Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 1st Year Botany Study Material 2nd Lesson Biological Classification Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 1st Year Botany Study Material 2nd Lesson Biological Classification
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the nature of cell walls in diatoms?
Answer:
- In Diatoms, the cell walls form two thin overlapping shells, epitheca over hypotheca which fit together as in a soap box.
- The walls are embedded with silica and are indestructible. The cell walls left behind by diatoms in their habitat and accumulate over billions of years as diatomaceous earth or kieselguhr.
Question 2.
How are Viroids different from Viruses?
Answer:
| Viruses | Viroids |
| 1) It is a nucleoprotein particle. | 1) It is a free RNA particle. |
| 2) Nucleic acid can be DNA or RNA. | 2) Viroid is formed only by RNA. |
| 3) Viruses infect all types of living organisms. | 3) Viroids infect only plants. |
Question 3.
What do the terms phycobiont and mycobiont signify? [Mar. ’17, A.P. : Mar. ’13]
Answer:
1) Phycobiont :
The group of Algae that live as symbionts in lichens.
2) Mycobiont :
The group of fungi that live as symbionts in lichens.
Question 4.
What do the terms ‘algal bloom’ and ‘red tides’ signify?
Answer:
1. Algal bloom :
Excessive growth of algae mostly cyanophyceae members due to the enrichment of excessive nutrients in a water body. t
2. Red tides :
Sea appears red due to the rapid multiplication of a dinoflagellate, Gonyaulax Red tides in Meditarrenian sea.
Question 5.
State two economically important uses of heterotrophic bacteria.
Answer:
- They help in making curd from milk.
- They are helpful in nitrogen fixation in roots of leguminous plants.
![]()
Question 6.
What is the principle underlying the use of cyanobacteria in agricultural fields for crop improvement? [Mar. 2019, ’15 A.P]
Answer:
- Cyanobacteria Eg : Nostoc, Anabaena, can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialised cells called heterocysts.
- They improve soil fertility by adding organic matter. ,
Question 7.
Plants are autotrophic. Name some plants which are partially heterotrophic.
Answer:
- Insectivorous plants are partially heterotrophic.
Eg : Bladderwort and Venus fly trap. - Parasitic plant, cuscuta is also partially heterotrophic.
Question 8.
Who proposed five kingdom classification ? How many kingdoms of this classification contain eukaryotes?
Answer:
- R.H. Whittaker (1969) proposed Five Kingdom Classification.
- Four kingdoms namely Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia, consists of eukaryotes, while kingdom Monera consists of Prokaryotes.
Question 9.
Give the main criteria used for classification by Whittaker. [Mar. – 2020, 2018 • Mar. 15 – T.S.]
Answer:
The main criteria for five kingdom classification of Whittaker are cell structure, thallus organisation, mode of nutrition, reproduction and phylogenetic relationships.
Question 10.
Name two diseases caused by Mycoplasmas. [May ’14]
Answer:
- Witches broom in plants.
- Pleuropheumonia in cattle.
- Mycoplasmal urethritis in humans.
![]()
Question 11.
What are slime moulds? Explain what is meant by plasmodium with reference to slime moulds.
Answer:
1. Slime moulds are saprophytic protists.
2. Plasmodium :
An aggregation formed by a slime mould under suitable conditions, which may grow and spread over several feet.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the characteristic features of Euglenoids?
Answer:
Euglenoids:
- These are unicellular, flagellate, fresh water organisms found in stagnant water.
- Cell wall is absent.
- The body is covered by thin flexible pellicle.
- They bear two flagella, usually one long and one short. They swim actively by flagella.
- The anterior part of the cell bears an invagination consisting of cytostome (cell mouth), cytopharynx (gullet) and reservoir.
- A photosynthetic stigma or eye spot is present in the reservoir.
- Chloroplast is present. The pigments in it are identical to those present in higher plants. Performs photosynthesis.
- In the absence of sunlight they behave like heterotrophs depending on smaller organisms for food.,
- Reproduction is by longitudinal binary fission Palmella stage is found in Euglena.
Question 2.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of two kingdom classification?
Answer:
a) Two kingdom classification with Plantae and Animalia was developed during cinnaeues tissue, that included all plants and animals respectively.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 1) Organisms were easily classified into plants and animals and was easy to understand. | 1) But a large number of organisms did not fall into either of the two categories. This system did not distinguish between the eukaryotes and prokeryotes; unicellular and multicellular organisms and photo-synthetic and non photosynthetic organisms. |
| 2) All cell wall containing organisms were included in plantae kingdom. So Bacteria, Algae, Fungi, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, gymno- sperms and angiosperms were placed under plants. | 2) This placed together groups which widely differed in other character- sties prokeryotic bacteria and Blue green algae were brought together and placed with other groups which are eukaryotic. It also grouped together the unicellular (eg.: Chlamydomonas) and multicellular, (eg : spirogyra) ones. This systems did not differentiate between the heterographic group, fungi and the autotrophic green plants. Fungi consists of chitin in their cell wall, while green plants have cellulosic cell walls. |
![]()
Question 3.
Give the salient features and importance of Chrysophytes. [Mar. – 2018, Mar. ’15 – A.P. : Mar. ’13]
Answer:
- This group includes diatoms and desmids (golden algae).
- They are green, microscopic, float in water currents.
- In diatoms the cell walls form two thin overlapping shells, epitheca and . hypotheca which fit together as in a soap box.
- The cell walls are embedded with silica which are indestructible. They pile at the bottom of water reservoir to form diatomaceous earth.
- Diatoms are divided into two types based oh symmetry.
i) CentraIe diatoms are radially symmetrical.
ii) Pennales are bilaterally symmetrical. - Asexual reproduction is by binary fission and sexual reproduction is by the formation of gametes.
Question 4.
Give a brief account of Dinoflagellates. [Mar. 2019, ’17 – A.P, Mar. ’15 – T.S]
Answer:
- Dinoflagellates are marine. They appear as yellow, green, brown, blue or red depending upon the pigments present in the cells.
- Cell wall is made up of cellulose plates.
- Two flagella are present. One lies longitudinally and the other lies transversely in the furrow between the wall plates.
- Flagella produce spinning movements. So these are called whirling whips.
- Nucleus is called Mesokaryon as chromosomes are condensed without histones.
- Example : Nostoc shows bioluminescence.
Gonyaulax make the sea appear red.
Question 5.
Write the role of fungi in our daily life. [Mar. ’14]
Answer:
- Mushroom and toadstools are edible fungus.
- Unicellular fungi like yeast are used to make beer and bread.
- Fungi like Rhizopus commonly grow on stale bread, pickles, jams, cheese, on moist food stuff and spoils them. They are called moulds.
- Fungi causes diseases in plants and animals.
Eg : Wheat rust is caused by puccinia.
Late blight of potato by phytopthora. - Orange rot, Red rot in sugarcane are caused by fungus.
- White spots on mustard leaves are due to parasitic fungus. (Albugo)
- Some fungi are the source of antibiotics and peninllium.
Long Answer type Questions
Question 1.
Give the salient features and comparative account of different classes of Fungi studied by you.
Answer:
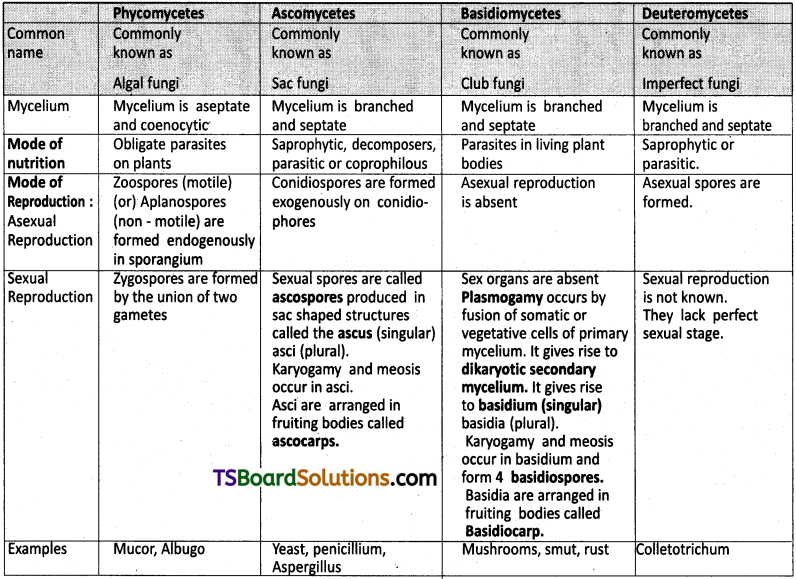
Question 2.
Describe briefly different groups of Monerans you have studied.
Answer:
Kingdom Monera includes all prokarytes like Archebacteria, Eubacteria, Mycoplasma and Actinomycetes.
Archebacteria :
- These are different type of bacteria as they have a different cell wall structure. They can survive in extreme conditions like salty areas (halophiles), hot springs (thermacidophiles) and marshy areas (methanogens).
- The cell wall does not contain peptidoglycan as in bacteria but contain pseudomurein.
- The cell membrane contains branched lipid which is responsible for their survival in extreme conditions.
- Methanogens live in the guts of several ruminant animals like cowand buffaloes and help in their digestion.
- They help in the production of,biogas such as methane from the dungs of the animals.
Eubacteria:
- They occur everywhere even in extreme habitats.
- They live as parasites, and symbionts also.
- Basing on the shape bacteria are grouped under four categories. They are 1) Spherical coccus 2) Rod shaped Bacillus 3) Comma, shaped Vibrium 4) Spiral shape Spirillum
- In Bacteria, cell wall consists of peptidoglycan also called murein or ‘ mucopeptide.
- Infolding of cell membrane called mesosomes responsible for respiration.
- Cell organelles are absent except ribosome.
- As it is prokaryotic, the genetic material DNA is naked without nuclear membrane.
- It shows autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition.
- Excessive growth of cyanobacteria due to nutrients present in sewage causes Algal blooms.
- Rapid growth of red dinoflagellate like Gonyaulax make sea appear red or red tides in Mediterianian sea.
- Chemo autotrophic bacteria oxidise various inorganic substances.
- Chemo heterotrophs are saprophytes which grow on dead organic matter and parasite which causes diseases.
- Asexual reproduction is mainly by binary fission or by spores during unfavourable condition. Sexual reproduction is done by transfer of genetic material from one bacteria to other.
Mycoplasma :
- Mycoplasma are the smallest living cells and can survive without oxygen.
- They do not have any cell wall.
- Mostly they are pathogenic in plants and animals. They cause witches broom in plants, pleuropneumonia in cattle and mycoplasmal urethritis in humans.
Actinomycetes :
- These are branched filamentous bacteria.
- Cell wall contains mycolic acid.
- Most of them are saprophytic and decomposers. Mycobacterium and Corynebacteriurn are parasites.
- Antibiotics are produced from the genus Streptomyces.
![]()
Question 3.
Enumerate the salient features of different groups of protista.
Answer:
Kingdom Protista includes unicellular, aquatic, eukaryotes. It includes Chrysophytes, Dinoflagellates, Euglenoids, Slime moulds and Protozoans.
1. Chrysophytes:
- It includes diatoms and desmids (golden algae).
- They are green, microscopic, float in water currents.
- In Diatoms the cell walls form two thin overlapping shells, epitheca and hypotheca which fit together as soap box.
- The cell walls are embedded with silica which are indestructible. They pile at the bottom of water reservoir to form diatomaceous earth.
- Diatoms are divided into two types based on symmetry.
i) Centrale diatoms are radially symmetrical.
ii) Pennales are bilaterally symmetrical. - Asexual reproduction is by binary fission and sexual reproduction is by the formation of gametes.
2. Dinoflagellates:
- Dinoflagellates are marine. They appear as yellow, green, brown, blue or red depending upon the pigments present in the cells.
- Cell wall is made up of cellulose plates.
- Two flagella are present. One lies longitudinally and the other lies transversely in the furrow between the wall plates.
- Flagella produce spinning movements. So these are called whirling whips.
- Nucleus is called Mesokaryon as chromosomes are condensed without histones.
- Example : Nostoc shows bioluminescence.
Gonyaulax make the sea appear red.
3. Euglenoids :
- These are unicellular, flagellate, fresh water organisms found in stagnant water.
- Cell wall is absent.
- The body is covered by thin flexible pellicle.
- They bear two flagella, usually one long and one short. They swim actively by flagella.
- The anterior part of the cell bears an invagination consisting of Cytostome (cell mouth), Cytopharynx (gullet) and reservoir.
- A photosynthetic stigma on eye spot is present inthe reservoir.
- Chloroplast is present. The pigments in it are identical to those present in higher plants. Performs photosynthesis.
- In the absence of sunlight they behave like heterotrophs depending on smaller organisms for food.
- Reproduction is by longitudinal binary fission Palmella stage is found in Euglena.
4. Slime moulds:
- They show saprophytic nutrition.
- Slime moulds are multinucleated protoplasm surrounded by plasma membrane.
- They are aquatic; move along with decaying twigs.
- Under favourable Conditions they aggregate to form plasmodium. They may spread upto several feet.
- Under unfavourable conditions, plasmodium differentiates and forms fruiting bodies which bear spores at their tips. These spores are wind dispersed and can survive for many years.
5. Protozoans:
All protozoans are heterotrophs and live as parasites. The four major groups of protozoans are given below.
i) Amoeboid protozoans:
- These organisms live in fresh water, sea water or moist soil.
- They have locomotory organ called pseudopodia or false feet.
- Marine forms have silica shells on their surface. Example: Amoeba.
ii) Flagellated protozoans:
- These members are either free-living or parasitic.
- They have flagella.
- They cause diseases like sleeping sickness. Example : Trypanosoma.
iii) Ciliated protozoans:
- These are aquatic and actively moving organisms because of cilia.
- They have a cavity that opens to outside of the cell surface.
Example : Paramecium.
iv) Sporozoans :
It includes diverse organisms that have an infectious sporelike stage in their life cycle. Example : Plasmodium.
InText Question Answers
Question 1.
State two economically important uses of
a) Heterotrophic bacteria.
b) Archaebacteria.
Answer:
a) Use of heterotrophic bacteria :
- They help in making curd from milk.
- They convert dead plants and animals into simpler substances and make them available to plants.
b) Use of archaebacteria :
1) They live in the guts of several ruminant animals such as cow and buffaloes and help in their digestion.
![]()
Question 2.
Give a comparative account of the classes of Kingdom Fungi on the basis of the following i) Mode of nutrition ii) Mode of reproduction.
Answer:
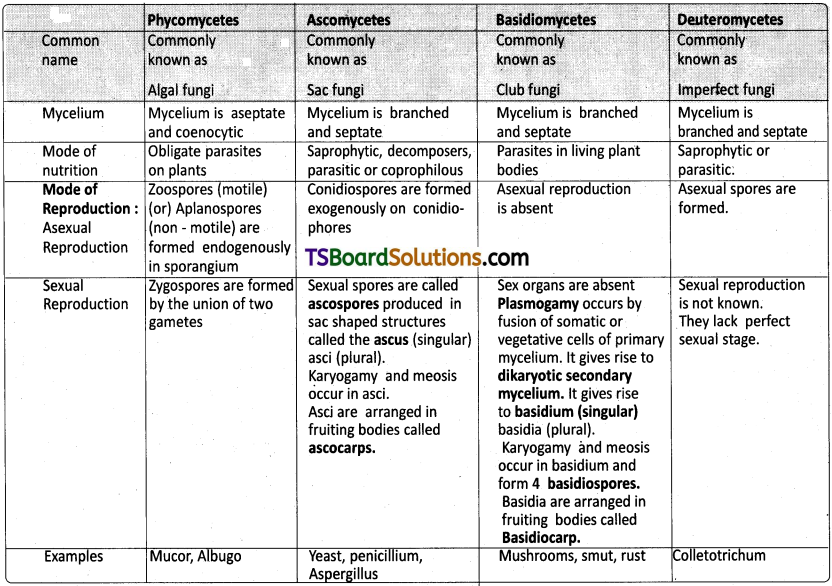
Question 3.
Give a brief account of viruses with respect to their structure and nature of genetic material. Also name four common viral diseases.
Answer:
- Viruses are acellular, ultramicroscopic, nucleoprotein particles.
- Viruses are obligate parasites. They are inert outside the host cell.
- Viruses contain nucleic acid and protein.
- The protein part forms a coat called capsid. It is made up of small sub units called capsomeres.
- The nucleic acid which is genetic material may be DNA or RNA.
- No virus contains both DNA and RNA.
- Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) and Human Immuno Virus (HIV) are examples for virus having RNA.
- Bacteriophages contain DNA as genetic material.
- Four common Viral Diseases : 1) AIDS, 2) Influenza 3) Small pox 4) Mumps.
Question 4.
Organise a discussion in your class on the topic. Are viruses living or non-living?
Answer:
The main points to be discussed in class :
a) Viruses can be regarded as living organisms because
- They are formed by macromolecules which occur in living beings.
- Presence of genetic material
- Ability to multiply or reproduce
- Occurrence of mutations
- Infectivity and host specificity
- Occurrence of antigenic property
- Viruses are killed by autoclaving and ultraviolet rays.
- Viruses are responsible for infectious diseases like common cold, influenza, chicken pox, mumps etc.
b) Viruses can be regarded as non-living organisms because
- Protoplasm absents
- Ability to get crystallized & TMV
- Inability to live independently
- High specific gravity which is found only in non-living objects
- Absence of respiration
- Absence of storing energy system
- Absence of growth and division.
![]()
Question 5.
Suppose you accidentally find an old preserved permanent slide without a label and in your effort to identify it, you place the slide under microscope and observe the following features :
a) unicellular body
b) well defined nucleus
c) biflagellate condition – one flagellum lying longitudinally and the other transversely.
What would you identify it as ? Can you name the kingdom it belongs to?
Answer:
It is identified as Dinoflagellates.
It belongs to kingdom : Protista.
Question 6.
Polluted water bodies have usually high abundance of plants like IMostoc and Oscillatoria. Give reasons.
Answer:
Polluted water bodies have excessive growth of plants like Nostoc and Oscillatonia because of the excessive nutrients present in it. It results in algal booms.
Question 7.
Cyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria have been clubbed together in Eubacteria of kingdom Monera as per the five kingdom classification, even though the two are vastly different from each other. Is this grouping of the two types of taxa in the same kingdom justified? If so why?
Answer:
Yes. because both are unicellular prokaryotic organisms.
Question 8.
What observable features in Trypanosoma would make you classify under the kingdom Protista?
Answer:
They are aquatic, single-celled eukaryotes.
![]()
Question 9.
At a stage of their life cycle, ascomycetous fungi produce fruiting bodies like cleistothecium, perithecium or apothecium. How are these three types of fruiting bodies differ from each other?
Answer:
- The fruiting bodies are produced in Fungi.
- Ascomycetes are called Ascocarp.
- The globose ascocarp without opening is called cleistothecium.
- The flask-shaped ascocarp with an apical opening is called perithecium.
- The cup or saucer-shaped ascocarp is called apothecium.