Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Study Material 7th Lesson Internal Trade Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Study Material 7th Lesson Internal Trade
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define trade and explain its features.
Answer:
- Trade means buying and selling of goods and services for money or money’s worth.
- It involves exchange or transfer of goods & services.
Features :
- Trade os a branch of commerce. It connects with buying and selling activities.
- Trade creates possession utility.
- Trade involves sales or transfer of the ownership of goods and services from producer to the consumer.
- Trade includes home trade and foreign trade.
- Trading activities ae performed in market place.
- Trade involved low risk and limited capial investment.
Question 2.
Explain the services of wholesaler to manufactures.
Answer:
Wholesale trade involves purchasing goods in large quantities from producers or manu-facturers and selling in smaller lots to retailers.
Services to Manufactures :
- Enabling large scale production, by purchasing large quantities.
- Sharing / transfer of risk.
- Financial assistance in the form of advance payments.
- Advice regarding the market conditions.
- Removing the place barrier.
- Facilitating continuous production.
- Discharging the distribution function and thereby allowing the manufacturer to concentrate on production.
- Reducing the burden of storing the goods in a warehouse.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the services of a retailer to manufacturer.
Answer:
Retailer purchase goods from the wholesale and selling them in very small qauantitite sto the customers.
Services of Retailer to Manufacturer :
- Preparing a ready market for goods.
- Providing useful information to the market researchers and the producer.
- Risk bearing and risk sharing.
- Distribution of goods to different segments of the market and at different places.
Question 4.
Explain the objective of SEZ’s.
Answer:
SEZ means special Economic Zone.
SEZ’s are areas that offer incentives to resident busines. SEZ concept is introduced with a view to attract foreign investment and adapt latest technology.
Objectives of SEZ :
The following are the main objectives of SEZs.
- Generation of additional economic activity.
- Promotion of exports of goods and services.
- Promotion of investment from domestic and foreign sources.
- Creation of employment opportunities.
- Development of infrastructure facilities.
i) SEZ the exim policy 2000 envisaged that units would be able to import capital goods and raw materials duty free.
ii) SEZ units should be deemed to foreign territory for the purpose of trade operations < and tariffs. Question
Question 5.
Explain the advantages of SEZ’s.
Answer:
The following are the major benefits of SEZs.
i) Employment generation :
SEZs are viewed as highly effective tools for job creation.
ii) Economic development :
SEZs are viewed as the engines for economic development.
iii) Growth of labour-intensive manufacturing industry :
Establishment of SEZs would lead to fast growth of labour intensive manufacturing and service industries in the country.
iv) Balanced regional development :
SEZs are beautiful crafted initiatives for achieving the balanced regional development. v) Capacity building : SEZs are important for stronger capacity building.
vi) Export performance :
SEZ s create dynamism in the export performance if a country by eliminating false resulting from tariffs, other trade barriers and Corporate tax system.
Question 6.
Discuss the adyjzfipages and disadvantages of departmental stores.
Answer:
Advantages :
- It is established in a central location.
- It sells different types of products under a single roof in a specialised manner. It is thus convenient for the buyer.
- It facilitates economies of large scale distribution.
- It helps in eliminating middle men.
Disadvantages :
- The operating costs of departmental stores are high.
- As the size of the stores is large, it may at times be difficult for the departments to draw personal attention.
- The prices are usually high due to the large establishment costs and large working, capital requirements.
- It requires huge capital.
- Usually departmental stores are not situated in far off posh locaities which may cause difficulty for those living in middle segment residential localities in reaching the stores.
![]()
Question 7.
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of multiple shops.
Answer:
Multiple shops are identical shops which sell standardised products in different parts of a particular place or city or town.
For example :
Baskin Robins, Bombay dyeing. The multiple shops have the following advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages :
- They are in the reach of one and all.
- They sell standardised products.
- Customers repose lot of confidence in these establishments as these. Identical establishments are seen everywhere.
- They help in eliminating middlemen.
- They help in division of work and specialisation.
Disadvantages :
- The operating costs are high.
- They sell limited variety of products.
- They lack storage facilities.
- They require huge capital.
Question 8.
Explain the merits and demerits of mail order business.
Answer:
In mail order business, the trader sends a mail to the prospective buyer regarding the product. If the consumer is statisfied he will place the order by mail. The seller on receipt of the required of the required sum from the buyer, shall send the product by mail or post.
Advantages :
- The capital required is relatively less.
- There is convenience, both in buying and selling.
- The goods are reasonably priced.
- Operating costes are less.
- Middlemen are eliminated.
Disadvantages :
- It is very difficult to convince the buyer as the buyer will be able to check the goods. only after buying the goods.
- They lack efficient management.
- The lack storage facility.
- E-tailing, which is a form of e-commerce overtook mail order retail business.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What services are offered by wholesaler to retailer?
Answer:
Wholesaler purchase goods in large quantities from products and selling them in smaller lots to retailers.
Services to Retailer :
- Wholesaler making the goods available to retailers as time.
- Wholesaler gives marketing support to the relailers.
- He also gives credit facilities to retailers.
- sharing of specialised knowledge.
- Risk bearing and risk sharing.
Question 2.
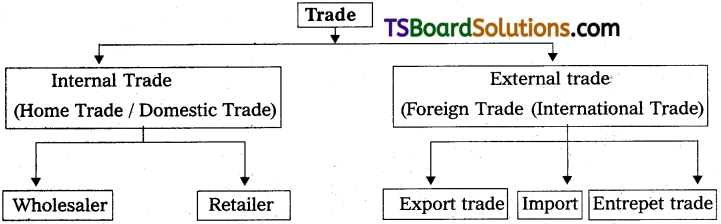
How do you classify the trade?
Answer:
- Trade means buying and selling of goods and services for money or money’s worth.
- Depending upon the geographical limits with in which trade is carried on, the trade in classify into two types.
a) Home trade / Internal trade / Domestic Trade.
b) External Trade / Foreign trade / International trade. - Internal trade is take place with in the geographicla boundaries of a particular country Internal trade is further divided into.
A) whole sale Trade
B) Retail Tsade. - External trade is take place between the countries. External trade is further divided into
a) Export trade
b) Import trade
c) Entrepet trade
Question 3.
What services are refers by retailer to the, consumers?
Answer:
Retailer purchase goods from the wholesaler in bulk quantities and sell them in very small quantities to the consumers for their personal consumption or use
Services of Retailer to consumers :
- Retailer provides wide variety of goods available to consumers.
- Retailer supply goods quickly and timely.
- Retailer, provides expert guidance and demonstrations of the product to the customers.
- He provides after sales service to customers for their purchases.
- Sometimes retailers provides home delivery service.
- Retailers provides credit facilities for consumer.
- Retailors make available goods to consumers convenient location.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the features of Internal Trade?
Answer:
- The trade which take place within the geographical boundaries of a country is called Internal Trade.
- Internal trade is also called as “Home trade” (or) “Domestic Trade”.
Features of Internal Trade :
Internal trade has the following features
- The selling and buying of goods take place within the boundaries of the same country.
- The payment are made by the purchaser to the seller in the home country in the domestic currency.
- Only a few formalities are requited to be completed by the trade.
- Risk is more becaus fo changes in demand from widely spread localised domestic markets.
- The influence of political, legal social, cultural and economic environment of the country is less when compared with the foreign trade.
- The goods are manufactured according to the requirements of domestic consumers and no specifications are received from the buyers.
- For physical flow of goods from manufacturing point to the consumeses point, only domestic transportation system is used, like Railways and roadways.
Question 5.
Who are the It itinerant Retailers?
Answer:
- Itinerant Retailes are those retailers who do not have a fixed place with sale of goods.
- For example : Hawkers & pedlars, street stalls, cheap jacks etc.
- Some of Itinerant Retailers are explained below.
A) Hawkers and pedlars :
The itinerats move from place to place with a view to search their customers. They sell low cost and unbranded products, at doorsteps of the customers.
B) Street stalls :
Street traders display their products on pavements, street comers of different localities in urban area. They usually operate their business near public places like railway sations, bus stands and street corners.
C) Cheap Jacks :
Cheap Jacks operat their business in small hired or rented shops for a specified period. When it is felt that the trade is not going on well at a particular place, they shift to another place.
D) Periodic Itinerants :
The periodic Itinerants deals with products which suit certain occasions like Deepawali, kites during Sankranthi etc. In local language, periodic market is called “Santha” or a “weekly market”.
Question 6.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of consumer co-operatives?
Answer:
- A consumer cooperative store is defined as “a voluntary association of persons based on co-operative principles for buying in common and selling in common”.
- Consmer cooperative store has the following advanages and disadvantages.
I. Advantages :
- The capital required is relatively less.
- There is convenience, both in buying and selling.
- The goods are reasonably priced.
- Operating costa are less.
- Middlement afe eliminaed.
- There are economies of large scale distribution.
- Co-operative societies enjoy certain benefits and incentives from the government.
II. Disadvantages :
- Capital is limied.
- They lack efficient management.
- The lack storage facility.
Question 7.
What are the zones covered by SEZ’s?
Answer:
SEZ means special economic zone. SEZ’s are areas that offer incentive to resident busi-ness. SEZ concept is introduced with a view to attract foreign investment and adopt latest technology.
SEZ implies the following Zones :
- Free Trade Zones (FTZ)
- Export Processing Zones (EPZ)
- Free Zones (FZ)
- Industrial Parks
- Free Ports
- Urban Enterprise Zones
At present there are eight functional SEZs are located at Maharashtra, Kerala, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal and Uttar Pradesh.
Question 8.
What incentives are offered by Telangana government for the SEZ’s?
Answer:
In Telangana state there are 29 SEZs in opetation in fields of Bio – technologys. IT, IT enabled services, Gems, Jewellery, Pharmaceutical, electronic software and handware, etc.
Incentives offered by Telangana government for the SEZ’s :
Some of the incentives offered by Central and State governments for setting up SEZs are as follows :
- Duty free import and domestic procurement of goods for the development, operation and maintenance of he company.
- 100% IT exemption on export income for the first 5 years, 50% for next 5 years and . 50% of the export profit reinvested in business for the next five years.
- Exemption of GST and levies imposed by state government.
- Single window clearances for all state governments approvals. Thus, the SEZs in Telangana State are being given special treatment for the development of industrial sector in the state.
Additional Questions
Question 1.
What is External Trade and Explain its’ types?
Answer:
- The trade refers to buying and selling between traders of two or more countries is called “External Trade”,
- External Trade is also called “Foreign Trade” or “International Trade”.
- External Trade s divided into 3 types.
A) Export Trade
B) Import Trade snf
C) Intrepot Trade.
A) Export Trade :
- When a trader of home country sells his goods to traader or customer of another countries, it is called Export Trade.
- For Eg.: A Trader from India maysells his goods to a customer in Iran.
B) Import Trade :
- When a trader of home country purchase goods from trader of another country, it is called import trade.
- For example: A trader from India may purchase goods from a trader from Singapore.
C) Entrepot Trade :
- When goods are imported from one country and later exported them to another country, it is called entrepot trade. It is also called “Re – export trade”.
- For Example: An India trader purchase raw material from a Srilankan trader and convert rawmaterial into finished goods and sell them to British trader. Here indian trader involved in Entrepot Trade.
![]()
Question 2.
What is Distribution chain, and explain the types of Distribution chain?
Answer:
- A Distribution chain is a chain of business or intermediaries through which goods or services are passes until it reaches the final buyer or consumer.
- Distribution chain can include producers, wholesalers, retailers and consuers.
- On the combination of producer, wholesaler; retailer and consumer, the distribution chain is divided into 3 channels they are
A) The first channel of distribution
B) The second channel of distribution and
C) The third and find channel of distribution.
A) The first channel / chain :
1) The first channel is the longest because it includes producer, wholesaler, retailer and consumer.
2) In this chain, producer sell product to whole saler who sells to a retailer, and then retailer sells to the consumer.
Producer ⇒ Wholesaler ⇒ Retailer ⇒ Consumer
B) The second channel / chain :
1) In this chain producer sells directly to a retailer who sells the product to the consumer.
2) In this channel, there is no wholesaler, only one intermediary i.e. retailer.
Producer ⇒ Wholesaler ⇒ Retailer ⇒ Consumer
C) The third and find channel / chain :
1) In this channel, the producer sells his products directly to the consumers.
2) This is shortest distribution channel, because cutting out both wholesaler and the retailer.
Producer ⇒ Consumer
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Internal Trade.
Answer:
Internal trade :
- Internal trade is conducted within the political and geographical boundaries of a particular country.
- It can take place at local or regional or national level.
- Internal Trade in also called “Domestic Trade or Home track.
Question 2.
Wholesale Trade.
Answer:
Wholesale trade :
- Wholesale trade involves purchasing goods in large quantities from producers or manufacturers and selling in smaller lots to retailers for resale to ultimate consumers.
- Wholesaler is importance between producer and retailor.
Question 3.
Retail Trade.
Answer:
Retail trade involves buying goods from the wholesaler and selling them in very small quantities to the consumers for their personal use.
Question 4.
Itinerants.
Answer:
- Itinerants retailers are those retailers who do not have a fixed place for sale of goods.
- Hawkers and pedlans, street stalls, cheap jacks are examples of itinerants.
![]()
Question 5.
Hawkers and Pedlars.
Answer:
Hawkers and Pedlars These itinerants move from place to place with a view to search their customers.
Features are :
- They sell low cost products.
- They usually sell unbranded products.
Question 6.
Periodic Itinerants.
Answer:
Periodic Itinerants :
- The periodic market traders deal with regular products and products which suit certain occasions.
- In local language, it is cailed Santha or a weekly market.
Question 7.
Street Stalls.
Answer:
- Street traders display their products on pavements, street comers of different localities in urban areas.
- They usually operate their business near public places like Railway station, bus stands, parks etc.
Question 8.
Cheap Jacks.
Answer:
Cheap Jacks :
- Cheap jacks, the other form of itinerant traders operate their business from small hired shops for a specified period.
- They keep moving from place to place. When they felt, trade in not going on wells.
Question 9.
Fixed Shop Retailers.
Answer:
- Fixed shop retailer Fixed shop retailers are those retailers who have a fixed place for sale of goods.
- Fixed shbp retailers divided into small scale fixed retail shops and large scale fixed retail shows.
![]()
Question 10.
General Stores.
Answer:
General stores :
- These are usually small shops and establishment located in residential area.
- They usually sell essential commodities on cash or credit basis.
Question 11.
Single Line Stores.
Answer:
Single line stores :
The retailers deal with a single /one line of products such as vegetables, bakery products, plastic goods are spld by single time stones, footwear.
Question 12.
Speciality Stores.
Answer:
- A speciality store deals in a particular type of product.
- They selling one type of product only (all brands).
Question 13.
Street Shops.
Answer:
- These are called street stalls because these types of retailers display their goods on tables or under the tent.
- These shops are also called “street stalls”.
Question 14.
Second Hand Goods Shops.
Answer:
- Second – hand goods shop deals in used articles or second hand goods such as old furniture and old books.
- In these shops goods price is low.
Question 15.
Second’s Shops.
Answer:
Second’s shops :
- “seconds shops deals in defective goods”.
- Goods are sold at a discounted rate in seconds shop,
Question 16.
Large Scale Fixed Retail Shops.
Answer:
- The large scale fixed retailers operate on a large scale and they are established with heavy investment.
- They deals in a large bulk of goods.
Question 17.
Multiple Shops.
Answer:
Multiple shops are identical shops which sell standardised products in different parts of a particular place or city or town. Eg : Bombay dyeing.
![]()
Question 18.
Consumer Co-operative Store.
Answer:
- A consumer co-operative store is defined as a voluntary association of persons based on co-operative principle for buying in common and selling in common.
- They sold goods at reasonable price and enjoy benefits and incentives from the government.
Question 19.
SEZ.
Answer:
- SEZ means special economic zones.
- SEZ’s are introduced with a view to attract foreign investment and adopt the latest technology.