money to the borrower upto a certain limit.
- The borrower is required to pay interest only on the amount of credit availed by him.
Question 4.
Car loan.
Answer:
- Car Loan or Vehicle loan is the facility provided by the banks to the customers allowing them to pay the value of the car in instalments.
- The payment of instalments includes interst amount determined by the abnk officials from time to time.
- These loans are granted to the salaried employees and self-employed individuals after providing necessary documents.
Question 5.
Credit card.
Answer:
- Credit Card is a magnetic Strip Card issued by the bank authorizing the customer to purchase the items now and pay the amount with in the prescribed period.
- Credit cards can be domestic cards and International cards. These cards are issued to individual customers and business firm operating an acccount in the banks.
- Credit Cards are generally issued based upon the individual’s credit worthiness.
Question 6.
Savings account.
Answer:
- This is meant mainly for professional men and middle-class people to help them deposit their small sayings.
- There is a restriction on the amount that can be withdrawn at a particular time or during a week.
- Interest is allowed on the credit balance of this account. The rate of interest is less than that on fixed deposit. The present rate of interest offered by SBI is 2.75% p.a.
Question 7.
Fixed Deposit.
Answer:
- These deposits are also known as time deposits. These deposits cannnot be withdrawn before the expiry of he period for which they are deposited.
- Fixed deposits are liked by depositors both for their safety and as well as for their interest they which is higher.
- The present rates of interest offered by SBI ranges between 4.5% and 6.10% p.a.
Question 8.
Foreign Bank.
Answer:
- Foreign Bank are the banks that were registered outside India and had originated in a foreign country.
- At pesent there are 45 foreign banks in India.
![]()
Question 9.
Term loan.
Answer:
- It is the loan required for long term needs for acquiring fixed assets.
- Term loans ae granged for moe than one year.
Question 10.
Demand loan.
Answer:
- Demand loan is a loan which is repayable on demand.
- These loans are repayable at short notice. .
Question 11.
Over draft.
Answer:
- It is an arrangement where in the account holders is allowed to draw an amount in excess of the balance held is the account.
- This overdraft is allowed to current account holidays only.
Question 12.
Scheduled Bank.
Answer:
1) Scheduled Banks ae banks which are included in the Second Schedule of the Banking Regulation Act, 1965. According to this schedule, a scheduled Bank :
i) Must have paid-up capital and reserve of not less than Rs. 5,00,000.
ii) Must also satisfy the RBI that its affairs are not conducted in a manner detrimental to the interests of is depositors.
2) scheduled banks include all commercial banks like nationalised, foreign, development, co-operative and regional rural banks. There are 202 scheduled banks as on 8th October 2018)
Question 13.
Non-scheduled Bank.
Answer:
- These are banks which are not included in the Second Schedule of the Banking Regulation Act, 1965. It means they do not satisfy the conditions laid down by that schedule.
- These banks are not allowed to borrow money from RBI for regular banking purposes. Periodic returns need not be submitted with RBI and cannnot become memeber of clearing hose.
Question 14.
ATM
Answer:
ATM (Automatic Teller Machine) is an unattended or unmanned device usually located on or off the bank premises. The operation mechanism beings when the card is inserted into ATM, the terminal reads and transmits the tape data to a processor, which activates the account. It works for 24 hours a day, 7 days a week (24 x 7).
Question 15.
Tele Banking
Answer:
“Tele banking refers to banking on telephone”. The customer can dial the branch’s designated telephone number which is connected to computer, by dialing his identification number, the software provided in the machine will become interactive with customer asking him to dial the code number of the service required by him and gives suitable answer. The customer can enquire about his balance, previous transactions or fund transfer between the accounts.
Question 16.
RTGS.
Answer:
- RTGS means Real Time Gross Settlement.
- RTGS is a fund transfer method through which money is sent in “real time” basis without any delays.
- This electronic fund transfer system allows the money sent by the remittens to immediately reacy the payee when the money transfer transaction is initiated.
Question 17.
ECS.
Answer:
- ECS means Electronic clearance Service.
- This scheme provides an alternative method of effecting bulk payent transactions peridically.
- At present, this service is available in the department of posts at 15 RBI locations and 21 SBI locations.
![]()
Question 18.
NEFT
Answer:
- NEFT means National Electronic Fund Transfer.
- NEFT is a country wide electronic fund transfer system for sending money from one bank to another in safe and hassle free manner.
- There is no ceiling on the minimum or maximum, that can be transfered through NEFT.
Question 19.
Mobile Banking.
Answer:
- The delivery of Banking services to a customer through mobile phone is called “Mobile Banking”.
- This service is provided free of Cost to all customers of the bank, irrespective of their mobile service network provider and make of the hand set owned by the customer.
- Customer to know his account balance and debit, crdit transactions of his account etc., through alerts.