Students must practice these Maths 2A Important Questions TS Inter Second Year Maths 2A Binomial Theorem Important Questions Very Short Answer Type to help strengthen their preparations for exams.
TS Inter Second Year Maths 2A Binomial Theorem Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Questions 1.
Find the 6th term in \(\left(\frac{2 x}{3}+\frac{3 y}{2}\right)^9\). [May ’13, AP – Mar. 2019]
Solution:
Given \(\left(\frac{2 x}{3}+\frac{3 y}{2}\right)^9\)
Here, x = \(\frac{2 x}{3}\); a = \(\frac{3 y}{2}\); n = 9
r + 1 = 6
⇒ r = 5
The general term in the expansion of (x + a)n is given by
Tr + 1 = \({ }^n C_r\) . xn – r . ar
The 6th term in the expansion of \(\left(\frac{2 x}{3}+\frac{3 y}{2}\right)^9\) is
T5 + 1 = \({ }^9 C_5\left(\frac{2 x}{3}\right)^{9-5}\left(\frac{3 y}{2}\right)^5\)
T6 = \({ }^9 \mathrm{C}_5 \cdot\left(\frac{2 \mathrm{x}}{3}\right)^4 \cdot\left(\frac{3 \mathrm{y}}{2}\right)^5\)
T6 = 126 . \(\frac{2^4 \cdot x^4}{3^4} \cdot \frac{3^5 y^5}{2^5}\)
T6 = 126 . \(\frac{3 x^4 y^5}{2}\)
T6 = 189 . x4y5
Question 2.
Find the 3rd term from the end in the expansion of \(\left(x^{-\frac{2}{3}}-\frac{3}{x^2}\right)^8\).
Solution:
Given \(\left(x^{-\frac{2}{3}}-\frac{3}{x^2}\right)^8\)
Here, x = \(\mathrm{x}^{\frac{-2}{3}}\); a = \(\frac{-3}{x^2}\); n = 8
r + 1 = 7
⇒ r = 6
The general term th the expansion of (x + a)n is
Tr + 1 = \({ }^n C_r\) xn – r ar.
The 7th term in the expansion of \(\left(x^{\frac{-2}{3}}-\frac{3}{x^2}\right)^8\) is
T6 + 1 = \({ }^8 C_6\left(x^{\frac{-2}{3}}\right)^{8-6} \cdot\left(\frac{-3}{x^2}\right)^6\)
T7 = 28 \(\left(x^{\frac{-2}{3}}\right)^2\left(\frac{3}{x^2}\right)^6\)
= 28 . \(x^{-4} \cdot \frac{3^6}{x^{12}}\)
= 28 . 36 . \(\frac{-40}{x^3}\)
The 3rd term from the end is 28 . 36 . \(x^{\frac{-40}{3}}\).
![]()
Question 3.
Find the 4th term from the end ¡n the expansion of (2a + 5b)8.
Solution:
Given (2a + 5b)8
Here x = 2a, a = 5b, n = 8.
The expansion has 9 terms so that, the fourth term from the end is 6th term from the beginning, in the expansion of (2a + 5b)8.
r + 1 = 6
⇒ r = 5
The general term in the expansion of (x + a)n is Tr + 1 = \({ }^n \mathrm{C}_r\) xn – r ar.
The r term in the expansion of (2a + 5b)8 is
T5 + 1 = \({ }^8 C_5\) (2a)8 – 5 (5b)5
= \({ }^8 C_5\) (2a)3 (5b)6
= \({ }^8 C_5\) . 23 . a3 . 53 . b5
∴ The 4th term from the end is \({ }^8 C_5\) . 23 . 55 . a3 . b5.
Question 4.
Find the middle term (s) in the expansion of \(\left(\frac{3 x}{7}-2 y\right)^{10}\) [March’12, May ‘10]
Solution:
Given \(\left(\frac{3 x}{7}-2 y\right)^{10}\)
Here x = \(\frac{3 x}{7}\); a = – 2y, n = 10
Since, n = 10 is even then
Middle term = \(\frac{n}{2}\) + 1 = \(\frac{10}{2}\) + 1
= 5 + 1 = 6th term.
r + 1 = 6
⇒ r = 5
The general term in the expansion of \(\left(\frac{3 x}{7}-2 y\right)^{10}\) is
Tr + 1 = \({ }^n C_r\) xn – r ar
= \({ }^{10} C_5\left(\frac{3 x}{7}\right)^{10-5}(-2 y)^5\)
6th term of \(\left(\frac{3 x}{7}-2 y\right)^{10}\) is
T5 + 1 = \({ }^{10} C_5\left(\frac{3 x}{7}\right)^5(-2 y)^5\)
= \({ }^{-10} C_5 \frac{3^5}{7^5}\) 25 . x5 . y5.
Question 5.
Find the middle term(s) in \(\left(4 a+\frac{3 b}{2}\right)^{11}\).
Solution:
Given \(\left(4 a+\frac{3 b}{2}\right)^{11}\)
Here x = 4a, a = \(\frac{3}{2}\)b; n = 11
Since, n = 11 is odd,
Middle terms = \(\frac{\mathrm{n}+1}{2}, \frac{\mathrm{n}+3}{2}\) = 6, 7 terms
6th term:
r + 1 = 6
⇒ r = 5
The general term in this expansion ¡s
Tr + 1 = \({ }^n C_r\) xn – r . ar
∴ 6th term of given expansion is
T5 + 1 = \({ }^{11} \mathrm{C}_5\) (4a)11 – 5 (\(\frac{3}{2}\)b)5
T6 = \({ }^{11} \mathrm{C}_5\) (4a)6 (\(\frac{3}{2}\)b)5
= \({ }^{11} C_5 \frac{4^6 \cdot 3^5}{2^5} \cdot a^6 \cdot b^5\)
T6 = \({ }^{11} C_5 \frac{2^{12} \cdot 3^5}{2^5} \cdot a^6 b^5\)
= \({ }^{11} \mathrm{C}_5\) . 27 . 35 . a6 . b5
7th term:
r + 1 = 7
⇒ r = 6
The general term in this expansion is
Tr + 1 = \({ }^n C_r\) xn – r . ar
∴ 7th term of given expansion is
T6 + 1 = \({ }^{11} C_5(4 a)^{11-6}\left(\frac{3}{2} b\right)^6\)
T7 = \({ }^{11} C_6(4 a)^5\left(\frac{3}{2} b\right)^6\)
= \({ }^{11} C_6 \frac{4^5 \cdot 3^6}{2^6}\) . a5 . b6
T7 = \({ }^{11} \mathrm{C}_6 \frac{2^{10} \cdot 3^6}{2^6}\) . a5 . b6
= \({ }^{11} \mathrm{C}_6\) 24 . 36 . a5 . b6.
![]()
Question 6.
Find the coefficient of x-7 in \(\left(\frac{2 x^2}{3}-\frac{5}{4 x^5}\right)^7\).
Solution:
Given \(\left(\frac{2 x^2}{3}-\frac{5}{4 x^5}\right)^7\).
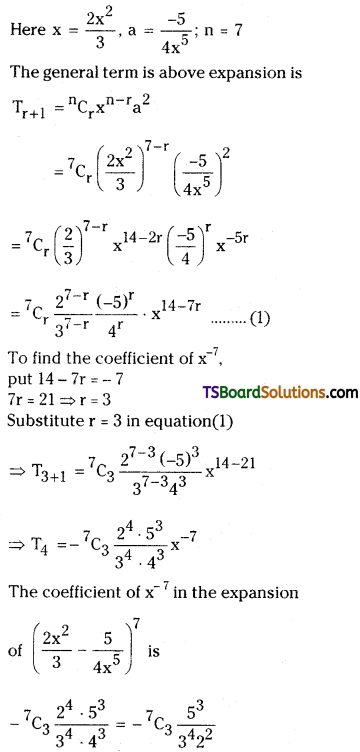
Question 7.
Find the coefficients of x9 and x10 in the expansion of (2x2 – \(\frac{1}{x}\))20
Solution:
Given (2x2 – \(\frac{1}{x}\))20
Here x = 2x2; a = \(-\frac{1}{x}\); n = 20
Now, the general term in this expansion is
Tr + 1 = \({ }^n C_r\) xn – r . ar
= \({ }^{20} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{r}}\) (2x2)20-r (\(-\frac{1}{x}\))r
= \({ }^{20} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{r}}\) 220-r x40-2r (- 1)r x– r
= \({ }^{20} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{r}}\) 220-r (- 1)r x40-3r …………(1)
I) To find the coefficient of x9:
put 40 – 3r = 9
⇒ 3r = 31
⇒ r = \(\frac{31}{3}\)
Since, r is a positive integer, this is not possible.
This means, that the expansion of \(\left(2 x^2-\frac{1}{x}\right)^{20}\) does not possess x9 term.
This means that,
The coeff. of x9 in the exp. of \(\left(2 x^2-\frac{1}{x}\right)^{20}\) is zero.
ii) To find the coefficient of x10:
Put 40 – 3r = 10 of substituting r = 10 in equation (1), we get
T10 + 1 = \({ }^{20} \mathrm{C}_{10}\) 220-10 (- 1)10 x40-30
T11 = \({ }^{20} \mathrm{C}_{10}\) . 1 . x10
= \({ }^{20} \mathrm{C}_{10}\) 210 x10
The coeff. of \(\left(2 x^2-\frac{1}{x}\right)^{20}\) in the expansion of is \({ }^{20} \mathrm{C}_{10}\) 210.
![]()
Question 8.
Find the term independent of x in the expansion of \(\left(\frac{3}{\sqrt[3]{x}}+5 \sqrt{x}\right)^{25}\).
Solution:
Given, \(\left(\frac{3}{\sqrt[3]{x}}+5 \sqrt{x}\right)^{25}\)
Here, x = \(\frac{3}{\sqrt[3]{x}}\), a = 5√x, n = 25
The general term in this expansion is
Tr + 1 = \({ }^n C_r\) xn-r ar
= \({ }^{25} C_r\left(\frac{3}{\sqrt[3]{x}}\right)^{25-r}(5 \sqrt{x})^r\)
= \({ }^{25} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{r}} 3^{25-\mathrm{r}} \mathrm{x}^{\frac{-25+\mathrm{r}}{3}} \cdot 5^{\mathrm{r}} \cdot \mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{r} / 2}\)
= \({ }^{25} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{r}} 3^{25-\mathrm{r}} 5^{\mathrm{r}} \times \frac{-25+\mathrm{r}}{3}+\frac{\mathrm{r}}{2}\) ………………..(1)
To find the term independent of x:
i.e., the coeff. of x0 put \(\) = 0
⇒ – 50 + 2r + 3r = 0
⇒ 5r = 50
⇒ r = 10
Substitute r = 10 in equation (1),
T10+1 = \({ }^{25} \mathrm{C}_{10} 3^{15} 5^{10} \mathrm{x}^{\frac{-25+10}{3}+\frac{1}{10}}\)
T11 = \({ }^{25} \mathrm{C}_{10}\) . 315 . 510 . x0
∴ The term independent of x in the given expansion is
T11 = \({ }^{25} \mathrm{C}_{10}\) . 315 . 510 . x0
Question 9.
Find largest binomial coefficients in the expansion of (1 + x)24.
Solution:
Given (1 + x)24
Here, n = 24, an even integer.
∴ The largest binomial coefficient is \({ }^{\mathrm{n}} \mathrm{C}_{\left(\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}\right)}={ }^{24} \mathrm{C}_{12}\).
Question 10.
If \({ }^{22} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{r}}\) is the largest binomial coefficient in the expansion of (1 + x)22 find the value of \({ }^{13} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{r}}\). [TS & AP – May 2015; May ’11] [AP. Mar. 2016]
Solution:
Given, (1 + x)22
Here n = 22 an even integer.
∴ The Largest binomial coefficient = \({ }^{\mathrm{n}} \mathrm{C}_{\left(\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}\right)}={ }^{22} \mathrm{C}_{\left(\frac{22}{2}\right)}={ }^{22} \mathrm{C}_{11}\)
Given that the largest binomial coeff. = \({ }^{22} \mathrm{C}_{11}\)
[∵ \({ }^n C_r={ }^n C_s\)
⇒ n = r + s (or) r = s]
⇒ \({ }^{22} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{r}}={ }^{22} \mathrm{C}_{11}\)
⇒ r = 11
Now, \({ }^{13} C_r={ }^{13} C_{11}={ }^{13} C_2\)
= \(\frac{13 \times 12}{2 \times 1}\) = 78.
![]()
Question 11.
If n is a positive integer, then prove that \(\sum_{r=1}^n \mathbf{r} \cdot C_r\) = n . 2n – 1. [May ’97]
Solution:
We know that,
(1 + x)n = C0 + C1x + C2x2 + C3x3 ± …………… + Cnxn ……………(1)
Now differentiating (1) on both sides with respect to ‘x’ we get
n(1 + x)n – 1 = 0 + C1(1) + C2(2x) + C3(3x2) + …………….. + Cn (nxn-1)
n(1 + x)n-1 = C1 + 2x . C2 + 3x2 . C3 + nxn – 1Cn
Now, put x = 1 we get
n(2)n – 1 = C1 + 2(1) C2 + 3(1)2C3 + …………… + (n) (1)n – 1 Cn
n2n – 1 = C1 + 2C2 + 3C3 + …………. + nCn
C1 + 2C2 + 3C3 + …………… nCn = n . 2n – 1
\(\sum_{r=1}^n\) r . Cr = n . 2n – 1
Question 12.
If the coefficients of (2r + 4)th, (3r + 4)th terms in the expansion of (1 + x)21 are equal, find ‘r’. [TS – Mar, 2015]
Solution:
Given (1 + x)21
The general term in the expansionof (x + a)n is
Tr + 1 = nCr xn – r . ar.
(2r + 4)th term in the expansion of (1 + x)21 is
T(2r + 3) + 1 = \({ }^{21} \mathrm{C}_{2 \mathrm{r}+3}\) (1)21 – (r + 3) (x)2r + 3
T2r + 4 = \({ }^{21} \mathrm{C}_{2 \mathrm{r}+3}\) x2r + 3
The coefficient of (2 + 4)th term is \({ }^{21} C_{2 r+3}\)
(3r + 4)th term in the expansion of (4 + x)21 is .
T(3r + 3) + 1 = \({ }^{21} \mathrm{C}_{3 \mathrm{r}+3}\) (1)21 – (3r + 3) x3r + 3
T3r + 4 = \({ }^{21} \mathrm{C}_{3 \mathrm{r}+3}\) x3r + 3
The coeff. of (3r + 4)th term is \({ }^{21} \mathrm{C}_{3 \mathrm{r}+3}\)
Given that, two coeff. are equal.
\({ }^{21} \mathrm{C}_{2 \mathrm{r}+3}={ }^{21} \mathrm{C}_{3 \mathrm{r}+3}\)
\({ }^n C_r={ }^n C_s\)
⇒ n = r + s (or) r = s
n = r + s
21 = 21 + 3 + 3r + 3
5r = 15
⇒ r = 3
r = s
2r + 3 = 3r + 3
⇒ r = 0.
Question 13.
Prove that C0 + 2 . C1 + 4 . C2 + 8 . C3 + …………. + 2n . Cn = 3n. [AP – Mar. ’15; May ’07] [TS – Mar. ’18]
Solution:
We know that,
(1 + x)n = C0 + C1x + C2x2 + C3x3 + ………….. + Cnxn …………….(1)
put x = 2 in the equation (1) we get,
(1 + 2)n = C0 + C1(2) + C2(2)2 + C3(2)3 + …………….. + Cn.(2)n
∴ C0 + 2 . C1 + 4 . C2 + 8 . C3 + …………… + 2n Cn = 3n .
![]()
Question 14.
Prove that C0 + 3 . C1 + 32 . C2 + ………….. + 3n . Cn = 4
Solution:
We know that,
(1 + x)n = C0 + C1x + C2x2 + C3x3 + ………….. + Cnxn …………….(1)
Put x = 3 in equation (1), we get
(1 + 3)n = C0 + C1 (3) + C2 (3)2 + C3 (3)3 + ………………… + Cn . 3n
C0 + 3 . C1 + 32 . C2 + 33 . C3 + …………… + 3n Cn = 4n.
Question 15.
Prove that \(\frac{\mathrm{C}_1}{\mathrm{C}_0}+2 \cdot \frac{\mathrm{C}_2}{\mathrm{C}_1}+3 \cdot \frac{\mathrm{C}_3}{\mathrm{C}_2}+\ldots \ldots\) + \(\mathbf{n} \cdot \frac{\mathbf{C}_{\mathbf{n}}}{\mathbf{C}_{\mathbf{n}-\mathbf{1}}}=\frac{(\mathbf{n}+\mathbf{1})}{2}\)
[March ’88]
Solution:
L.H.S:
\(\frac{\mathrm{C}_1}{\mathrm{C}_0}+2 \cdot \frac{\mathrm{C}_2}{\mathrm{C}_1}+3 \cdot \frac{\mathrm{C}_3}{\mathrm{C}_2}+\ldots \ldots+\mathrm{n} \cdot \frac{\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{n}}}{\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{n}-1}}\)
= \(\frac{{ }^n C_1}{{ }^n C_0}+2 \cdot \frac{{ }^n C_2}{{ }^n C_1}+3 \cdot \frac{{ }^n C_3}{{ }^n C_2}+\ldots . .+n \cdot \frac{{ }^n C_n}{{ }^n C_{n-1}}\)
= \(\frac{\mathrm{n}}{1}+2 \cdot \frac{\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{n}-1)}{1 \cdot 2}}{\frac{\mathrm{n}}{1}}+3 \cdot \frac{\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{n}-1)(\mathrm{n}-2)}{1 \cdot 2 \cdot 3}}{\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{n}-1)}{1 \cdot 2}}+\ldots \ldots+\mathrm{n} \cdot \frac{1}{5}\)
= n + (n – 1) + (n – 2) + …………… + 1
= 1 + 2 + 3 + ………….. + n
= Σn = \(\frac{n(n+1)}{2}\) = R.H.S
Question 16.
Find the number of terms in the expansion of (2x + 3y + z)7. [May ’14, March ’14, ’13] [TS – Mar. 2019]
Solution:
Given (2x + 3y + z)7
Here, n = 7
∴ Number of terms in the expansion of
(2x + 3y + z)7 = \(\frac{(n+1)(n+2)}{2}\)
= \(\frac{(7+1)(7+2)}{2}=\frac{8 \times 9}{2}\) = 36.
![]()
Question 17.
Find the number of terms with non-zero coefficients in (4x – 7y) + (4x + 7y) .
Solution:
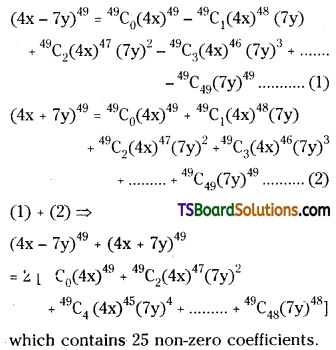
Question 18.
Find the sum of last 20 coefficients in the expansion of (1 + x)39.
Solution:
The last 20 coefficients in the expansion of (1 + x)39 are \(\).
We know that
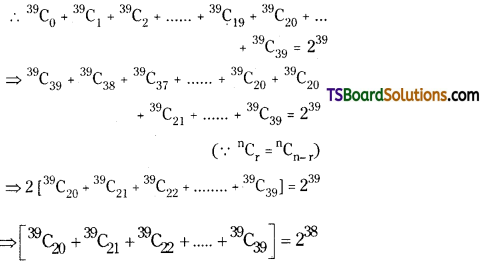
Question 19.
If A and B are coefficients of xn in the expansion of (1 + x)2n and (1 + x)2n-1 respectively, then find the value of \(\frac{A}{B}\).
Solution:
Coefficient of xn in the expansion of (1 + x)2n is \({ }^{2 \mathrm{n}} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{n}}\)
Coefficient of xn in the expansion of (1 + x)2n-1 is \({ }^{2 n-1} C_n\)
∴ A = \({ }^{2 \mathrm{n}} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{n}}\) and B = \({ }^{2 n-1} C_n\)
∴ \(\frac{A}{B}=\frac{{ }^{2 n} C_n}{2 n-1}=\frac{\frac{2 n !}{n ! n !}}{\frac{(2 n-1) !}{(n-1) ! \cdot n !}}\)
= \(\frac{2 n !}{(2 n-1) ! n !} \cdot(n-1) !=\frac{2 n}{n}\)
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{A}}{\mathrm{B}}\) = 2.
Question 20.
Find the set E of x for which the binomial expansion (2 + 3x)-2/3. [March ‘11, ‘06] [TS – Mar. 2016]
Solution:
Given, (2 + 3x)-2/3 = 2-2/3 (1 + \(\frac{3}{2}\)x)-2/3
The binomial expansion of (2 + 3x)-2/3 is valid when
\(\left|\frac{3 x}{2}\right|<1 \Rightarrow|x|<\frac{2}{3}\)
⇒ x ∈ (\(\left.\frac{-2}{3}, \frac{2}{3}\right)\)).
![]()
Question 21.
Find the set E of x for which the binomial expansion of (3 – 4x)3/4. [AP-Mar. 2017] [May ’12]
Solution:
Given (3 – 4x)3/4 = \(3^{\frac{3}{4}}\left(1-\frac{4 x}{3}\right)^{\frac{3}{4}}\)
The binomial expansion of (3 – 4x)3/4 is valid
when \(\left|\frac{-4 x}{3}\right|<1 \Rightarrow\left|\frac{4 x}{3}\right|<1\)
x < \(\frac{3}{4}\)
x ∈ (\(\frac{-3}{4}\), \(\frac{3}{4}\))
E = (\(\frac{-3}{4}\), \(\frac{3}{4}\))
Question 22.
Find the 7th term of \(\left(1-\frac{x^2}{3}\right)^{-4}\).
Solution:
Given \(\left(1-\frac{x^2}{3}\right)^{-4}\)
Comparing this with (1 + x)n
where x = , n = – 4,
r + 1 = 7
⇒ r = 6
The general term in the expression of (1 + x)n is
Tr + 1 = \(\frac{n(n-1) \ldots \ldots(n-r+1)}{5 n}\) . x
= \(\frac{(-4)(-4-1)(-4-2)(-4-3)(-4-4)(-4-5)}{6 !}\) \(\left(\frac{-x^2}{3}\right)^6\)
= \(\frac{(-4)(-5)(-6)(-7)(-8)(-9)}{6 \cdot 5 \cdot 4 \cdot 3 \cdot 2 \cdot 1} \cdot \frac{x^{12}}{3^6}\)
= 84 . \(\frac{28}{243}\) x12.
![]()
Question 23.
Find the set E of the values of x for which, the binomial expansion (2 + 5x)-1/2 is valid. [TS – Mar. 2017]
Solution:
Given (2 + 5x)-1/2
The binomial expansion of (2 + 5x)-1/2 is valid when
|\(\frac{5 x}{2}\)| < 1
|x| < \(\frac{2}{5}\)
x ∈ (- \(\frac{2}{5}\), \(\frac{2}{5}\)).
Question 24.
Find the 7th term in the expansion of \(\left(\frac{4}{x^3}+\frac{x^2}{2}\right)^{14}\). [AP – May 2016]
Solution:
\({ }^{14} C_6 \cdot \frac{2^{10}}{x^{12}}\)
Question 25.
Find the 5th term in the expansion of (3x – 4y)7.
Solution:
241920 x3 y4.
Question 26.
Find the middle term(s) in \(\left(\frac{3}{a^3}+5 a^4\right)^{20}\).
Solution:
\({ }^{20} \mathrm{C}_{10}\) (15)10 (a)10.
Question 27.
Find the middle term(s) in the expansion of (4x2 + 5x3)17.
Solution:
\({ }^{17} \mathrm{C}_{9}\) 48 . 59 . x43
Question 28.
Find the coefficient of x11 in (2x2 + \(\frac{3}{x^3}\))13
Solution:
\({ }^{13} \mathrm{C}_3\) 210 . 33
Question 29.
Find the term independent of x in the expansion of \(\left(\sqrt{\frac{x}{3}}+\frac{3}{2 x^2}\right)^{10}\).
Solution:
\(\frac{5}{4}\)
Question 30.
Find the largst binomial coefficients in the expansion of (1 + x)19.
Solution:
\({ }^{19} \mathrm{C}_9 ;{ }^{19} \mathrm{C}_{10}\)
Question 31.
If the coefficients of (2x + 4)th, (r – 2)th terms in the expansion of (1 + x)21 are equal find ‘r’.
Solution:
6
![]()
Question 32.
Find the set E of x for which the binomial expansion (7 + 3x)-5. [May ’09]
Solution:
\(\left(\frac{-7}{3}, \frac{7}{3}\right)\)
Question 33.
Find the set E of x for which the binomial expansion (7- 4x)-5 is valid.
Solution:
\(\left(\frac{-7}{4}, \frac{7}{4}\right)\)
Question 34.
Find the 6th term of \(\left(1+\frac{x}{2}\right)^{-5}\).
Solution:
\(\frac{-63}{16}\) x5.