Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 1st Year Botany Study Material 1st Lesson The Living World Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 1st Year Botany Study Material 1st Lesson The Living World
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What does ICBINT stand for?
Answer:
ICBN stands for International Code for Botanical Nomenclature.
Question 2.
What is flora?
- Flora is the actual account of habitat, distribution and systematic listing of plants of a given area.
- It provides the index to the plant species found in a particular area.
Question 3.
Define Metabolism. What is the difference between anabolism and catabolism?
Aswer:
- Metabolism refers to the sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in the body of a living organism.
- The constructive metabolic process in which complex molecules are formed from simpler molecules is called anabolism. The destructive metabolic process in which complex molecules are broken down into simpler molecules is called catabolism.
Question 4.
Which is the largest botanical garden in the world? Name a few well known botanical gardens in India.
Answer:
- Royal Botanical Garden (RBG) at Kew, England is the largest botanical garden in the world.
- Indian Botanical Garden, Howrah and National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow are well known botanical gardens in India.
Question 5.
Define the terms couplet and lead in taxonomic key. [Mar. – 2018, Mar. 15, A.P.]
Answer:
1) Couplet :
A pair of contrasting characters that represents the choice made between two opposite options.
2) Lead :
Each statement in the taxonomic key.
Question 6.
What is meant by manuals and monographs? [May ’17, May ’14]
Answer:
- Manuals are recorded descriptions useful in providing information for identification of names of species found in an area.
- Monographs contain information on any one taxon.
![]()
Question 7.
What is systematics?
Answer:
- Systematics is the study of different kinds of organisms, their diversities and also the relationship among them.
- Systematics includes identification, nomenclature and classification. It takes into account evolutionary relationships between organisms.
Question 8.
Why are living organisms classified?
Answer:
- Classification is the process by which anything is grouped into convenient categories based on some easily observable characters.
- It is a device to study all the living organisms with ease.
Question 9.
What is the basic unit of classification? Define it. [Mar. ’20, ’17; Mar. 14, 13]
Answer:
- Species is the basic unit of classification.
- Species can be defined as a group of individual organisms with fundamental similarities. Eg : Solanum tuberosum (Potato)
Question 10.
Give the scientific name of Mango. Identify the generic name and specific epithet.
Answer:
- The scientificname of Mango is Mangifera indica.
- Mangifera is generic name and indica is specific epithet.
Question 11.
What is growth? What is the difference between the growth in living organisms and growth in non-living objects?
Answer:
- Growth may be defined as permanent and irreversible increase in size overtime.
- The growth in living organisms is from inside and by cell divisions. Whereas in non-living objects growth is due to accumulation of material on the surface.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by identification and nomenclature? How is a key helpful in the identification and classification of an organism?
Answer:
- Determining whether a collected plant is entirely new or already known is called identification. Providing a correct scientific name to an identified plant is called nomenclature.
- Correct identification can be done by directly comparing the characters of the plant with an authentic herbarium specimen or indirectly with the help of key in floras.
- Key or taxonomic key is an artificial analytic device having a list of statements with dichotomatic table of alternate characteristics which is used in identifying organisms.
- Usually a couplet or two contrasting characters are used. The one present in the organism is chosen while the other is rejected.
- Taxonomic key is helpful in the identification and classification of an organism based on.the similarities and dissimilarities.
- Each statement in the key is called a lead.
- Separate taxonomic keys are required for each taxonomic category such as family, genus and Species for identification purpose.
![]()
Question 2.
What are taxonomical aids? Give the importance of herbaria and museums.
Answer:
Herbarium, Botanical gardens, Zoological parks and Museums are taxonomical aids.
Herbarium:
- Herbarium is a store house of collected plant specimen.
- Plants identification can be done directly comparing the characters with an authentic herbarium specimen.
- Plant specimens that are collected are dried, pressed and preserved on the sheets.
- These sheets are arranged according to the system of classification.
- These sheets provide the information about the date, place of collection, English name, local name and scientific name, family name even the collector’s name etc.
- Herbaria serves as a quick referred system in taxonomic studies.
- Royal Botanical garden at Kew, England has largest herbarium. It is an international centre for plant identification.
- Nowadays herbarium is preserved as Digital herbarium. The digital images of the herbarium specimens and the related information is preserved and published on internet for wider use.
This digital herbarium is intended to take advantage of internet and digital photography technologies to provide online facility.
Museum :
Generally in schools and colleges biological museums are present. In these museums, they preserve the plants and animals specimens collected for study and reference. Specimens are preserved in the containers or jars in preservative solutions or they may be preserved as dry specimens.
Question 3.
Define a taxon. Give some examples of taxa at different hierarchial levels.
Answer:
Any system of classification is made up of different units such as species, genus, family, order, class, division, kingdom which are arranged in a hierarchial sequence. Irrespective of its rank in the sequence every unit is called Taxon.
Hierarchy is the arrangement of organism in a definite sequence. The following is the taxonomical categories showing hierarchial arrangement in ascending order.
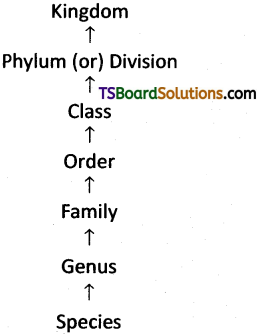
Examples of Taxa at different hierarchial levels :
| Kingdom | Plant kingdom | Plant kingdom |
| Division | Spermatophyta | Spermatophyta |
| Class | Dicotyledonae | Monocotyledonae |
| Order | Sapindales | Poales |
| Family | Anacardiaceae | Poaceae |
| Genus | Mangifera | Triticum |
| Species | Indica | Vulgare |
| Common name | Mango | Wheat |
![]()
Question 4.
How are botanical gardens useful in conserving biodiversity? Define the terms Flora, Manuals, Monographs and Catalogues.
Answer:
Plants found in botanical gardens can be regarded as live specimens. Plants are grown in these gardens for identification purposes. Each plant is labelled indicating its botanical name and its family. Botanical gardens are useful in knowing our bioresources and their diversity.
Flora :
Flora is a book containing the details of the habitat and distribution of plants of a particular area. Every district in each state has its own flora.
Manuals :
These are small books useful in providing information for identification of names of species found in an area. It specially designed for ready reference.
Monograph :
They contain information on any one taxon.
Catalogues :
Books which help in correct identification of plants.
Question 5.
Explain binomial nomenclature.
Answer:
- Every plant should have only one correct scientific name.
- Every scientific plant name has two components. They are the generic name and the specific,epithet. This system of providing a name with two components is called Binomial nomenclature.
- Scientific name should be in Latin or Latin derivative.
- Both the words’ when handwritten they must be underlined or printed in italics to indicate their Latin origin.
- The generic name will be in the noun form and always begins with capital letter. The specific name will be in the adjective form and starts with small letter. For example, Solanum tuberosum is the name of the potato plant in which “Solanum” is the genus and “tuberosum” is the species.
- The author’s name may be given in abbreviated form at the end of the scientific name.
For example :
Mangifera indica Linn. It indicates that the species was first described by Linnaeus.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by living? Give a detailed account of any four defining features of life forms.
Answer:
Organisms which are self replicating, evolving and self regulating, having interactive systems, capable of responding to external stimuli are said to be living.
The defining features of life forms are
1. Metabolism :
All living organisms are made of chemicals. These chemicals undergo various chemical reactions. The sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in the body of a living organism is called metabolism. Cellular organisation of the body required for metabolism is the defining feature of life forms.
2. Consciousness :
Response to external stimuli is called irritability. Plants repond to external factors like light, water/temperature, other organisms, pollutants etc. All organisms are aware of their surroundings. This is called consciousness. Consciousness is the defining property of living organisms/Human being is the only one who is aware of himself that means has self consciousness.
3. Interactions :
Properties of tissues are not present in the constituent cells but arise as a result of interactions among the constituent cells. Similarly properties of cellular organelles are not present in the molecular constituents of the organelle but arise as a result of interactions among the molecular components comprising the organelle. Such underlying molecular interactions are also apparent in macromolecules such as starch. These interactions result in emergent properties at a higher level of organisation.
4. Genetic material :
All living organisms present, past and future are linked to one another by the sharing of common genetic material.
![]()
Question 2.
Define the following terms with examples, (i) Class (ii) Family (iii) Order (iv) Genus (v) Division.
Answer:
i) Class :
Class includes related orders. For example, in plant kingdom orders like Malvales, Rosales, Polemoniales etc., are included in the class : Dicotyledonae.
ii) Family :
Family is a group in which different genera of common characters are put together. Families are characterised on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. For example, three different genera Solanuim, Nicotiana, and Datura are placed in the family Solonaceae.
iii) Order :
Different families with similar characters are put into an order. The similar characters are less in number as compared to different genera included in a family. Plant families like Convolvulaceae, Solanaceae are included in the order Polemoniales mainly based on floral characters.
iv) Genus :
Genus is a group of different species with related characters. For example, potato and brinjal are two different species but belong to the genus-Solanum.
v) Division :
Different classes with similarities are grouped into division. Classes like Dicotyledonae and Monocotyledonae with a few similar characters are assigned to a higher category called division : Spermatophyta.
In the case of animals related classes are included in a phylum.
InText Question Answers
Question 1.
Some of the properties of tissues are not constituents of their cells. Give two examples to support the statement.
Answer:
- Vascular tissues like xylem and phloem help in conduction of water, mineral salts and organic substances from one place to other.
- Sclerenchyma tissue gives mechanical support to the plant body.
Question 2.
What do we learn from identification of individuals and populations?
Answer:
- From the identification of individuals and population we learn their correct scientific names and the description of the organisms.
- Identification is useful in agriculture, forestry to know our bioresources and their diversity.
- Identification helps to determine whether a collected organism is entirely new or already known.
![]()
Question 3.
Given below is the scientific name of Mango. Identify the correctly written name, (i) Mangifera Indica (ii) Mangifera indica.
Answer:
Mangifera indica.
Question 4.
Can you identify the correct sequence of taxonomical categories ?
a) Species, Order, Division, Kingdom.
b) Genus, Species, Order, Kingdom.
c) Species, Genus, Order, Phylum.
Answer:
a) Species, Order, Division, Kingdom.
Question 5.
Define the following terms.
(i) Species (ii) Class (iii) Family (iv) Order (v) Genus.
Answer:
Species :
Species is the basic unit of classification. All those plants which are identical in all respects are regarded as species.
Class :
Class includes related orders. For example, in plant kingdom orders like Malvales, Rosales, Polemoniales etc., are included in the class : Dicotyledonae.
Family :
Family is a group in which different genera of comfhon characters are put together. Families are characterised on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. For example, three different genera Solanum, Nicotiana, and Datura are placed in the family Solonaceae.
Order :
Different families with similar characters are put into an order. The similar characters are less in number as compared to different genera included in a family. Plant families like Convolvulaceae, Solanaceae are included in the order Polemoniales mainly based on floral characters.
Genus :
Genus is a group of different species with related characters. For example: Potato and brinjal are two different species but belong to the Genus : Solanum.
Question 6.
Illustrate the taxonomical hierarchy with suitable examples of a plant.
Answer:
Flierarchy of categories is the arrangement of organisms in a definite sequence of categories. Descending order starts from kingdom to species. Ascending order starts from species to kingdom. This hierarchial system of classification was introduced by Linnaeus. The hierarchy includes seven categories – kingdom, division, or phylum, class, order, family, genus and species.
Question 7.
What are the distinctive characteristics exhibited by living organisms? Describe them in brief.
Answer:
The distinctive characters exhibited by living organisms are Growth, reproduction, irritability, metabolism, ability to self replicate, self organise, interaction and emergence.
Growth :
Living organisms grow by cell division. In animals growth is seen up to a certain age. However, cell division occurs in certain tissue to replace lost cells. In plants growth is present throughout the life.
Reproduction :
Production of progeny is referred on reproduction. Progeny are more or less similar to parents. Reproduction may be vegetative, asexual and sexual methods.
Irritability :
Response to stimuli is called irritability. Plants respond to external factors like light, water temperature etc. All organisms are aware of their surroundings and this is called consciousness.
Metabolism :
The sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in the body of the living organism is called Metabolism.
Interaction and emergence :
Properties of cellular organelles are not present in the molecular constituents but as a result of interactions they emerge properties at next higher level of organisation.
Question 8.
Life forms exhibit ‘unity in diversity’ :
Discuss with your teacher.
![]()
Question 9.
List out the principles followed to provide scientific names for newly found organism.
Answer:
- Every plant should have only one correct scientific name.
- Every scientific plant name has two components. They are the generic name and the specific epithet. This system of providing a name with two components is called Binomial nomenclature.
- Scientific name should be in Latin or Latin derivative.
- Both the words, when hand written they must be underlined or printed in italics to indicate their Latin origin.
- The generic name will be in the noun form and always begins with capital letter. The specific name will be in the adjective form and starts with small letter. For example, Solanum tuberosum is the name of the potato plant in which “Solanum” is the genus and “tuberosum” is the species.
- The author’s name may be given in abbreviated form at the end of the scientific name.
For example :
Mangifera indica Linn. It indicates that the species was first described by Linnaeus.