Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Study Material 6th Lesson Setting up a Business Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Study Material 6th Lesson Setting up a Business
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the steps involved in the preliminary stage of setting up of a business.
Answer:
For setting up a business, certain procedures are to be followed. These procedures are governed by the current rules and regulations of the state and central Governments. The following steps involved in the preliminary stage of setting up of a business.
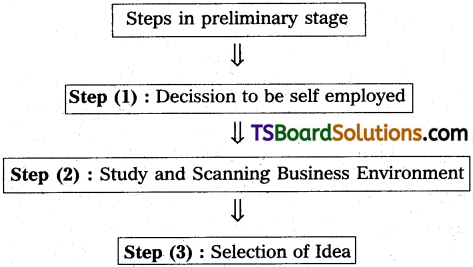
Step (1): Decision to be self – employed
1. The decision to become entrepreneur is influenced by a number of factors. All the factors are divided into two types i.e. (A) Internal Factors & (B) External factors.
2. The internal factors like Education back ground, occupational experience, desire to work independently, family background etc are motivated the person to fruitify his proposition to become entrepreneur when external factors such as financial assistance, technology anjd raw materials and infrastructural facilities are available.
Step (2) : Study and Scanning Business Environment
1. After taking a decision to be self-employed, the entrepreneur should study following business environment prevailing with respect to the proposed industrial unit:
- Administrative Framework.
- Policy Guidelines.
- Rules and Regulations.
2. Administrative framework constitutes sources of ideas to the enterpreneurs which are provided by (a) Development commissions (b) Associated institution and (c) State governments. The policy guidelines and rules and Regulations are provided by the government concerned.
Step (3) : Selection of Idea :
- After selecting the suitable project to manufacture certain product or to provide any service, an entrepreneur should undertake market survey of the product line chosen by him.
- This would help him to gain in sight into the “Existing Market conditions” and “Market Reactions” for the product. He can also ascertain the advantages and disadvantages of launching the new product.
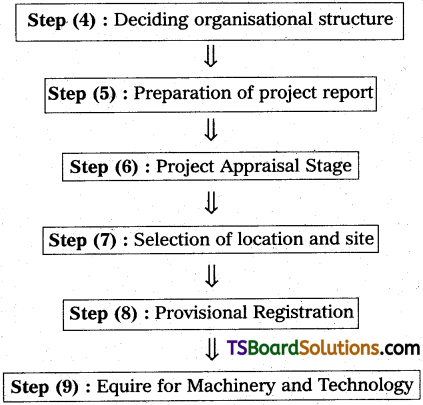
Step (4) : Deciding Organisational Structure :
1. The options for the organisational patterns of the business unit are as follows :
(i) Proprietary, (ii) Partnership Firm, (iii) Co-operative Society, (iv) HUF and (v) Company.
2. The following factors are to be considered while choosing a firm of organisation.
Size of Business, Capital Investment, Nature of Business,. Degree of Control, Tax incidence and Government Stipulation.
Step (5) : Preparation of Project Report
- After decided the product and organisation, the entrepreneur has to put his ideas and other information is black and white.
- This should be so well presented that it provides all relevant information in refeence to the project.
Step (6) : Project Appraisal Stage
- The velocity of a project depends on the technical feasibility, marketability of a profitable price and management of the unit.
- Project Appraisal is the process of examining the viability of a project which is based on technical feasibility, and marketability of the products.
Step (7) : Selection of Location and Site
- For any Industrial project, selection of a suitable industrial site is very important decision and it is based on several considerations like, Nearness to market and nearness to raw material, availability of power and water, availability of transporting system and skilled workers etc.
- A plot can be obtained from (a) State Government Industrial Development, (b) Industrial Cooperative Societies (c) Private Parties.
Step (8) : Provisional Registration
- Provisional Registration enables a party to take the necessary steps to bring the unit into existence.
- Application for Provisional Registration is submitted to the District Industries Centre (DIG).
- The issue of provisional registration! is normally automatic and is given within seven days on the receipt of the Application.
- The initial validity of the provisional registratioin is Six months, it may be renewed for a further period Of six months on submission of satisfactory proof that the party has taken effective steps to establish the unit but could not complete the same.
Step (9) : Enquire for Machinery and Tocimology :
- The requirement of machinery/equipmen, spare parts, tools, etc., should be properly assessed and the proper size of plant and machinery should be decided upon.
- The names of various manufactures of the required machinery may be ascertained and quotations obtained. After careful comparison of machinery specifications, quality, delivery time and price, decision is to be taken for purchase of a particular machinery. Availability of after sales service is an important point to be kept in mind.
- In case the Plant and Machinery are to be obtained from the Hire Purchase Scheme of National Small Industries Corporation (N.S.I.C.) the quotations are to be obtained from the suppliers approved by N.S.I.C.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the steps involved in the implementation stage of setting up of a business.
Answer:
The second stage in the setting up of a business is the implementation stage. It involves 12 steps which are given below :
Step (1) : Statutory Licences / Clearance :
- Various administrative bodies have been set up to consider requests for the issue of industrial licence, import of capital equipment, foreign collaboration etc. These bodies are expected to decide the requests within the stipulated time limit.
- The industrial licence is issued on furnishing evidence that the prescribed conditions are fulfilled.
- A licence from Government of India is necessary for the manufacture of any article included in the schedule to the IDR Act, 1951. Such a few industries are metallurgical industries, fuels, boilers and steam generating plants, electrical equipments, telecommunications, transportation, industrial machinery, fertilizers, chemicals etc.
Step (2) : Arrangement of Finance :
Business units can obtain finance for their projects under three main categories :
1. Term Loan :
Long term requirements for acquiring fixed assets like land and building, plant and machinery and for security deposit and working capital margin.
2. Bridge Loans :
This loan is granted for a short duration to enable the entrepreneur to continue with the implementation of the project till the term loan, applied for and sanctioned is disbursed by the financial institution.
3. Working Capital :
Short – term advances for working capital in the form of pledge / hypothecation / cash / credit / bills facility.
Step (3) : Application for Financial Assistance :
1. After the project is finalized, provisional registration and other formalities are completed, the entrepreneur has to submit an appliation for financial assistance along with the Project Report to the financial institution / bank for a term loan.
Encloseres with Application for term Loan :
2. Along with the appliation submitteu ! – the Financial Institution / Bank, the following documents have to be enclosed :
a) Copy of the Project Report
b) Copy of the partnership deed / memorandum and articles of assocaition
c) Quotations in respect of plant and machinery
d) Income – tax assessment order or incometax clearance relating to partners/ directors.
e) Architect’s estimates in respect of factory building.
f) Copies of balance sheet and profit and loss account for the previous years relating to the associate concerns, if any, of the promoters.
Step (4) : Building Construction and Civil Works :
1. After the sanction and disbursement of first installment of loan from financial institution Building Construction activities are started. If the pre-built factory is obtained from State Government. Industrial Estate, this activity is already completed by taking the possession of the shed. If the plot is already acquired the civil work follow.
2. Before commencing construction activities, the entrepreneur should obtain necessary licence from the Corporation or Municipal authorities other local authorities and should also ensure that the plan of the building conform to the norms stipulated by the Inspector of Factories.
Step (5) : Placement of Order and Procurement of Fixed Assets and Plant and Machinery
The orders are placed with selected suppliers. The timings of placing the order are decided on the delivery of suppliers so that the procurement of Plant and Machinery should synchronise with the completion of the building construction.
Step (6) : Power and Water Connection :
As the application for power and water connection has already been made, the required formalities are completed and water and electrical connections are obtains.
Step (7) : Procurement of Personnel and their Training
- Two of the most critical points to be considered in terms of employees are productivity and Trust.
- Untrained and unmotivated employees can cause a business to fail just as surely as strong competition or economic downtowns.
- Before hiring process is started, careful analysis of business needs and specific duties of each new employee are required to be written very clearly. Determine the pay in terms of salary and benefits.
- It enables to clarify and prioritise the‘skills, experience and qualities the enterprise seeking. The enterprise has to determikne the need to hire new and full time employees. This is also the time to formulate the Personnel Policy. An optimum balance between technical and commercial staff must be maintained.
Step (8) : Procurement of Raw Material :
- The new enterpreneur will have to ensure timely flow of raw materials in anticipation of actual requirement before launching his hew product into the market.
- He has to keep more sources of supply of the required raw materials, instead of depending on a single source of supply.
Step (9) : Installation and Commissioning of Plant and Machinery
- The new entrepreneur should formulate a suitable layout which would facilitate production operations in the best possible manner.
- The prospective entrepreneur should formulate a blue print covering the actual layout of factory and segregate the areas allocated for carrying out different operations in systematic manner.
- Normally the suppliers of Plant and Equipment provide the services of installation and commissioning of their Plant and Equipment. However the entrepreneur along with his technical staff should co-ordinate the installations of different Plant and Equipment for perfect machinery and synchronisation.
Step (10) : Marketing
- Marketing is the complex process of creating customers for products and services;
- Effective marketing planning and promotion begin with gathering factual information about the market place.
- A very important part of marketing plan should be overall promotional objectives : to communicate message, create an awareness of product or service, motivate customers to buy and increase sales.
Step (11) : Permanent Registration
- Permanent Registration is obtained from District Industry Centres (DIC),. When the entrepreneur has taken all the steps to establish the unit i.e. where the factory building is ready, power connectioni is given, the machinery is installed etc., they may apply for Permanent Registration of a unit.
- Within seven days of the receipt of appliation, the District Industries Officer or other designated officer informs the party, of the date and time for inspection of unit
- On being satisfied that the unit is capable of production activity, a permanent registration Certificate will be issued by the Directorate of Industries.
Step (12) : Profit Generation and Repayment of Loan :
- A successful entrepreneur should be ever vigilant about his cost of production and profit generation. If profits are not generated, he should find out the reasons and try to minimize his costs and adjust his production volume.
- If, for any unforeseen reasons he is not able to make profits at a reasonable level of production, he should immediately take steps to remedy the situation.
- Regarding the repayment of loan amount, normally banks and financial institutions insist on its payment along with interest charges by the borrower as per repayment schedule formulated in respect of the project. Normally permitted for repaying the instalments of the principal amount varies from 12 months to 24 months from the date of the first release of the loan.
Question 3.
Discuss the entrepreneurial opportunities provided by the state of Telangana.
Answer:
The opportunities provided by the government are very important environmental factor which induce the entrepreneurs to setup their enterprise. The Industrial policy framework for the state of Telangana has provided a grafti – free, hassle – free environment in which the entrepreneurial spirit of local, domestic and international investors will thrive to takeup their industrial units in the State of Telangana as the preferred investment destination. The various opportunities provided by Government of Telangana are detailed below :
1. An online and help desk grievance redressal system is available in place where entrepreneur is encouraged to report instances as corruption of any delays in performing timely tasks by Telangana state government departments.
2. The departments have developed a Minimum Inspection System where each industrial unit is inspected only once the 3/4 years and the cycle of inspections to be fixed in advance.
3. Self certification is encouraged and automatic renewals are implemented. There is a web based E – helpline facilities as well as physical help-desks at Hyderabad and District Head quarters.
4. The government introduced a Telangana State Industrial Project Approval and Self – Certification System (TS – iPASS) whereby a right to single window clearance, on the lines of the right to information, is bestowed for all applicants.
5. The Telangana State Government recognized 14 sectors as thrust areas, investments in which will be accorded a higher priority over others.
6. The special provision for the micro, small and medium enterprises are as follows :
(a) Adequate number fo smaller plots in industrial parks for SMEs and developed sheds for Micro units.
(b) Special fund for IP registrations assistance.
(c) Special fund for technology transfer and modernization of MSME sector.
(d) Marketing assistance to participate in national and international trade shows and buyer seller meets.
(e) Separate state level Bankers Committee for industries, particularly small and medium enterprises.
7. The government crated a corpus fund jointly with the industries and their associations which will act as a safety net for SMEs that face any crisis and run the risk of imminent sickness.
8. Each of districts of the state excluding Hyderabad have one or more industrial parks exclusively for women.
9. Special support to SC/ST entrepreneurs is offered through TS-PRIDE i.e., Telangana State Programme for Rapid Incubation of Dalit Entrepreneurs Some of the activities are as follows :
(a) A special direct funding programme for financing SC/ST entrepreneurs.
(b) Payment of Margin money on behalf of SC/ST entrepreneurs by the government and creation of Rs 5 crores for Margin Money Refund Scheme.
(c) State departmental procurement policy in tune with GDI’s SME procurement policy of 20%.
(d) Organising Intensive entrepreneur and skill development programmes.
(e) Subsidy eligibility if funded by CRISIL rated NBFCs.
10. To improve the productivity and income of Traditional Arts and Handicrafts like Nirmal Paintings. Dokra metal work, Bidriware, Pembarthy Brassware as well as textiles like Pochampally Ikat, Gadwal sarees and Warangal carpets, the Government of Telangana provides various programmes under T – HART Telangana State Handicrafts and Artisans Revival with Technology Program.
11. About 20 lakh acres of land is identified as unfit for cultivation in Telangana, which is transferred to the Telangana State Industrial Infrstructure Corporation for establishing industrial parks.
12. The TS IIC develops all required infrastructure in the industrial parks like approach roads, water supply, industrial tower, and common effluent treatment facilities and thereby the investor can begin the construction of his unit from the day of getting sanction letter.
13. The details of land in the industrial parks are made avilable on the website of TSIIC and the department of Industries and commerce. All required information like distance of the industrial park from nearest highway/railway station / airport / town, size of individual plots, photographs of the lands, google maps etc., are displayed.
14. Every Industrial park have plots earmarked for common facilities like electricity sub-stations, police outposts, five stations, e-seva centres, banks, petrol stations, canteens, local shopping etc.
15. The skill development programmes which are aimed to train the young entrepreneurs are undertaken by Telangana State Accelerated SSI sikns Training Centres of the Industries and Commerce Department.
16. The Telangana State Industrial Development and Entrepreneur Advancement Incentive Scheme is offering the following incentive^ to the entrepreneurs.
(a) Stamp duty reimbursement
(b) Land cost rebate
(c) Power cost reimbursement
(d) Power cost reimbursement
(e) Interest subsidy etc.
17. A conductive State taxation structure is devised for industrial growth and finance resource augmentation by the Telangana State Government. This helps in bringing inter-state tax rationalization on industrial inputs and outputs with neighbouring states.
Thus, the new industrial policy of government of Telangana provides many . opportunities to the industrislists, investors and entrepreneurs in the new state and promises to fulfill their aspirations.
![]()
Question 4.
Define startup and explain its prerequisites.
Answer:
I. 1) Meaning :
- A startup is a company that is in the first stage of its operations.
- Startup companies attempt to capitalise on developing a product or service for which the entrepreneurs believe that there is demand in the market.
- The start ups are founded by one or more entrepreneurs with high costs and limited revenue. Hence, they require capital from different sources to meet their new venture requirements.
2) Definition :
The purpose of the government schemes startups are defined as an entities of private limited company under the Companies Act, 2013 Or a registered partnership firm under Indian Partnership Act 1932 or limited liability partnership under the Limited Partnership Act, 2008. They should work towards innovation or registered in India not prior to ten years, with annual turnover not exceeding Rs. 100 crores in any preceding financial year. They should work towards innovation, development, deployment of commercialization of new products, processes or services driven by technology or intellectual property.
3) Pre-requisites :
The pre-requisites of startups are as follows :
1. Company Age :
Period of existence and operations should not be exceeding 10 years from the Date of Incorporation.
2. Company Type :
Incorporated as a Private Limited Company, a Registered Partnership Firm or a Limited Liability Partnership.
3. Annual Turnover :
Should have an annual turnover not exceeding Rs. 100 crore for any of the financial years since its incorporation
4. Original Entity :
Entity should not have been formed by splitting up or reconstructing an already existing business.
5. Innovative and Scalable :
Should work towards development or improvement of a product, process or service and/or have scalable business model with high potential for creation of wealth & employment.
Question 5.
Explain the success of any two Indian enterpreneurs.
Answer:
India is a highly populated country with a population of morethan 130 crores. Every year on an average 1.2 crore are graduating from the universities. It is not.possible for any economy to provide employment to all of them. The successful entrepreneurs stories shall help them to become self employed. With this background view, an attempt is made to study the stories of some of the successful entrepreneurs of India and the state of Telangana.
1) Lakshmi Niwas Mittal :
Lakshmi Niwas Mittal is an Indian – bom steel magnet who is currently in the U.K. He is known as king of steel. He was bom on 15th June, 1950 at Sadulapur town in Rajasthan State. After graduating he served as a trainee at the mill, and in 1976 he opened his own steel mill in Indonesia. He spent more than a decade learning how to run it efficiently.
In 1989 Mittal purchased the state owned steel works in Trinidad and Tobago, which had been losing huge sums of money. A year later that facility had doubled its output and had become profitable. He used a similar formula for success in a series of acquisitions all around the world, purchasing failing outfits and sending in special management teams to recognize the business.
Mittal’s company controlled about’ 40% of American Market for the flat rolled steel used to make cars. In 2004 Mittal merged his companies, Ispat International and LNM Holdings and acquired Ohio-based International steel Group.
Status of Mittal:
- Lakshmi Mittal serves as chairman & CEO of Arcelor Mittal, the world’s biggest steel maker whose revenue is $ 70.6 billion.
- The Newly created Mittal steel Co, NV, emerged from the deal as world’s largest steel maker and oversaw another merger when mittal steel joined with Arcelor to form Arcelor Mittal.
- Mittal has donated Rs. 3300 crores in July, 2020 to Oxford University to develop Covid-19 vaccine.
2) Sahitya Raj :
Sahitya Raj is young and successful woman entrepreneur from Hyderabad. She is an Electronics Engineer with an MBA degree. Sahitya Raj was working as a SAP-BI consultant at IBM, till 2017. As an employee of IBM, she got the opportunity to travel across the world. But her passion to become an entrepreneur made her to start the firm “Sweetooth” in the year 2018 as a small production unit at Madhapur in Hyderabad. She started a small kitchen in her rented apartment and delivered the products to the people known to her. The response received gave her confidence to carry on the business on a large scale. She is chose as one of the top fire entrepreneurs of 2020 by we Hub, Govt, of Telangana.
The product offered by Sahitya Raj are Gulabjamin, Cheese Cakes, butter scotch, rasmalai, burger buns, chocolates, etc. The Swertooth produces around 250 products which are available at popular cafes and restaurants across Hyderabad. Some of the clients are Barista Cafe, cream stone, zee left etc.
Sahita Raj’s Startup :
- Sweetooth has grown from the home kitchen to a large production unit which employees more than 30 people.
- It’s turnover is around Rs. 32 lakh a month business in the short span of time.
- Decently, it has setup its retail outlets in IT Tech parks across Hyderabad.
- Luring COVID period, she took under online business to serve the needs of the customers of sweetooth.
- She is chosen as one of the top 5 women entrepreneurs for the year 2019-20 by WE HUB Govt, of Telangana.
Question 6.
Explain how the funds required for the startups can be generated?
Answer:
I. Funding of Startups :
Funding of the Startups may come from one or more sources. The following are the various sources for mobilizing the required finance for the Startups.
1. Organic Growth :
Grow the business Slowly based on its own sales, without the need to raise any external funds. Thus, the ned for funds depends on sales volume and new fund generated is used for expansion of the business.
2. Startup Loan :
The enterpreneur who starts a new business or he has been trading for longer than two, years, he is eligible for government backed startup loan. This loan is unsecured personal loan for business and repayable at fixed rate of interest.
3. Friends and Family :
The entrepreneurs of startups can also raise funds from friends and relatives. They may pay a fair rate of interest, sign a legal promissory note and repay the money as agreed.
4. Personal Savings :
Personal savings are commonly used funds to pay for startup costs. Since these funds are owners funds, they won’t incur any interest expense and financing startup becomes a easy task.
5. Supplier Credit :
The suppliers with whom startup company do business can be a source of funds if they extend favourable credit terms to startup. Normally a credit period of 30 days is extended to the company.
6. Leasing :
Leasing is a rental arrangement that gives startup the use of an asset. This will reduce the amount of initial investment required for the business unit.
7. Term Loans :
These loans are granted for a specific purpose and repayable at a regular intervals over a specified length of time. Term loan may range from short term to long term.
8. Factoring :
It is a transaction in which business sells its accounts receivable or invoices to a third party commercial financial company. Here, the entrepreneurs receive cash more quickly instead of waiting for customers payment.
9. Community Schemes :
These schemes are available to help individuals and business- denied credit by banks and lending companies. These schemes provide help with everything from bridging loans and working capital to funds for purchasing property and equipment.
10. Credit Cards :
The starts ups can also use business or personal credit card to pay business startup costs. The interest rate is lower but he has to repay the amount at regular intervals, otherwise it may attract penal interest also.
11. Venture Capitalists :
Venture capitalists invest their funds in the startups along with angle investors. They may refer to invest funds in such startups which are making revenues. Hence, many startups resent venture capital companies for failing to invest in a new venture or risky venture.
12. Government – Assisted Loans :
There are several loan programms in which government either directly lends to small business owners or provide a guarantee or repayment for other small business lenders.
Thus, we find different sources for mobilising the funds for financing the startups. These startups can also avail a number of benefits from government schemes with which the companies will have growth and prosperity.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How a Startup is. Registered?
Answer:
Registration of Startup :
The process of registering Startup is detailed below :
1. Incorporating the Business :
The entrepreneurs have to firstly incorporate their business as a Private Limited Company or a partnership firm or a Limited Liability Partnership.
2. Registering as a Startup :
The entrepreneurs have to register their startups as Startups. For this they have to fillup the form online – log on the startup India website and the Telangana state Website. The application form is to be filled up with details of business.
![]()
Question 2.
How the startups are funded?
Answer:
Funding of the Startups may come from one or more sources. The following are the various sources for mobilizing the required finance for the Startups.
1. Organic Growth :
Grow the business slowly based on its own sales, without the need to raise any external funds. Thus, the ned for funds depends on sales volume and new fund generated is used for expansion of the business.
2. Startup Loan :
The enterpreneur who starts a new business or he has been trading for longer than two years, he is eligible for government backed startup loan. This loan is unsecured personal loan for business and repayable at fixed rate of interest.
3. Friends and Family :
The entrepreneurs of startups can also raise funds from friends and relatives. They may pay a fair rate of interest, sign a legal promissory note and repay the money as agreed.
4. Personal Savings :
Personal savings are commonly used funds to pay for startup costs. Since these funds are owners funds, they won’t incur any interest expense and financing startup becomes a easy task.
5. Term Loans :
These loans are granted for a specific purpose and repayable at a regular intervals over a specified length of time. Term loan may range from short term to long term.
6. Government – Assisted Loans :
There are several loan programms in which government either directly lends to small business owners or provide a guarantee or repayment for other small business lenders.
Question 3.
What factors influence a person to become an entrepreneur?
Answer:
The decision to become entrepreneur is influenced by a number of factors which are presented in the following chart.

6. Other factors.
All these internal and external factors are highly necessary for entrepreneurial activity to take place. The small entrepreneur motivated by internal factors, can fruitify his proposition to become entrepreneur when external factors such as financial assitance, technology and raw materials and infrastructural facilities are available. These facilities or assitance serve as a park in the lightening of the entrepreneurial idea.
Question 4.
What factors to be considered in the selection of an idea?
Answer:
For selecting suitable project to manufacture certain product or to provide any service following factors should be considered.
- Is it an Innovative idea?
- Whether competition in the area is less?
- Whether raw material is easily available.
- Whether infrastreatural facilities viz. Industrial land, power, water etc., are available?
- Whether the entrepreneur has relevant experience and reasonable knowledge in the field?
- If the product is being manufactured already, whether the demand-supply gap is large?
- Whether Government policy encourages production of product ?
- What is the profit margin available?
Question 5.
List out the various aspects to be covered in preparing a project report.
Answer:
1. According the task of project report preparation encompasses information under various heads. Necessary documents, quotations and enquiry should be attached . with the details under given heads to herm a project report.
2. It may not be out of place to emphasise that the project report should be prepared by entrepreneur himself. This not only would save his money but also clarify many doubts thereby making him more optimistic of the success of the project report.
3. A project report should normally cover brief introduction of the proposed project, constitution and nature of the unit, the details and promoters and products, marketing 1 and competitions, manufacturing process, machinery and plant capacity, raw materials availability, land and building, general management and technical staff involved, cost of the project means of finance, working capital requirements, cost of production and profitability, project schedule, repayment schedule, security offered etc.
Question 6.
What are the important confederations to be made in the selection of location and site of business enterprise.
Answer:
For any industrial project, selection of a suitable industrial site is vey important decision. The followiong are the importance consideration to be made in the selection of location site :
- Nearness to market and nearness to raw materials.
- Availability is power and water.
- Availability of modem transporting system.
- Taking an industrial shed with essential services such as water and power.
- Availability of required skills.
- Climatic conditions.
- Concessions applicable for industrially backward areas.
- Availability of freight, express and parcel delivery services.
- Insured that the site allow for future extension.
![]()
Question 7.
Under which categories, the business units obtain their finances?
Answer:
Business units can obtain finance for their projects under force main categories.
1) Term loan :
Long term requirements for acquiring fixed assets like land and building, plant, machinery and for security deposits and working capital margin.
2) Bridge loan :
This loan is granted for a short duration to enable the entrepreneur to continue with implementation of the project till the term loan, applied for and sanctioned is disbursed by the financial institution.
3) Working capital :
Short term advances for working capital in the form or pledge/ hypothecation/cash/credit facility.
Question 8.
What are the formalities pertaining to permanent registration of a business unit?
Answer:
- Permanent registration is obtained from district industry centres.
- When the entrepreneur has taken all the steps to establish the unit i.e, where the factory building is ready, power connection is given, the machinery is installed etc., they may apply for permanent registration of unit.
- Within seven days of the receipt of application, the district industries officer designated officer informs the party of the date and time for inspection of unit. The inspection includes an assessment of installed capacity of the unit.
- On being satisfied that the unit is capable of production activity, a permanent registration certificate will be issued by the directorate of industries.
Question 9.
What are the thrust areas of investment indefined by the Government of Telangana?
Answer:
The Telangana State Government recognised 14 sectors as thrust areas, investments in
which will be accorded a higher priority over others. The thrust areas are
- Life sciences including bulk drugs, formulations, vaccines, nutracenticals, biological, R & D facilities.
- IT hardware including bio-medical device, electronics, cellular communications.
- Precision engineering including aviation, aero-space, defence.
- Food processing and nutrition products including dairy, poultry, meat and fisheries,
- Automobiles, transport vehicles, Auto components, tractors and farm equipments.
- Textiles and apparel, leather and leather value added products.
- FMCG and domestic appliances.
- Engineering and capital goods.
- Gems and jewellery.
- Waste management arid green technologies.
- Solar parks and renewable energy.
- Woodland mineral based industry.
- Transportation.
- Plastic, chemicals and petro chemicals.
Question 10.
What are the special provisions enacted by the Telangana State for the MSMCs?
Answer:
The special provision for the micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) are as follows:
- Adequate number of smaller plots in industrial parks for SMEs and developed sheds for micro units.
- Special funds for addressing incipient sickness.
- Special fund for IP registrations assistance.
- Special fund for anti-pirating assistance.
- Special fund for technology transfer and modernization of MSME sector.
- Reimbursement of land conversion charges for units in own land.
- Marketing assistance to participate in national and international trade shows.
- Consultant panel to respond to MSME entrepreneur needs.
- Separate state level bankers committee for industries Of SME’S. “
Question 11.
How the special support is extended by the government of Telangana to the SC/ST entrepreneurs in our state?
Answer:
Special support to SC/ST entrepreneurs is offered through TS-PRIDE. Some of the activities are as follows :
- A special direct funding programme for financing SC/ST entrepreneurs.
- Payment of margin money on behalf of SC/ST entrepreneurs by the Gcvemmenf and creation of ₹ 5 crores for margin money refund scheme.
- Preferential allotment of plots in industrial parks and reservation of 22% land in Industrial Estates.
- Supplier diversity opportunities in large industries.
- State departmental procurement policy in tune with GOI’s SME procurement policy of 20%.
- Organising intensive entrepreneur and skill development programmes programmes.
- Subsidy eligibility if funded by CRISIL rated NBFCs.
- Representation in all the districts and state level committee.
- Interest subsidy for service sector units, other than transport sector.
Question 12.
What are the steps initiated by Telangana Government for improving the productivity and income of traditional arts and handicrafts of our region?
Answer:
To improve the productivity and income of Traditional arts and Handicrafts like Nirmal paintings, Dokra metal work, Bidriware, Pembarthy Brassware as well as textiles, like Pochampally Ikat, Gadwal sarees and Warangal carpets, the Government of Telangana provide various programmes under T-HART Telangana State Handicarfts and Artisans Revival with technology program.
- Cluster approach for specific arts and crafts.
- Identification and documentation of arts and crafts.
- Technology upgradation and design support centres.
- Skill upgradation and quality improvement.
- Common facility centres.
- Registration support.
- Niche product development.
- Marketing assistance and marketing events participation.
![]()
Question 13.
What are the incentives offered by Telangana State Industrial Development and Entrepreneurs Advancement Incentive Scheme to the entrepreneurs.
Answer:
The Telangana State Industrial Development and Entrepreneur Advancement Incentive Scheme is offered by the State Government under which the following incentives are offered to the entrepreneurs :
- Stamp duty reimbursement
- Land cost rebate
- Land conversion cost
- Power cost reimbursement
- Investment subsidy
- VAT reimbursement
- Interest subsidy
- Training and skill development cost reimbursement
- Quality and patent support
- Reimbursement of infrastructure development costs
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Startup:
Answer:
- A startup is a company that is in the first stage of its operations.
- Startup companies attempt to capitalise on developing a productor service for which the entrepreneurs believe that there is demand in the market.
- They should work towards innovation, development of a new products, processes or services driven by technology or intellectual proverty.
Question 2.
Project Report.
Answer:
It is the document prepared by the entrepreneur where he has to put his ideas and other information in black and white.
Question 3.
Project Appraisal
Answer:
It is the process of examining the viability of a project which is based on technical feasibility, and marketability of the products.
![]()
Question 4.
Provisional Registration.
Answer:
Provisional registration enables a party to take the necessary steps to bring the unit into existence. After providing satisfactoy proof of the unit having come into existence, it can be converted into a regular registration later. Application for provisional registration is submitted to the district industries centre.
Question 5.
Industrial Licence.
Answer:
- Various administrative bodies have been set upto consider requests for the issue of industrial licence.
- The industrial licence is issued on furnishing evidence that the prescribed conditions are fulfilled.
- Under the IDRAct 1951 an industrial licence is necessary for manufacturing of fuels, electronical equipments, telecommunications, transportations, chemicals etc.
Question 6.
Term Loans.
Answer:
It is the loan required for long term needs for acquiring fixed assets like land & buildings plant and machinery etc.
Question 7.
Bridge Loans.
Answer:
It is short term loan which enable the entreprenour to continue with the impl%nentation of the project till the term loan is applied and obtained.
Question 8.
Working Capital
Answer:
- Working capital is the capital that is required by a business to run its day-to-day operations.
- Short-term advance for working capital in the form of pledge/cash/credit/bills facility.
![]()
Question 9.
Uploading Documents :
Answer:
After duly filling, out the application form, the following documents are required to be uploaded.
- Letter of recommendation/support.
- Certificate of incorporation of the company.
- Registration certificate in case of the partnership firm.
- Description of the business and innovative nature of their products and services.