Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material 13th Lesson Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material 13th Lesson Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
Very Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
Question 1.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds and classify them into primary, secondary and tertiary amines. [TS 15]
(i) (CH3)3C NH2
(ii) CH3(CH2)2 NH2
(iii) (CH3 CH2)2 NCH3
Answer:
(i) 1,1- dimethylethanamine. It is a primary amine.
(ii) Propan -1 – amine. It is a primary amine.
(iii) N – methyl – N – ethylethanamine. It is a tertiary amine.
Question 2.
Explain why ethylamine is more soluble in water whereas aniline is not soluble.
Answer:
Ethylamine is soluble in water because it can form hydrogen bonds with water mole-cules. The phenyl group in aniline is bulky and hydrophobic. It opposes the formation of hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Hence, aniline is insoluble in water.
![]()
Question 3.
Why aniline does not undergo Friedel – Craft’s reaction ?
Answer:
Aniline does not undergo Friedel – Craft’s reaction (alkylation and acylation)’due to salt formation with AlCl3, the Lewis acid, which is used as a catalyst. Because of this, nitrogen of aniline acquires positive charge and hence acts as a strong deactivation group for further reaction.
C6H5 NH2 + AlCl3 → [C6H5NH2]+ [AlCl3]–
Question 4.
Gabriel phthalimide synthesis exclusively forms primary amines only. Explain.
Answer:
Because there is only one hydrogen bonded to the nitrogen of pathalimide, only one alkyl group can be placed on the nitrogen. This means that the gabriel synthesis can be used only for the preparation of primary amines.
Question 5.
Arrange the following bases in decreasing order of pKb values.
C2H5NH2, C2H5NHCH3, (C2H5)2 NH and C6H5NH2.
Answer:
C6H5NH2 > C2H5NHCH3 > C2H5NH2 > (C2H5)2 NH
pKb Values: 9.38 9.30 3.29 3.00
Question 6.
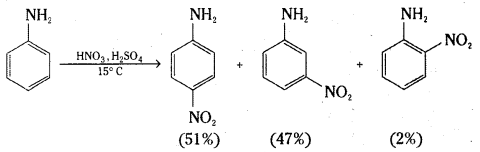
Arrange the following bases in increasing order of their basic strength. Aniline, p – nitro- aniline and p – toluidine.
Answer:
p – nitro Aniline < aniline < p – toluidine.
![]()
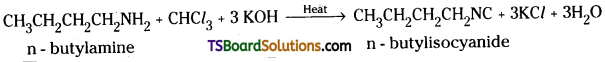
Question 7.
Write equations for carbylamine reaction of any one aliphatic amine. [TS Mar. 19; (IPE 14)]
Answer:
A primary amine, for example, n – butyla-mine forms foul smelling isocyanide or carbylamine when heated with chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide.
Question 8.
Give structures of A, B and C in the following reaction.
![]()
Answer:
A is C6H5CN Phenylcyanide or Benzonitrile
B is C6H5COOH Benzoic acid
C is C6H5CONH2 Benzamide
Question 9.
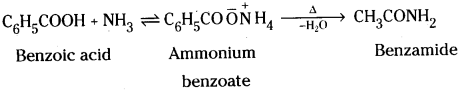
Accomplish the following conversions : [IPE 14]
i) Benzoic acid to Benzamide
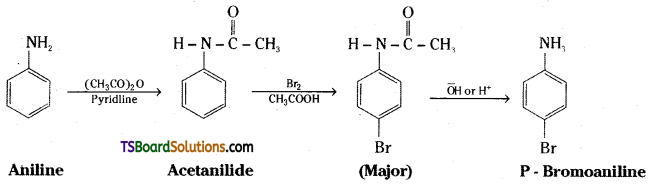
ii) Aniline to p – Bromoaniline
Answer:
i) Benzoic acid reacts with ammonia to give ammonium benzoate which on fur-ther heating at temperature gives benza-mide.
![]()
ii) The amino group of aniline is protected by acetylation. Acetanilide, so obtained, is reacted with bromine in acetic acid followed by hydrolysis to get p – bromoaniline.
Question 10.
Why cannot aromatic primary amines be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis ?
Answer:
Aromatic primary amines cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis because arylhalides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion formed by phthalimide.
Short Answer Questions (4 Marks)
Question 11.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
i) CH3CH2NH CH2CH2CH3
ii) PhCH2 CN
iii)
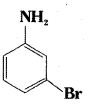
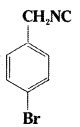
iv)
Answer:
i) N – Ethylpropanamine
ii) Phenylethanenitrile or Benzylcyanide
iii) 3 – Bromoaniline or 3 – Bromobenzenamine
iv) 4 – Bromophenyl methylisocyanide
![]()
Question 12.
Give one chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds.
i) Methylamine and dimethylamine
ii) Aniline and N – methylaniline
iii) Ethylamine and aniline
Answer:
i) Methylamine on heating with chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide forms foul smelling isocyanide or carbylamine. Dimethylamine does not give this test.
ii) Aniline (a primary amine) gives positive carbylamine test N – methylaniline (a secondary amine) does not give this test. Thus when aniline is heated with chloroform and alcoholic KOH forms fouls melling phenylisocyanide or carbylamine.
iii) Ethylamine reacts with nitrous acid to give nitrogen gas and ethylalcohol. Aniline reacts with nitrous acid (NaNO2 + HCl) at low temperatures (0 – 5°C) to form diazonium salt.
Question 13.
Account for the following :
i) pKb of aniline is more than that of methylamine.
ii) Reduction of alkylcyanide forms primary amine whereas alkylisocyanide forms secondary amine.
Answer:
i) In aniline the -NH2 group is directly attached to the benzene ring. It results in the unshared electron pair on nitrogen atom to be in conjugation with the benzene ring and thus making it less available for protonation. Such a situation is absent in methylamine. Hence PKb value of aniline is greater than that of methylamine.
ii) In, alkylcyanides, the alkylgroup is linked to the carbon of the cyanide ion while in isocyanides the alkyl group is linked to the nitrogen of cyanide.
R – C ≡ N R – N ≡ C
Hence, alkylcyanide gives primary amine whereas alkyl isocyanide gives secondary amine on reduction.
Question 14.
How do you prepare the following?
i) N, N – Dimethyipropanamine from ammonia
ii) Propanamine from chloroethane
Answer:
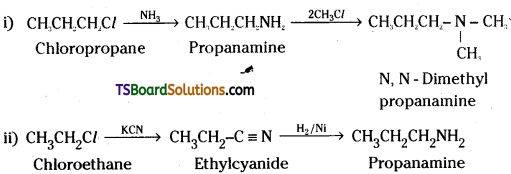
Question 15.
Compare the basicity of the following in gaseous and in aqueous state and arrange them in increasing order of basicity. [TS 15[
CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH, (CH3)3N and NH3
Answer:
The alkyl (methyl) group has electron – releasing inductive effect. It pushes the electrons towards nitrogen and makes the electron pair more available for sharing with the proton of the acid. Hence, in the gaseous state the basicity of the amines follows the order.
(CH3)3N > (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > NH3
In the aqueous state the basicity of the amines depends upon inductive effect, solvation effect and steric hindrance of the alkyl group. Hence, the order basic strength of the methyl substituted amine in the aqueous solution is
(CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N > NH3
![]()
Question 16.
How do you carryout the following conversions ?
i) N – Ethylamine to N, N – Diethyl propanamine
ii) Aniline to p – Aminobenzene sulphonamide
Answer:
i) N – ethylamine is first reacted with propylchloride to convert it to N – ethyl propanamine. It is then reacted with ethyl chloride to convert it to N, N – Diethyl propanamine.
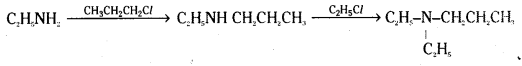
ii) Aniline is converted to acetanilide by reaction with acetylchloride. Acetanilide is treated with chlorosulphonic acid and the product on reaction with ammonia followed by hydrolysis gives sulphanilamide.
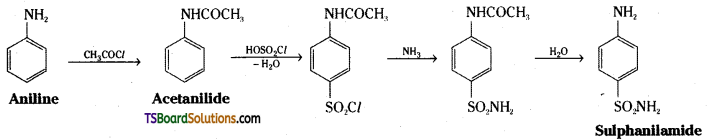
Question 17.
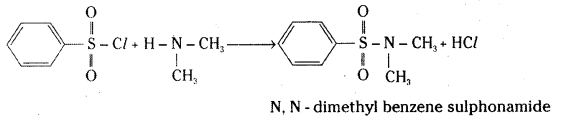
Explain with a suitable example how benzene sulphonylchloride can distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
Answer:
Benzene sulphonylchloride (Hinsberg reagent) reacts with a primary amine, ethylamine, to give N – ethylbenzene sulphonyl amide.
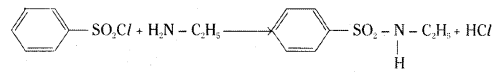
This compound contains hydrogen attached to nitrogen. It is acidic in nature and hence it is soluble in sodium hydroxide solution.
When benzene sulphonyl chloride reacts with a secondary amine, for example diethyl amine, to give N, N – diethyl benzene sulphonamide. It does not contain hydrogen attached to nitrogen. It is not acidic and hence it is insoluble in sodium hydroxide solution.
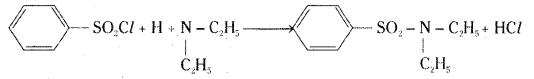
Tertiary amines do not react with Hinsberg reagent.
![]()
Question 18.
Write the reactions of
i) aromatic and
ii) aliphatic primary amines with nitrous acid.
Answer:
Aromatic primary amines react with nitrous acid at low temperatures (0 – 5°C) to form diazonium salts.
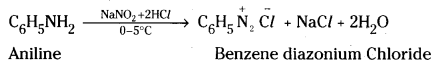
Aliphatic primary amines react with nitrous acid to form alcohol and nitrogen gas.
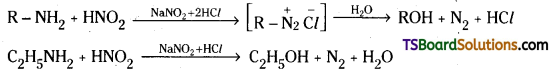
Question 19.
Explain why amines are less acidic than alcohols of comparable molecular masses.
Answer:
The acidic character of alcohols is due to the polar nature of O – H bond. The polarity of the N – H bond in amines is less than that of the O – H bond in alcohols of comparable molecular mass. Hence amines are less acidic than alcohols of comparable molecular mass.
Question 20.
How do you prepare Ethyl cyanide and Ethyl isocyanide from a common alkyl halide. [IPE 14]
Answer:
Ethyl chloride reacts with ethanolic potassium cyanide to form ethyl cyanide as the major product. However, when ethyl chloride reacts with ethanolic silver cyanide ethyl isocyanide will be the major product.
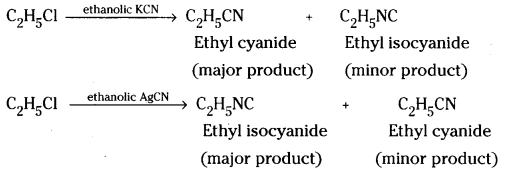
Long Answer Questions (8 Marks)
Question 21.
An aromatic compound ‘A’ on treatment with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound ‘B’ which on heating with Br2 and KOH forms compound ‘C’ of molecular formula C6H7N. Write the structures and IUPAC names of compounds A, B and C.
Answer:
The final product ‘C’ with molecular formula C6H7N is Aniline. The sequence of reactions can be explained as follows.
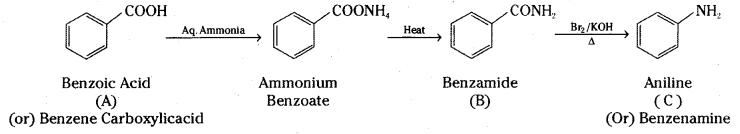
Compound A is Benzoic acid. On treatment with aqueous ammonia gives ammonium benzoate which on heating gives Benzamide (B). Benzamide on heating with bromine and potassium hydroxide (Hofmann hypobromite reaction) gives Aniline (C) with molecular formula C6H7N.
![]()
Question 22.
Complete the following conversations.
i) CH3NC + HgO → ?
ii) ? + 2H2O → CH3NH2 + HCOOH
iii) CH3CN + C2H5 Mg Br → ? ![]()
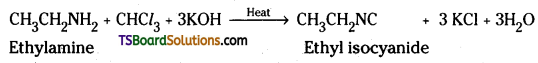
iv) CH3 CH2 NH2 + CHCl3 + KOH ![]() ?
?
v) 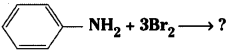
Answer:
i) HgO is a mild oxidising agent. It converts isocyanides to isocyanates. Thus, methyl isocyanide is converted to methyl isocyanate.
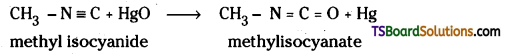
ii) Isocyanides on hydrolysis give amines and formic acid.
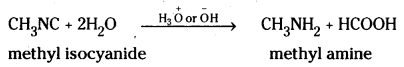
iii) Ethyl magnesium bromide adds on to methylcyanide or acetonitrile to give an addition product which on hydrolysis forms acetone.
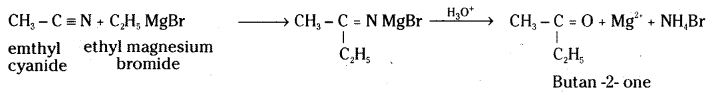
iv) Primary amine on heating with chloroform and alcoholic KOH gives foul smelling isocyanide or carbylamine.
v) Aniline on treatment with bromine water gives a white precipitate of 2,4,6 – tribromoaniline.
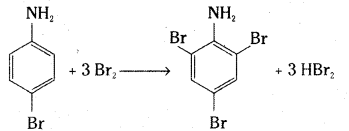
Question 23.
i) Write the structures of different isomeric amines corresponding to the molecular formula C9H13N.
ii) What reducing agents can bring about reduction of nitrobenzene ?
iii) Write the product formed when benzyl chloride is reacted with ammonia followed by treatment with methyl and ethyl chlorides.
Answer:
i)
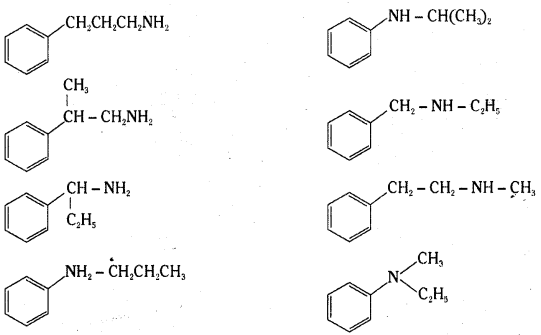
ii) The following reagents can bring about reduction of nitrobenzene.
a) Sn / HCl (or)Fe/HCl
b)Zn/NaOH
c) Zn / NH4Cl/ H2O
d)H2/Pd
iii)
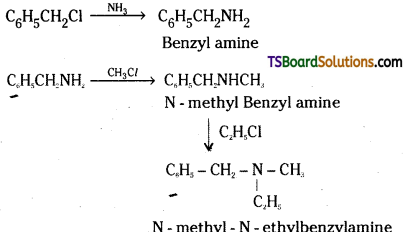
Question 24.
i) Identify the amide and cyanide which on reduction with appropriate reducing agent give n – butylamine.
ii) Write the mechanism of Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
Answer:
i) Butanamide, CH3CH2CH2CONH2 on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride yields n – butylamine
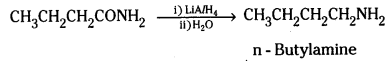
n – propylcyanide on reduction LiAlH4 or Na(Hg)/C2H5OH gives n – Butylamine.
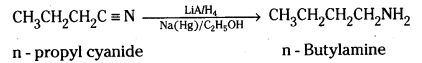
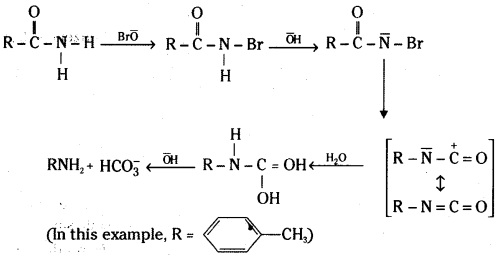
ii) Hoffmann bromamide reaction mechanism :
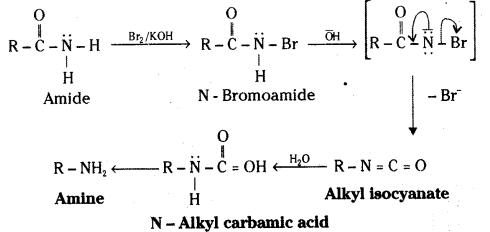
![]()
Question 25.
How do you make the following conversions ?
i) Chlorophenylmethane to phenylacetic acid
ii) Chlorophenylmethane to 2 – phenylethanamine
Answer:
i)
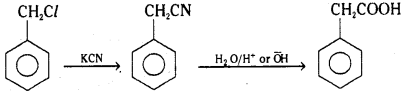
Chlorophenyl methane is reacted with potassium cyanide and converted to benzylcyanide which on hydrolysis gives phenylacetic acid.
ii)
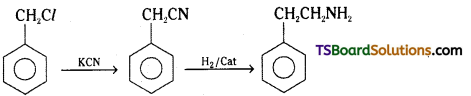
Chlorophenylmethane is reacted with KCN and converted to benzylcyanide which on reduction gives 2 – phenylethanamine.
Question 26.
Identify the starting amide which gives p – methyl aniline on reaction with bromine and sodium hydroxide and write all the steps involved in the reaction.
Answer:
p – methylbenzamide on reaction with bromine and sodium hydroxide (Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction) gives p – methylaniline.
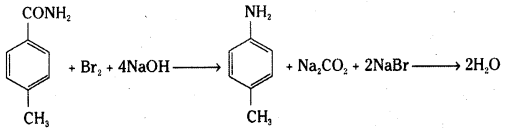
The following steps are involved in the reaction.
2NaOH + Br2 → NaBr + NaOBr + H2O
![]()
Question 27.
Explain wiy the order of basicity methylamine, N, N – dimethylamine and N, N, N – trimethylamine changes in gaseous and aqueous medium.
Answer:
In the gaseous state the basicity of the methyl substituted amines follows the order.
N, N, N – trimethylamine > N, N – dimethylamine > methylamine
It can be explained as follows. The methyl group has electron releasing nature. It pushes electrons towards nitrogen and thus makes the unshared electron pair on nitrogen more available for sharing with the proton of the acid.
Thus the methyl substituted ammonium gets stabilised due to to the dispersal of the positive charge by the +1 effect of thecilkyl group. Thus the basic nature of the methyl substituted amines increases with the increase in the number of methyl groups. This trend is followed in the gaseous phase.
In the aqueous phase, the substituted ammonium cations get stabilised not only by electron releasing effect of the methyl group but also by solvation with water molecules. Another factor that decides the basic strength of the alkylamines in aqueous state is steric hindrance of the alkyl groups:
Hence, due to the presence of two electron releasing methyl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, dimethylamine is a stronger base than methylamine. If so, trimethyl amine having three methyl groups attached to nitrogen should be expected to be more basic them dimethyl amine. But actually trimethylamine is considerably less basic than dimethyl amine.
Why so ? In methyl amine and dimethylamine the ‘electronic effect’ increases the basic strength of the amine. However, in trimethylamine the over crowding of the three methyl groups attached to nitrogen causes the ‘steric effect’ – to dominate over the ‘electronic effect’. This steric effect retards the protonation of nitrogen which results in an appreciably lower basic strength of trimethylamine. Hence the basic strength of the amines in the aqueous phase follows the order :
(CH3)2 NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N > NH3.
Question 28.
Write the equations involved in the reaction of Nitrous acid with ethylamine and aniline.
Answerw:
Ethyl amine reacts with nitrous acid to form ethyl diazonium salt which being unstable liberates nitrogen gas and forms ethyl alcohol.
![]()
Aniline reacts with nitrous acid at low temperatures (0 – 5°C) to form diazonium salt.
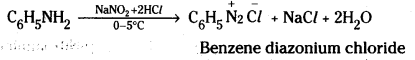
![]()
Question 29.
Explain with equations how methylamine, N, N – dimethylamine and N, N, N-trimethylamine react with benzene sulphonyl chloride and how this reaction is useful to separate these amines.
Answer:
Methylamine reacts with benzene suphonyl chloride to give N – methyl benzene sulphonamide.
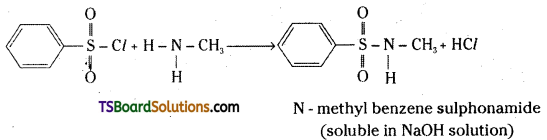
The hydrogen attached to nitrogen in sulphonamide is strongly acidic due to the presence of strong electron withdrawing sulphonyl group. Hence, it is soluble in alkali, say NaOH solution. N, N – dimethylamine reacts with benzene sulphonyl chloride to give N, N – dimethylbenzene sulphonair; le. Since this compound does not contain any hydrogen atom attached to nitrogen atom it is not soluble in alkali.
N, N, N – trimethylamine does not react with benzene sulphonyl chloride. This property of these three methylamines reacting with benzene sulphonylchloride in a different manner is used for their separation from a mixture.
Question 30.
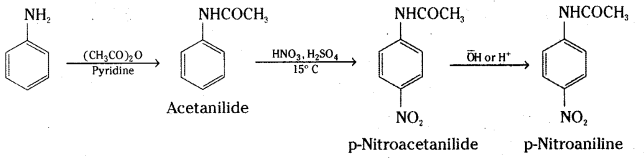
Explain why aniline in strong acidic medium gives a mixture of Nitro anilines and what steps need to be take to prepare selectively p-nitroaniline.
Answer:
In strongly acidic medium, aniline is protonated to form the anilinium ion which is meta directing. That is why besides the ortho and para derivatives, significant amount of meta derivative is also formed.
However, by protecting the -NH2 group by acetylation reaction with acetic anhydride, the nitration reaction can be controlled and the p-nitro derivative can be obtained as the major product.
![]()
Question 31.
i) Account for the stability of aromatic diazonium ions when compared to aliphatic diazonium ions.
ii) Write the equations showing the conversion of aniline diazonium chloride to
a) Chlorobenzene, b) Iodobenzene and c) Bromobenzene.
Answer:
i) The relative stability of aromatic diazonium ions can be ascribed to the fact that its structure is a resonance hybrid of the canonical forms involving the participation of the benzene ring.
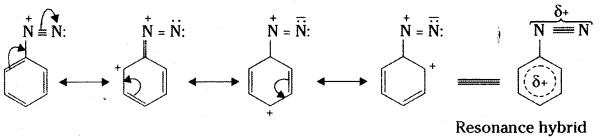
The hybrid structure shows that: a) benzene ring is deactivated to attack of electrophiles, (b) the C -N bond acquires some double bond character and becomes stronger. Alkyl diazonium ions cannot exhibit such resonance and hence C – N bond in them is weak. That is why they are unstable relative to their aromatic counterparts.
ii) a) Aqueous solution of benzene diazonium chloride when heated with cuprous chloride gives chlorobenzene.
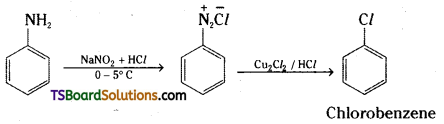
b) Iodobenzene is formed when benzene diazonium chloride solution is treated with potassium iodide.
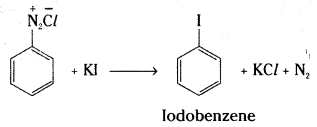
c) Bromobenzene is formed when benzenediazonium chloride solution is treated with hydrobromic acid in the presence of copper power.
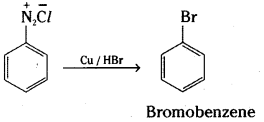
Question 32.
Complete the following conversions:
Aniline to i) Fluorobenzene iQ Cyanobenzene iif) Benzene and iv) Phenol
Answer:
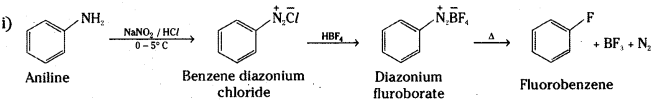
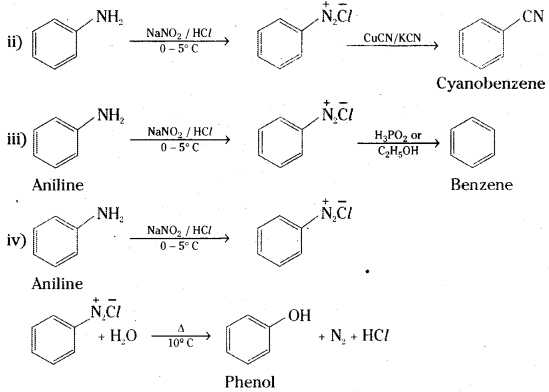
![]()
Question 33.
Explain the following name reactions : [AP 16, 15]
i) Sandmeyer reaction
ii) Gatterman reaction.
Answer:
i) Sandmeyer reaction: The diazonium group of a diazonium salt can be replaced by chlorine (-Cl) or bromine (-Br) by heating the aqueous solution of the diazonium salt with cuprous chloride or cuprous bromide. This reaction is called Sandmeyer reaction.
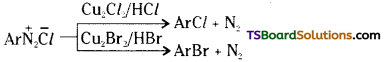
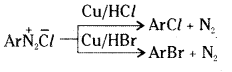
ii) Gatterman reaction : It is a modification of Sandmeyer reaction. The diazonium group is replaced by – Cl or – Br when the diazonium salt solution is treated with the corresponding halogen acid in the presence of copper powder.
Question 34.
Write the steps involved in the coupling of Benzene diazoniumchloride with aniline and phenol.
Answer:D
iazonium salts react with aromatic amines and phenols to give azocompounds having the general formula Ar – N = N – Ar. The reaction is known as coupling reaction. The coupling of benzene diazonium chloride with phenols is carried out in mild alkaline solution and with amines in weakly acidic medium.
Coupling with aniline :
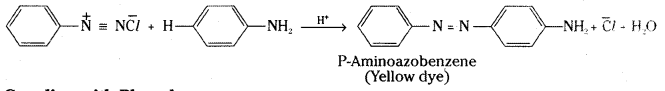
Coupling with Phenol :
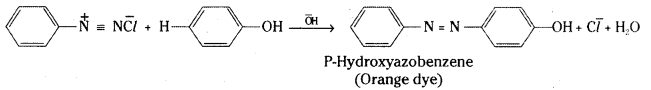
![]()
Question 35.
Write the equations involved in the conversion of acetamide and propanaldehydeoxime to methyl cyanide and ethyl cyanide respectively.
Answer:
Acetamide is converted to methyl cyanide by heating it with benzene sulphonyl chloride in pyridine at 70°C.
CH3 CO NH2 + C6H5SO2Cl ![]() > CH3CN + C6H5SO3H + HCl
> CH3CN + C6H5SO3H + HCl
Propanaldehydeoxime is converted to ethylcyanide by dehydrating with acetic anhydride.
CH3 – CH2 – CH = NOH + (CH3CO)2O → CH3 – CH2 – CN + 2CH3COOH
Intext Questions – Answers
Question 1.
Classify the following amines as primary, secondary or tertiary.
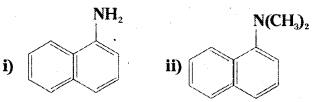
iii) (C2H5)2 CHNH2
iv) (C2H5)2 NH
Answer:
i) and
iii) are primary amines
ii) is a tertiary amine
iv) is a secondary amine
Question 2.
i) Write structures of different isomeric amines to the molecular formula, C4H11N
ii) Write IUPAC names of all the isomers.
iii) What types of isomerism is exhibited by different types of amines ?.
Answer:
Molecular formula C4H11N
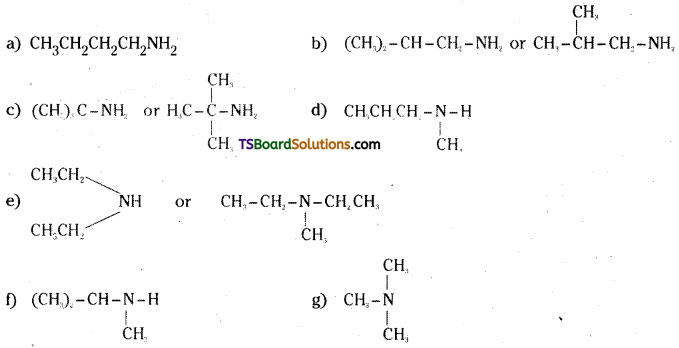
ii) IUPAC names ;
a) Butan-1-amine
b) 2-methyl propanamine
c) 2-methyl-propan-2-amine
d) N-methyl propan-1-amine
e) N-ethyl ethanamine
f) N-methyl-1-methylethanamine
g) N, N-Dimethylmethanamine
iii) Primary amines (a), (b) and (c) exhibit chain isomerism.
Secondary amines (a), (e) and (b) exhibit metamerism.
![]()
Question 3.
How will you convert
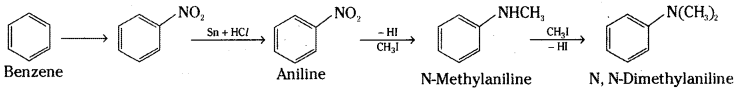
i) Benzene into aniline
ii) Benzene into N, N – dimethylaniline
iii) Cl – (CH2)4 – Cl into hexan -1, 6 – diamine ?
Answer:
i) Benzene is first converted into nitrobenzene by nitration. Nitrobenzene on reduction with tin and hydrohloric acid gives aniline.
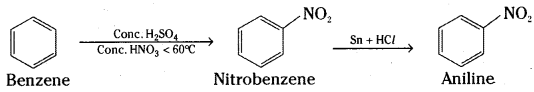
ii) Benzene is converted into aniline by nitration followed by reduction. Aniline on heating with excess of methyliodide gives N, N – Dimethylaniline.
iii) Cl – (CH2)4 – Cl is converted to NC – (CH2)4 – CN by reacting with ethanolic potassium cyanide. NC – (CH2)4 – CN on reduction with LiAlH4 or sodium and alcohol gives H2N (CH2)6 NH2.
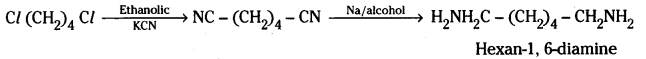
Question 4.
Arrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength :
i) C2H5NH2, C6H5NH2, NH3,C6H5CH2 NH2 and (C2H5)2NH
ii) C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2 NH, (C2H5)3N, C6H5NH2
iii) CH3NH2, (CH3)2 NH, (CH3)3N, C6H5NH2, C6H5CH2NH2
Answer:
i) C6H5NH2 < NH3 < C6H5CH2NH2 < C2H5NH2 < (C2H5)2 NH
ii) C6H5NH2 < C2H5NH2 < (C2H5)3N < (C2H5)2 NH
iii) C6H5NH2 < C6H5CH2NH2 < (CH3)3 N < CH3NH2 < (CH3)2 NH
Question 5.
Complete the following acid – base reactions and name the products.
i) CH3CH2CH2NH2 + HCl →
ii) (C2H5)3N + HCl →
Answer:
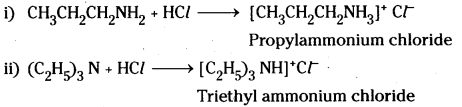
![]()
Question 6.
Write reactions of the final alkylation product of aniline with excess of methyl iodide in the presence Of sodium carbonate solution.
Answer:
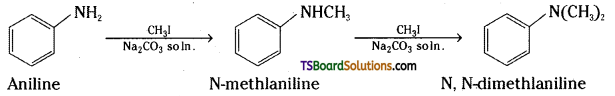
Thus, when aniline is treated with an excess of methyl iodide in a basic medium, the final product obtained is N, N-dimethylaniline.
Question 7.
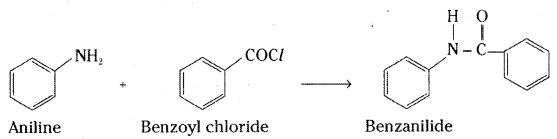
Write chemical reaction of aniline with benzoyl chloride and write the name of the product obtained.
Answer:
Aniline reacts with benzoylchloride to give benzanilide.
Question 8.
Write structures of different isomers corresponding to the molecular formula, C3H9N. Write IUPAC names of the isomers which will liberate nitrogen gas on treatment with nitrous acid.
Answer:
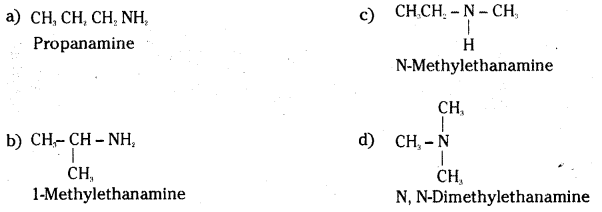
Propanamine (a) and 1- methylethenamine (b) being aliphatic primary amines liberate nitrogen gas on treatment with nitrous acid.
![]()
Question 9.
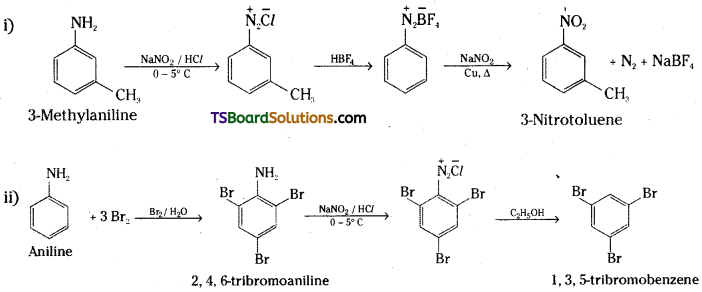
Convert
i) 3-Methylaniline into 3-nitrotoluene
ii) Aniline into 1, 3, 5 – tribromobenzene.
Answer: