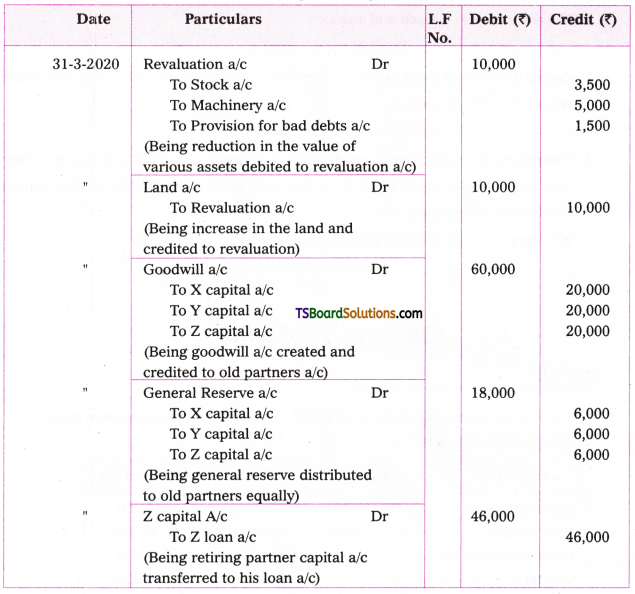
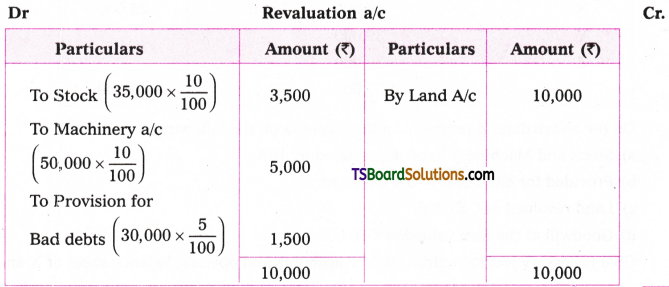
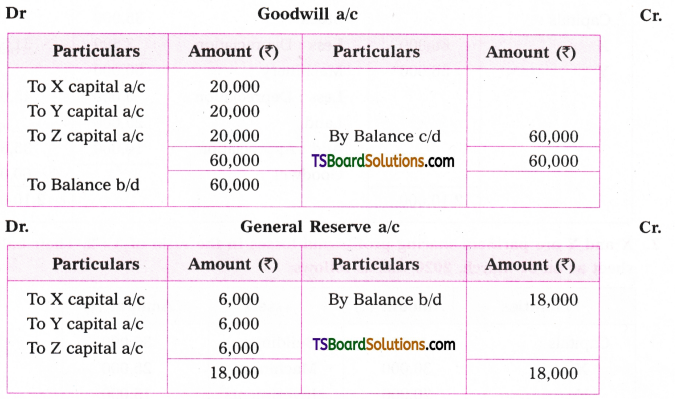
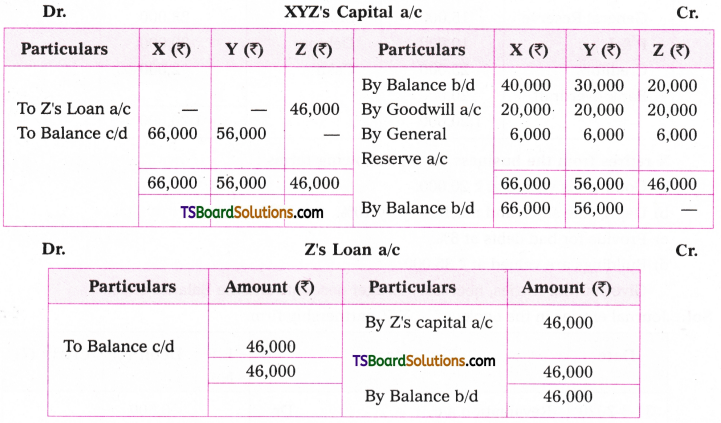
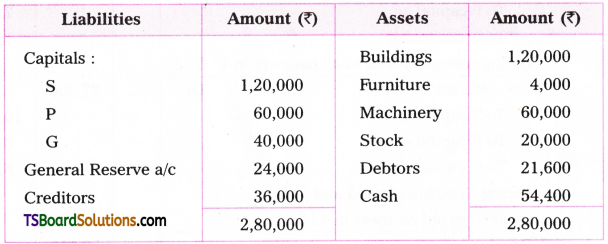
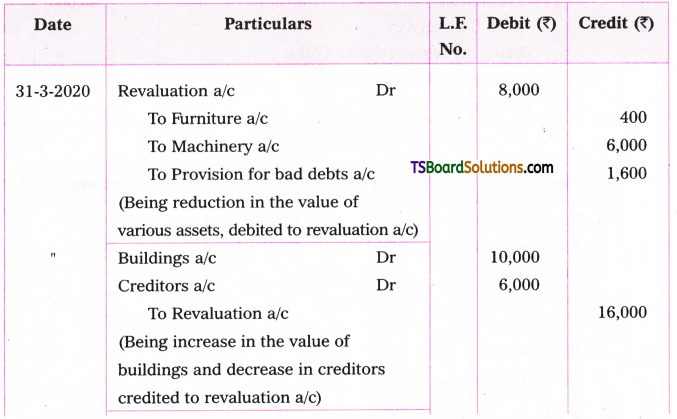
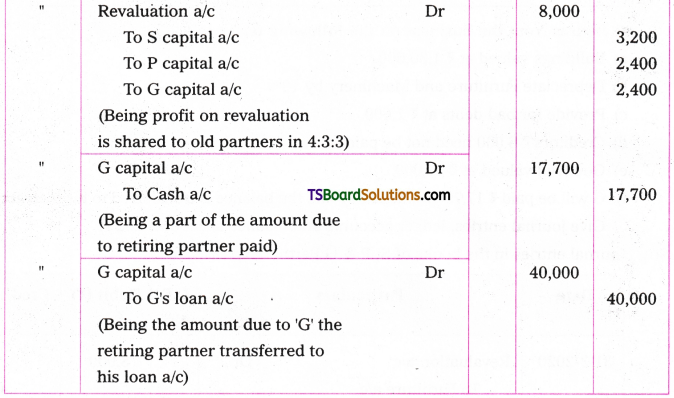
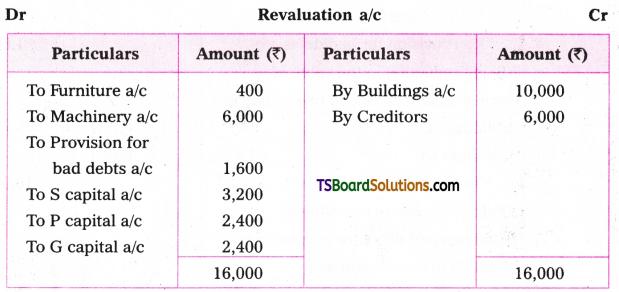
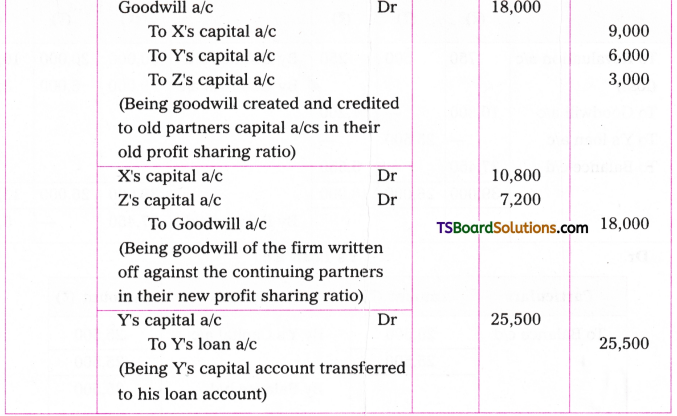
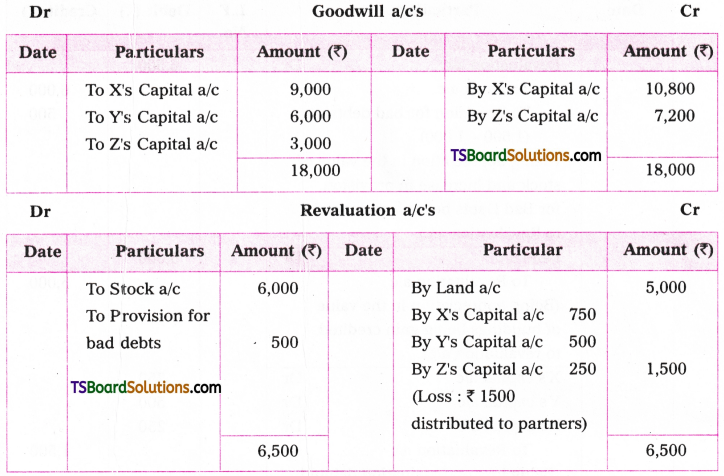
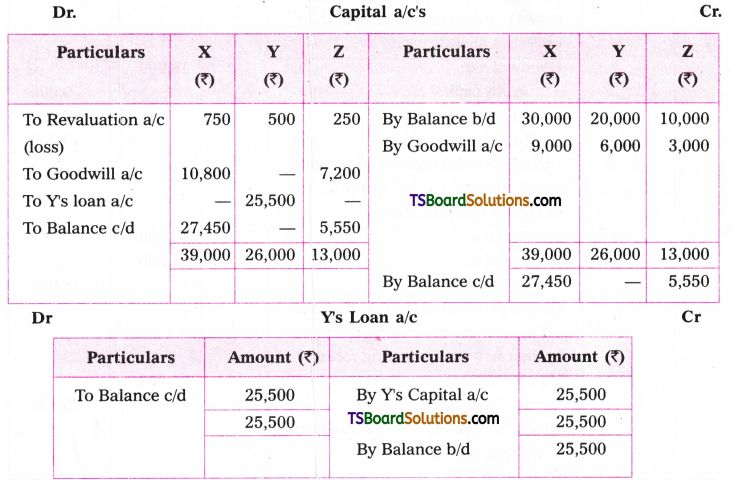
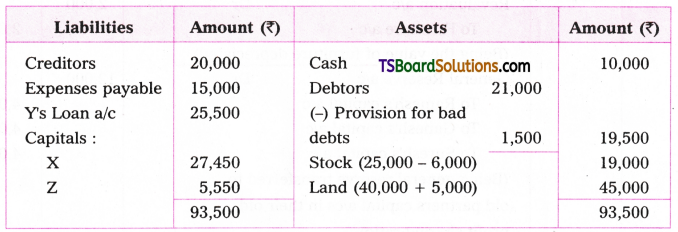
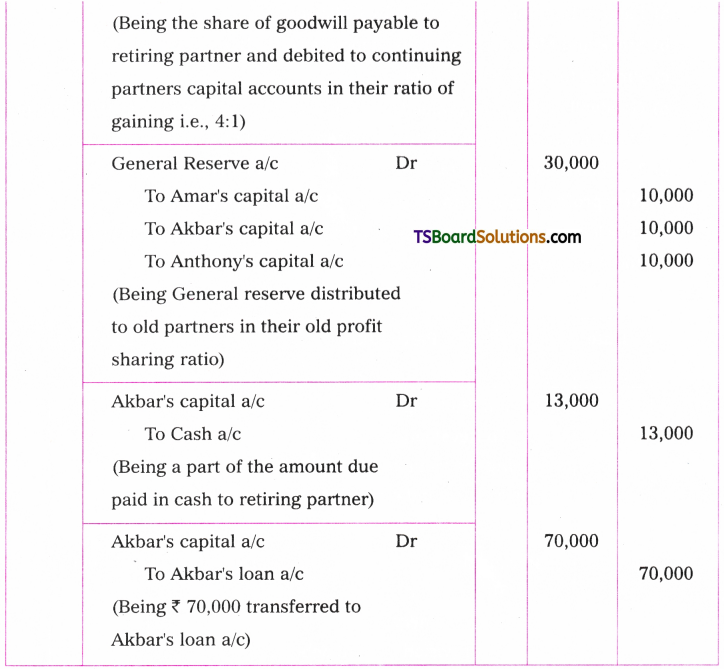
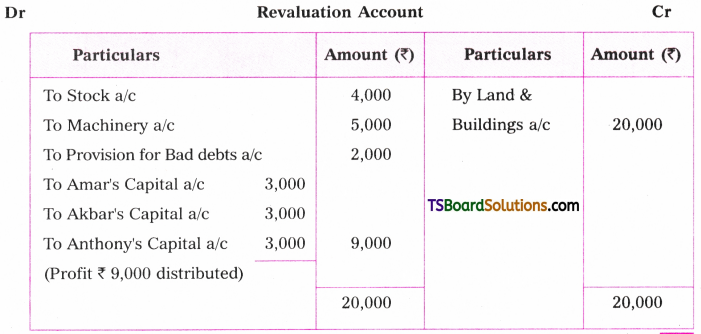
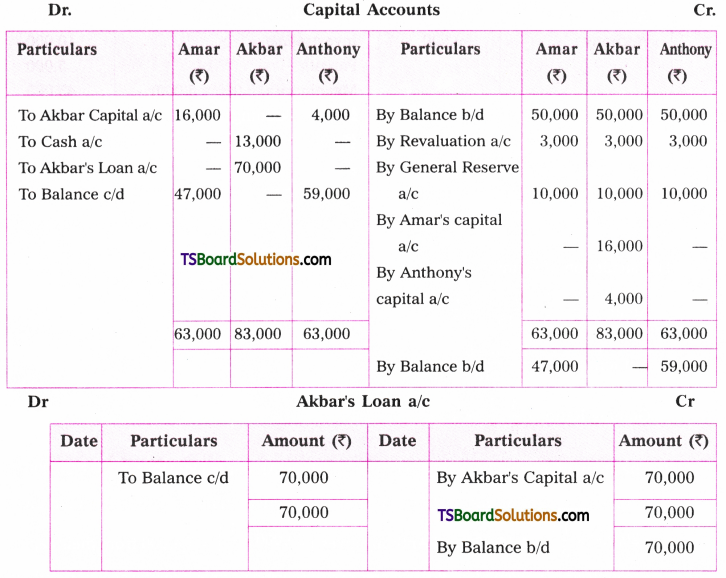
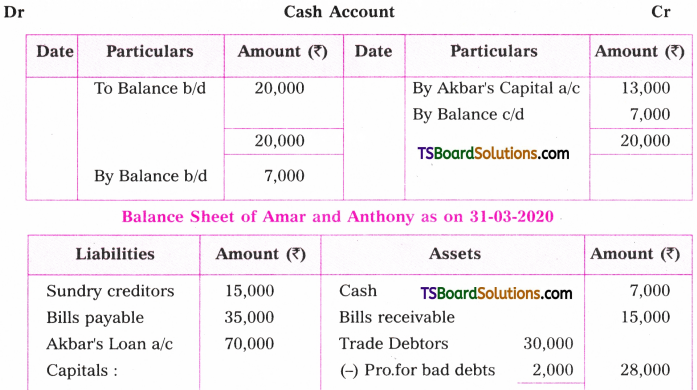
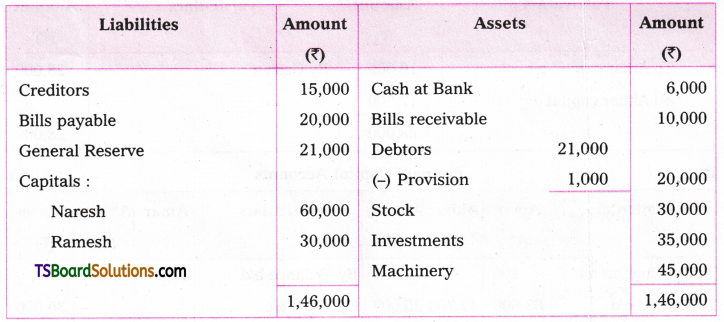
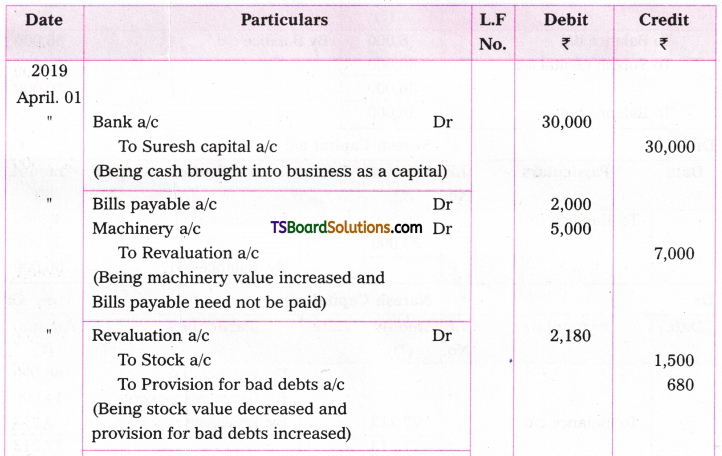
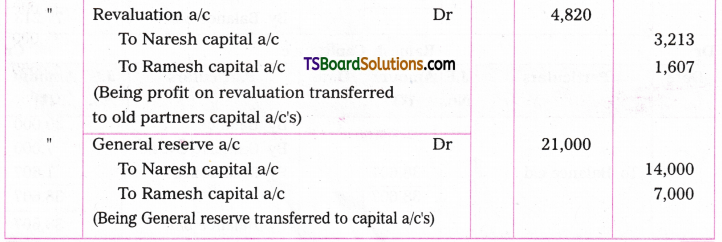
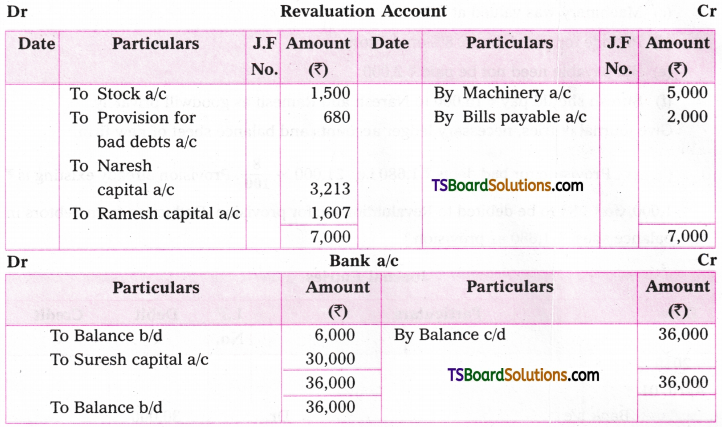
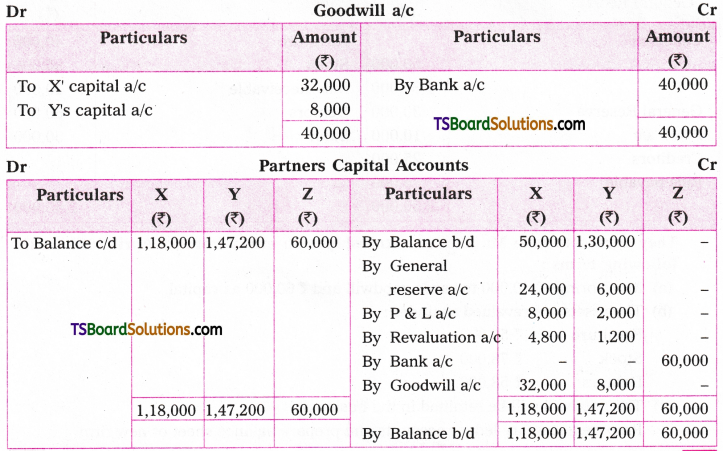
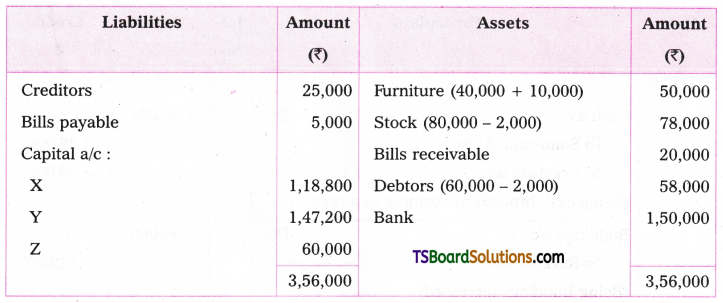
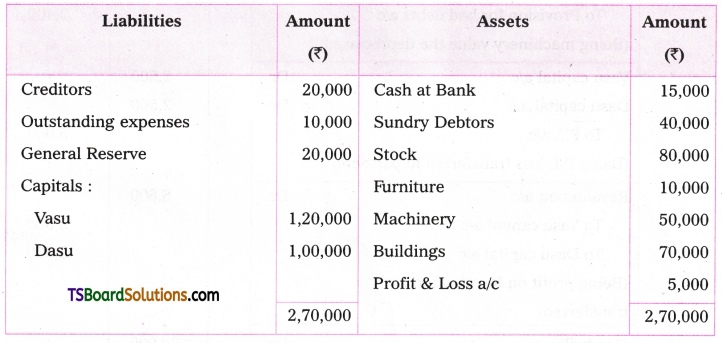
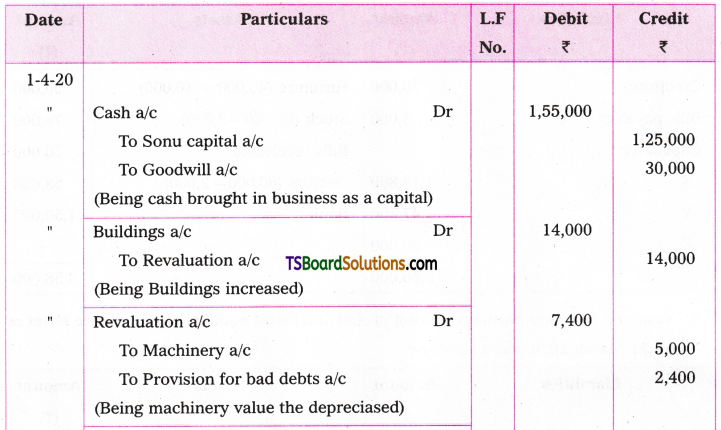
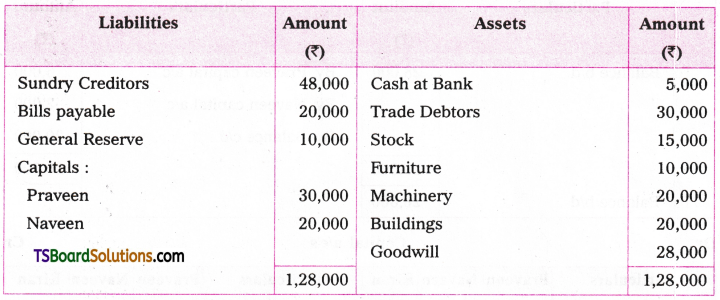
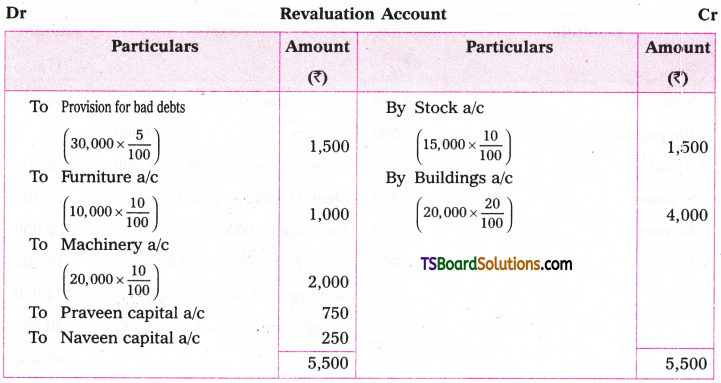
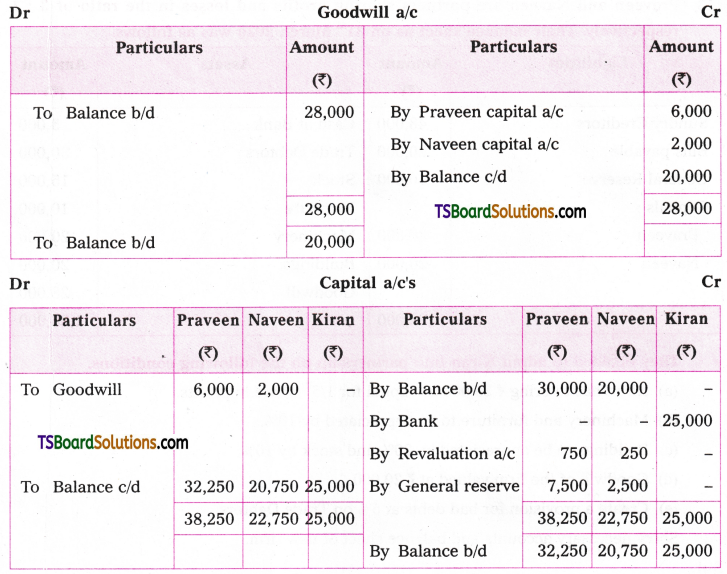
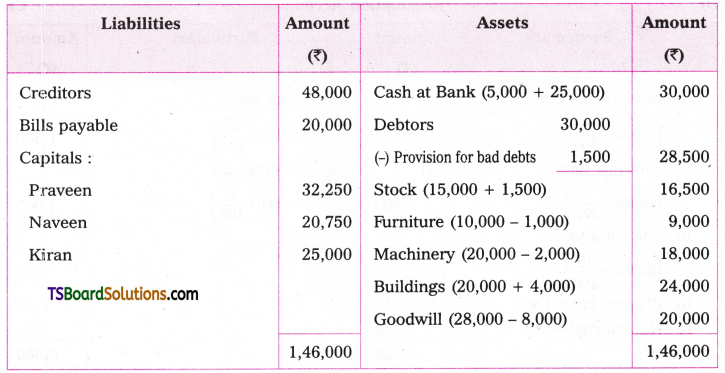
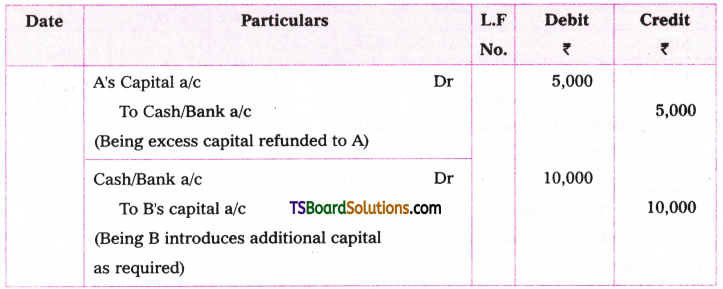
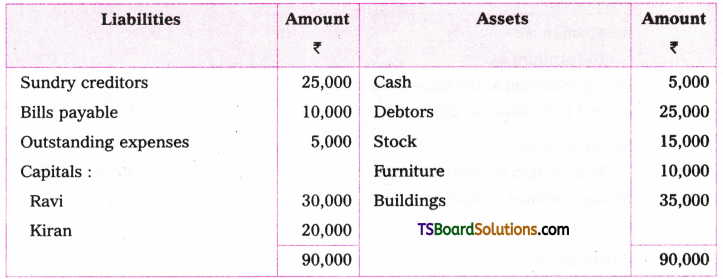
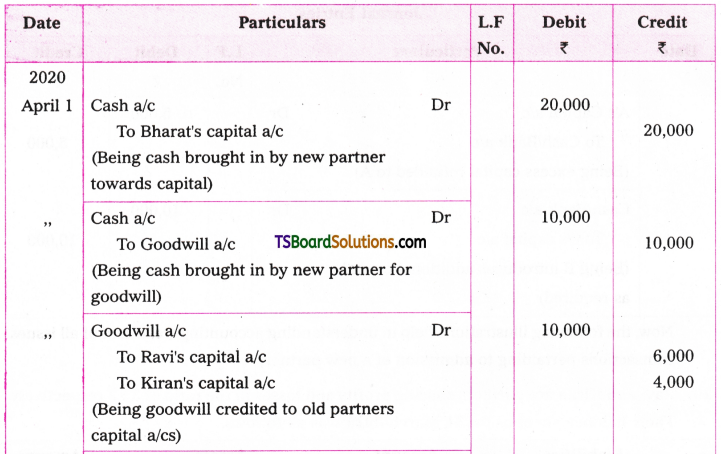
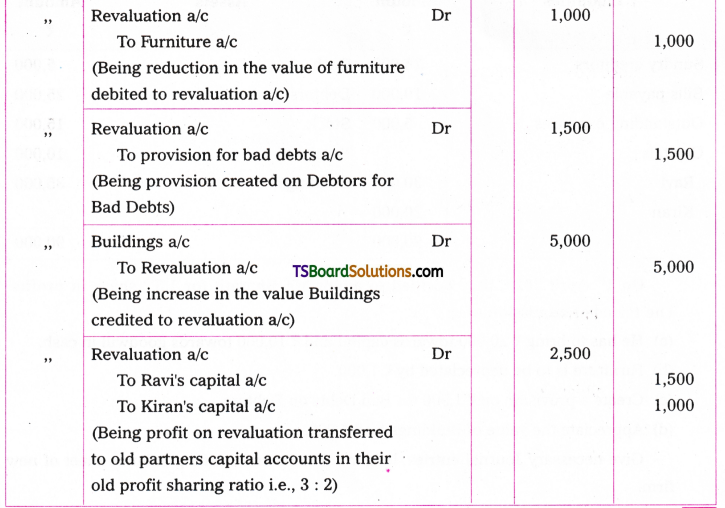
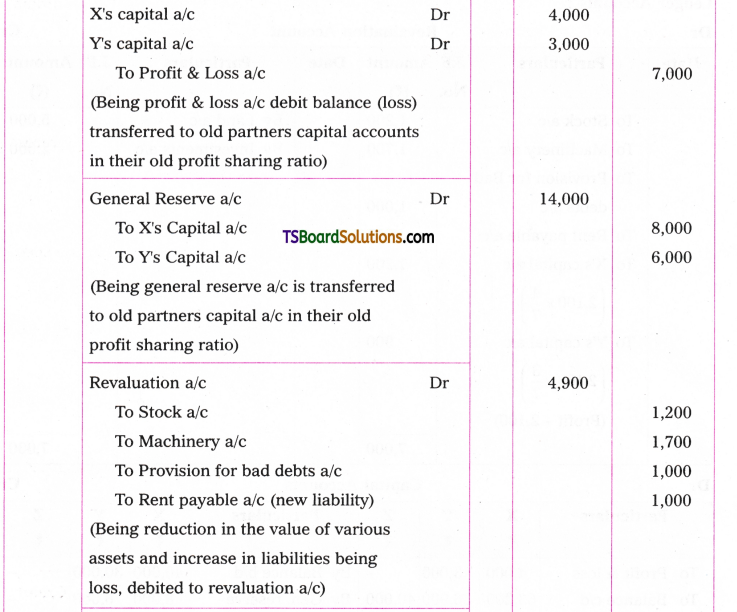
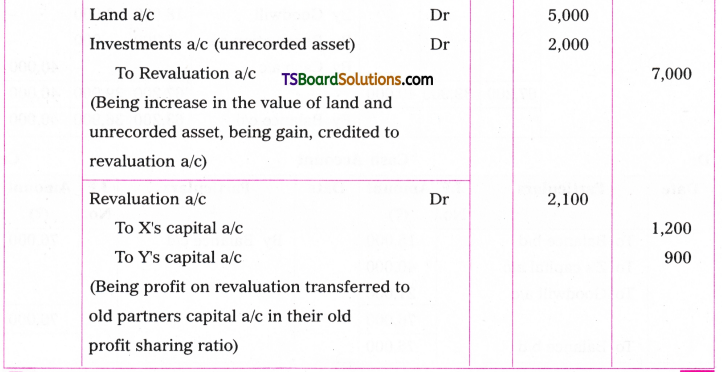
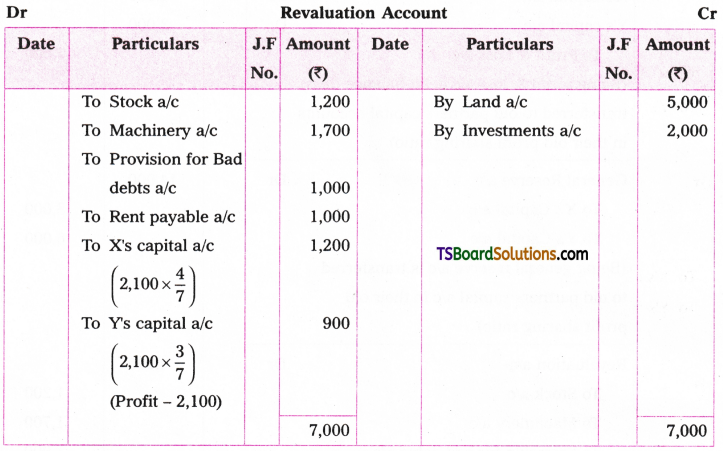
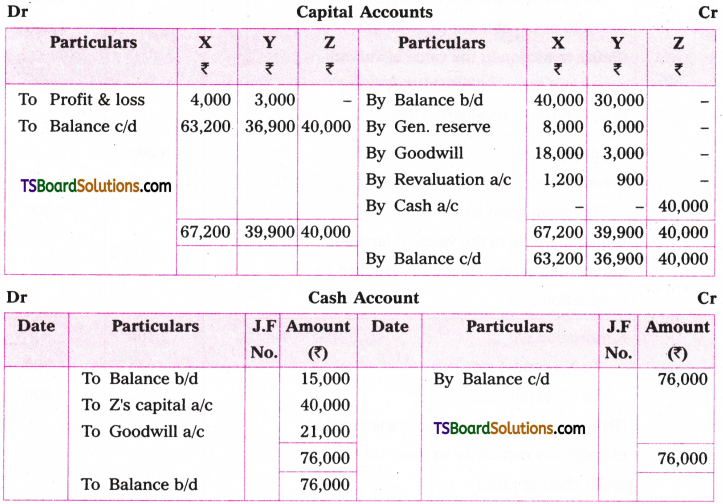
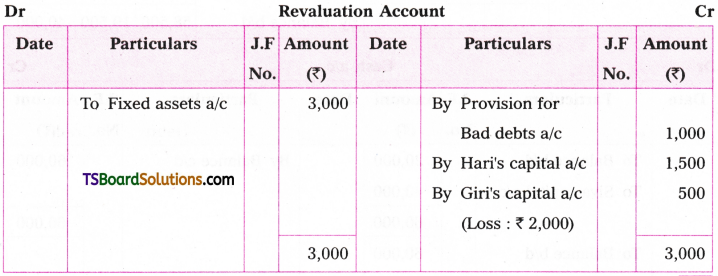
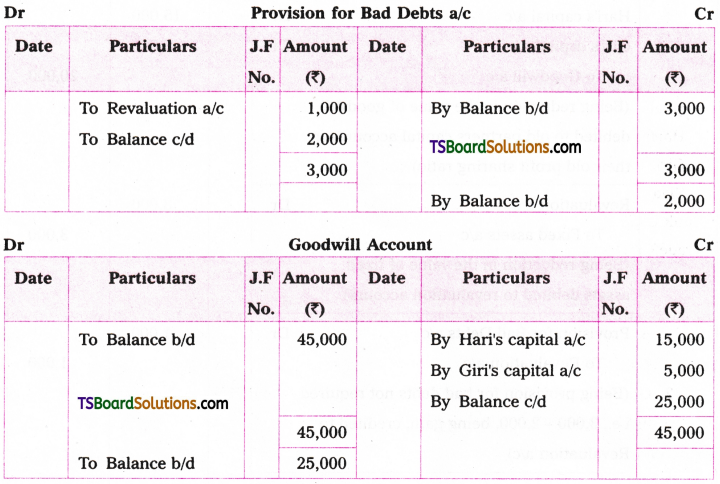
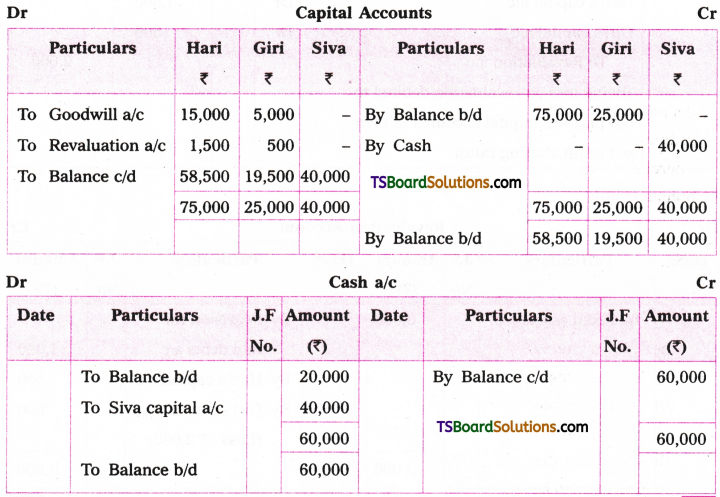
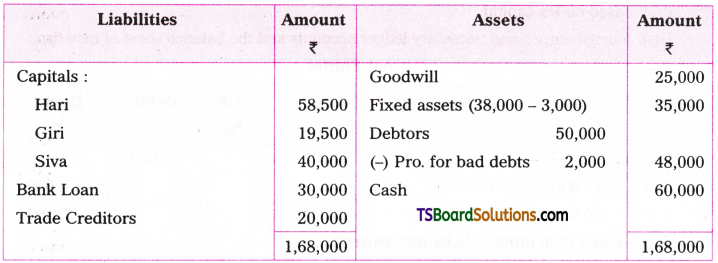
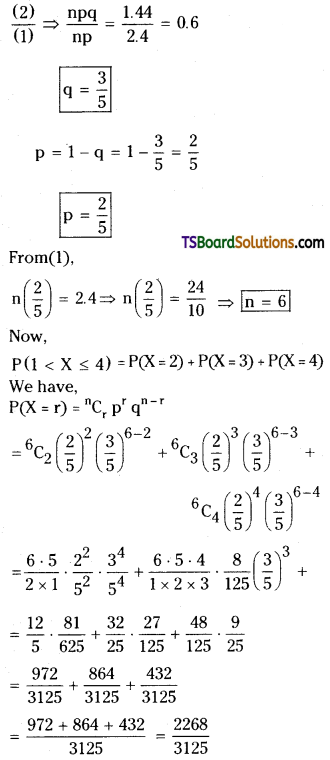Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 1st Year English Study Material Grammar Transformation of Sentences Exercise Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 1st Year English Grammar Transformation of Sentences
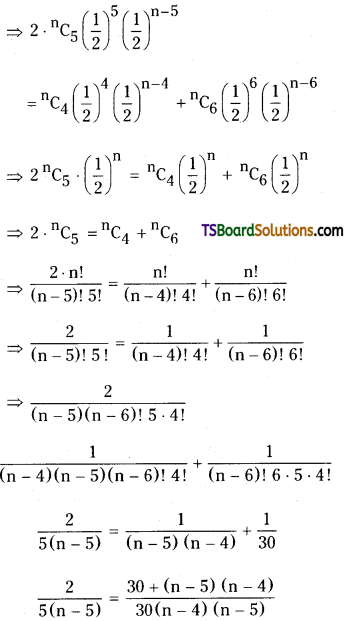
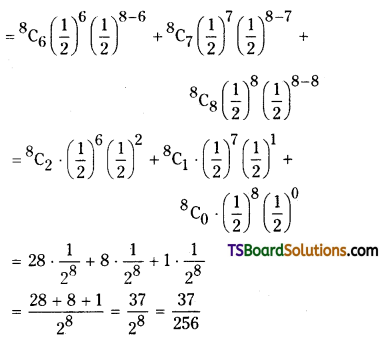
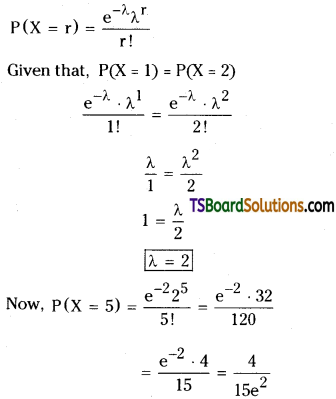
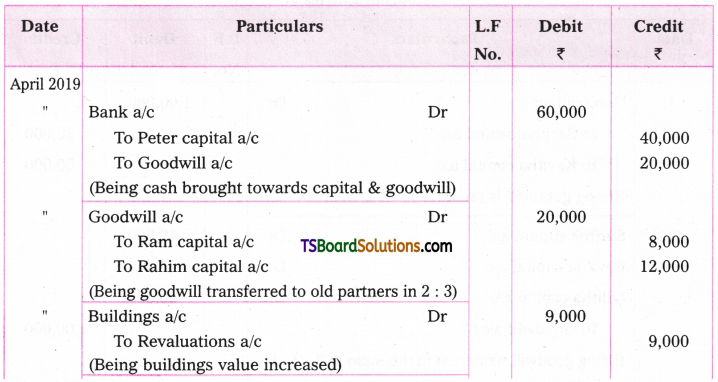
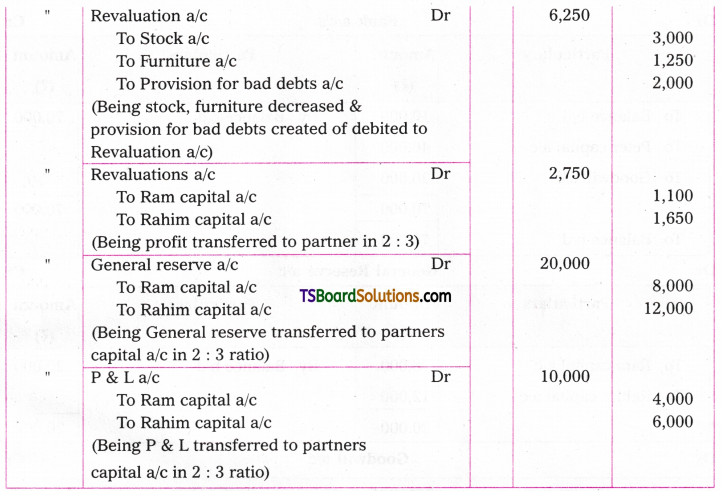
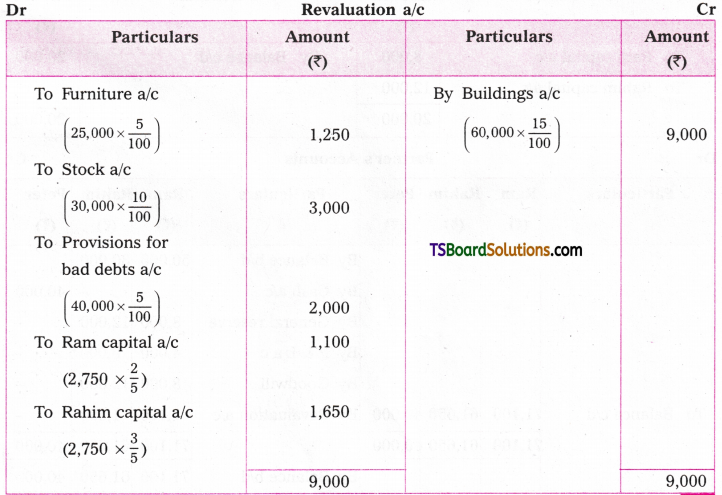
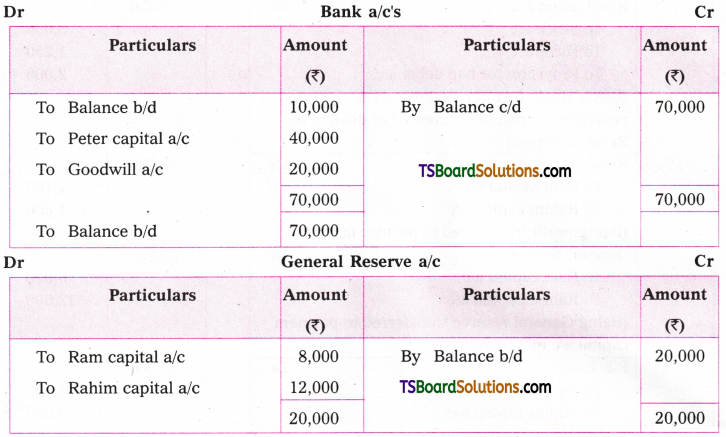
Q. No. 13 (4 × 1 = 4)
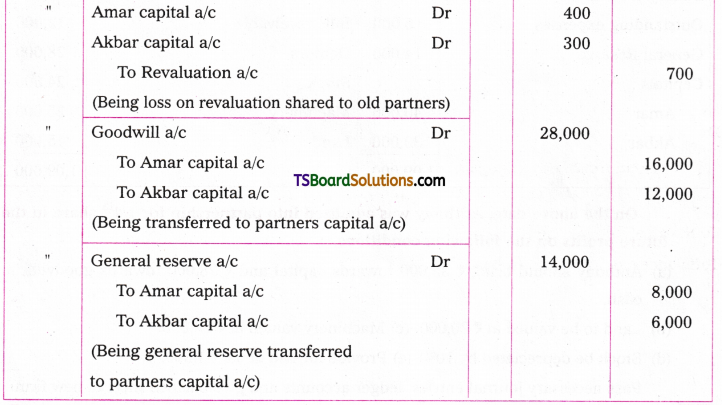
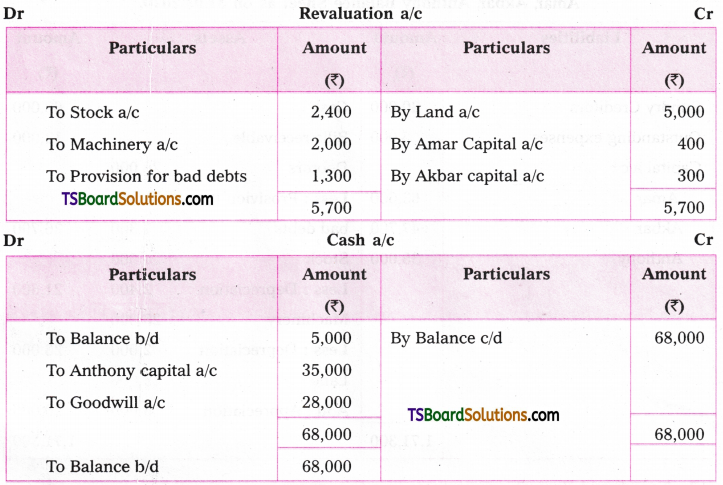
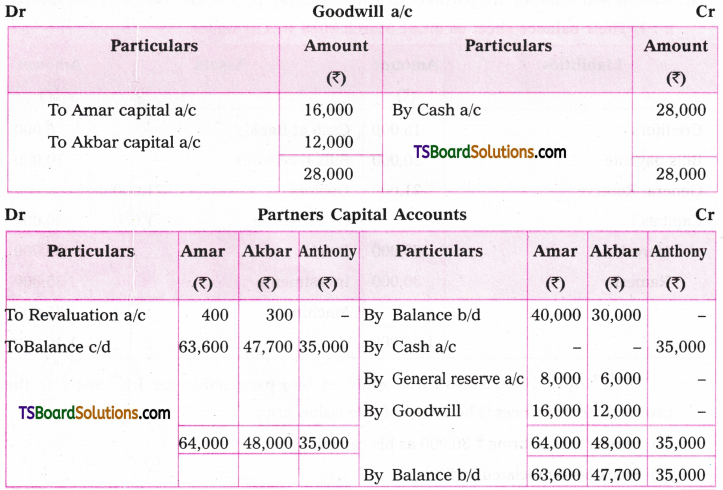
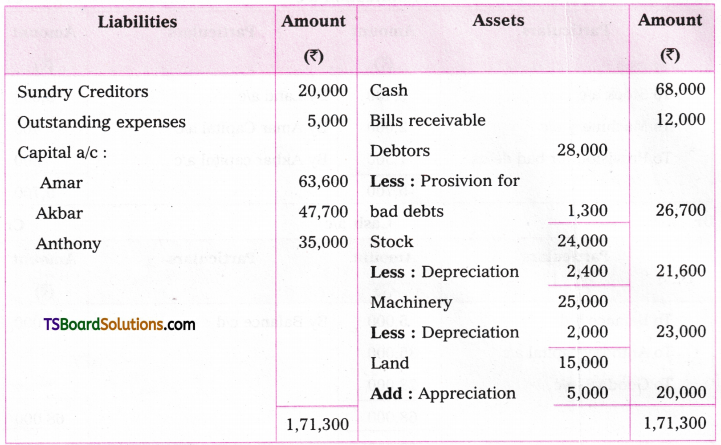
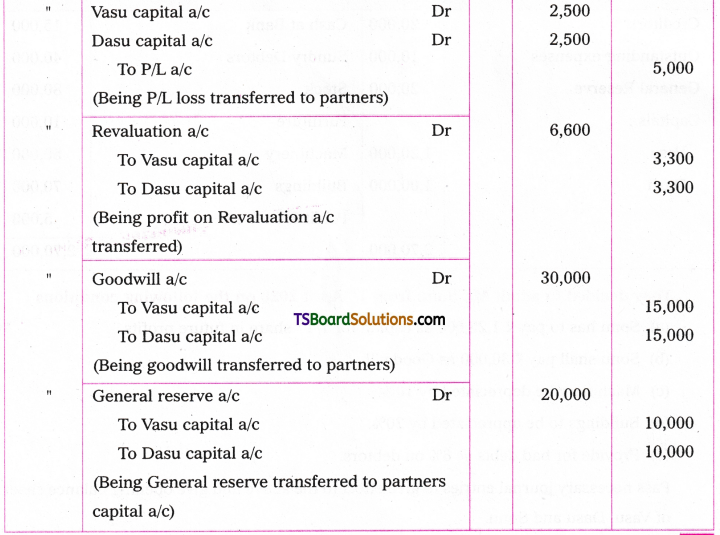
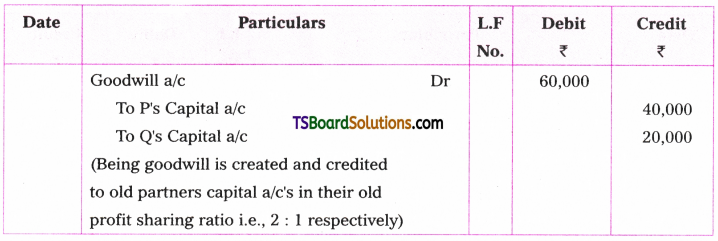
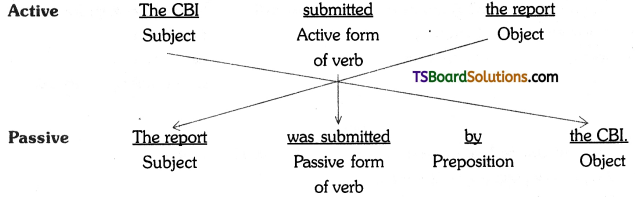
A. VOICE
The term ‘voice’ in grammar refers to one aspect of the verb. If the verb group in a sentence has ‘be + pp of the verb’, that sentence is said to be in the passive voice. If any of or both the elements (be + V3) are missing in the structure of the verb, the sentence is said to be in the active voice. (వాక్యంలోని verb groupలో ‘be + V3 ఉంటే ఆ వాక్యాన్ని passive voice అని, be + V3 లలో ఏ ఒక్కటి లేకున్నా active voice అని అంటారు.)
If the verb is in the passive form, the subject of that sentence is just the ‘sufferer’ of the action indicated by the verb, (verb passive లో ఉంటే ఆ వాక్యంలోని subject, verb సూచించిన పని ఫలితాన్ని అనుభవిస్తుంది. అందుకనే ఈ రూపానికి ‘passive’ ‘సోమరిగా’, ‘పనిచేయకుండా’ అని పేరు.)
If the verb group is in the active voice, the subject of that sentence is the ‘doer’ of the action shown by the verb. (Verb Active voice లో ఉన్నప్పుడు, ఆ వాక్యం యొక్క subject, verb సూచించిన పనిని చేస్తుంది. అందుకే ఈ రూపానికి ‘Active చురుకుగా పనిచేస్తున్న’ అని పేరు)
If the doer of an action is either unimportant or unknown, the passive structure is natural. (పనిచేసినవారు ప్రధానం కాకున్నా, తెలియకున్నా, passive నిర్మాణాలు సహజంగా ఉంటాయి. )
Someone admitted him to the hospital immediately. (AV)
He was admitted to the hospital immediately. (PV)
He was killed in the war.
Rice is grown in many parts of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
English is spoken all over the world.
The roads have been swept The syllabus was changed last year.
The shop has been closed.
The doubts have been cleared by my teacher Agent
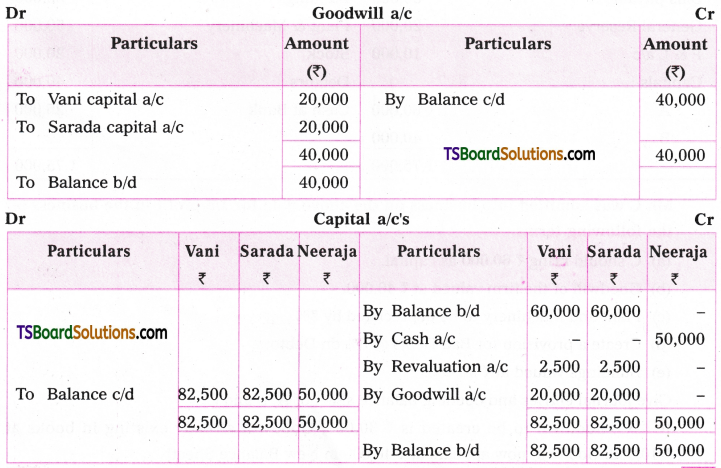
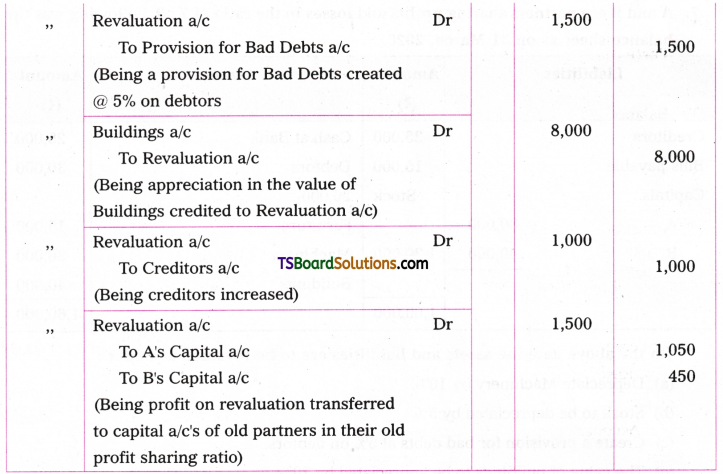
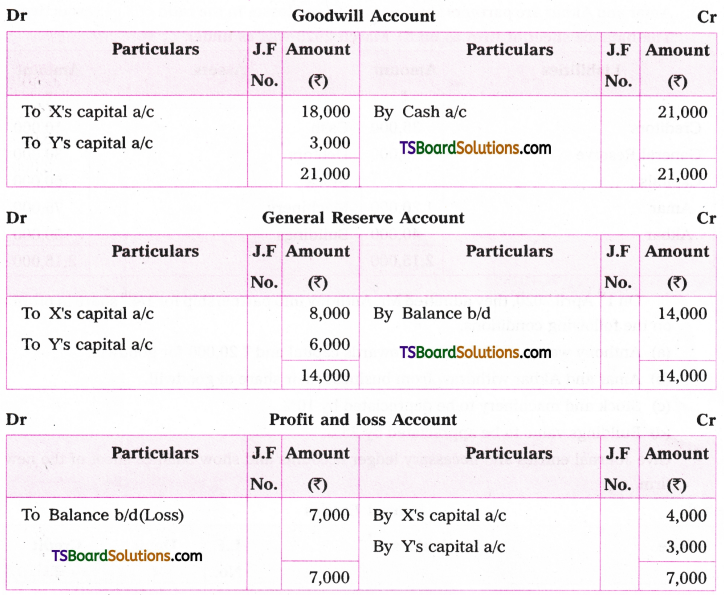
![]()
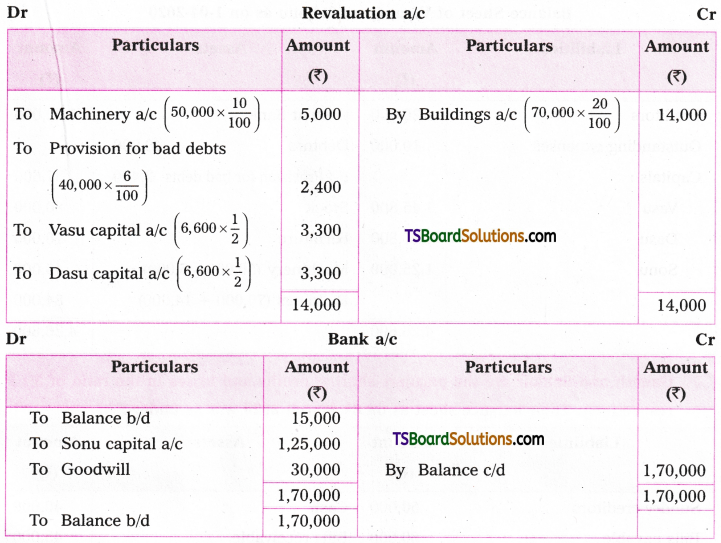
Transformation of sentences from one voice to the other involves five steps.
1. The object in the Active Voice sentence becomes the subject in the Passive Voice sentence.
Ex : They made (ten kites)Object (A.V)
(Ten kites) Subject were made by them. (P.V.)
If there are two objects in the A.V. sentence, either of them can be made the subject in the PV. sentence.

An interesting book was given to her brother by her.
Active :
- I told them an interesting story.
- I told an interesting story to them.
Passive:
- An interesting story was told to them.
- They were told an interesting story.
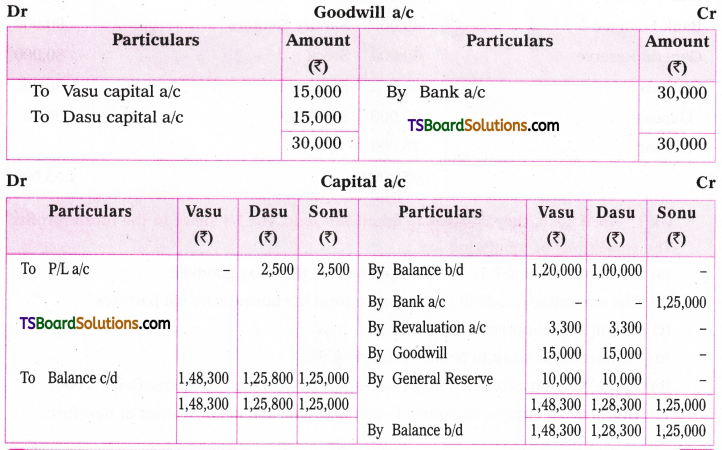
2. A suitable ‘be’ form is to be introduced. This is the most important step. Selection of the right be’ form is based on two factors : (a) the number and person of the subject in the passive voice and (b) the tense of the verb in the Active Voice.
The following table helps one select the right be form.
| S. No. | Subject in the Passive Voice | Tense of the verb in Active Voice | ‘Be form to be used in the Passive Voice |
| 1 | I | Simple Present | am |
| 2 | he, she, it singlar nouns | Simple Present | is |
| 3 | We, you, they plural nouns | Simple Present | are |
| 4 | I, he, she, it singular nouns | Simple Past | was |
| 5 | We, you, they plural nouns | Simple Past | were |
| 6 | I | Present Continuous | am being |
| 7 | he, she, it singular nouns | Present Continuous | is being |
| 8 | We, you, they plural subjects | Present Continuous | are being |
| 9 | 1, he, she, it singular nouns | Past Continuous | was being |
| 10 | We, you, they plural subjects | Past Continuous | were being |
| 11 ‘ | he, she, it Singular nouns | Present Perfect | has been |
| 12 | I, we, you, they plural nouns | Present Perfect | have been |
| 13 | Any subject | Past Perfect | had been |
| 14 | Any subject | will/shall/can/ may/would should/could/ might/ must, etc. | will, etc. +be |
| 15 | Any subject | will etc + have | will, etc. + have been |

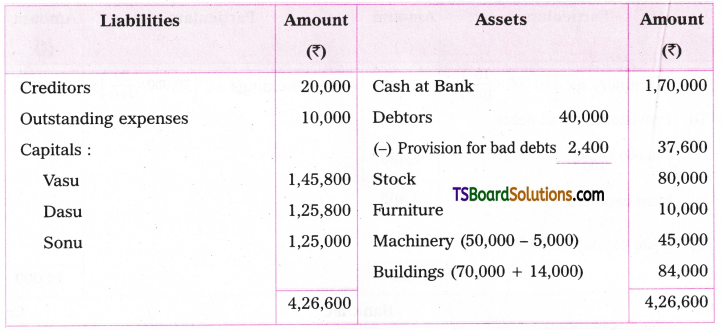
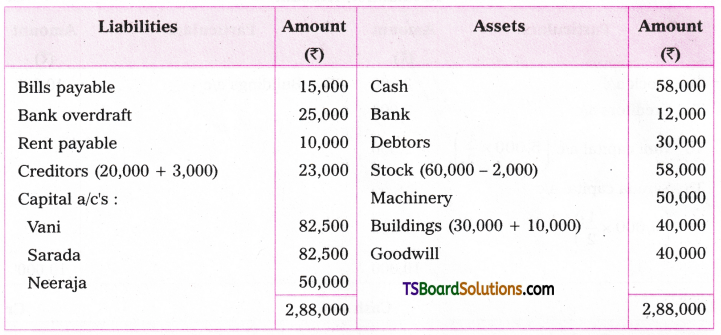
3. The main verb in the Active Voice sentence is to be changed into its past participle form. One must know the correct past participle forms of irregular verbs.

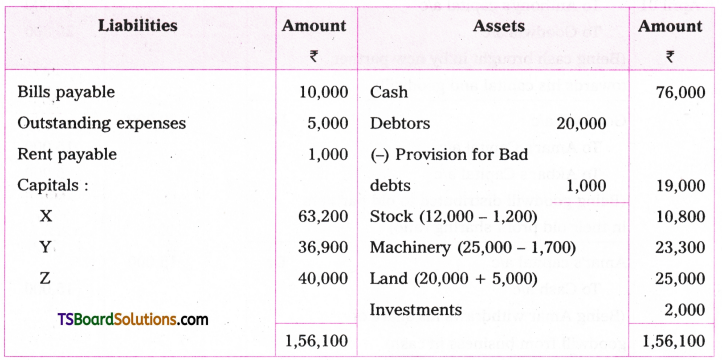
![]()
4. The preposition ‘by’ is used.
5. The subject in the Active voice sentence is made the object of the preposition ‘by’ in the passive voice sentence.
Ex : He broke the glass. (A.V.)
The glass was broken by him. (P.V.)
prep+object
If the subject in the A.V. sentence is either unimportant or a general one, ‘by + object’ may be dropped.
Ex : Someone removed the dead snake. (A.V.)
The dead snake was removed. (P-V.)
(by someone’ is dropped)
People call him ‘Babuji’. (A.V.)
He is called ‘Babuji’. (‘by people’ not necessary) (P.V.)
CHANGE IMPERATIVE SENTENCES INTO PASSIVE
We follow a slightly different method to change imperative sentences from the A.V. to the P.V. (Sentences with dropped subject and with V + object structure, conveying a request or an order are called imperative sentences.)
1. The passive voice sentence begins with ‘Let’.
Ex : Close the door. (A.V.) imperative
Let the door be closed. (P.V.)
2. The object in the A.V. sentence becomes the subject in the RV. sentence.
Answer this question. (A.V.)
Object
Let this question be answered. (P.V.)
Subject
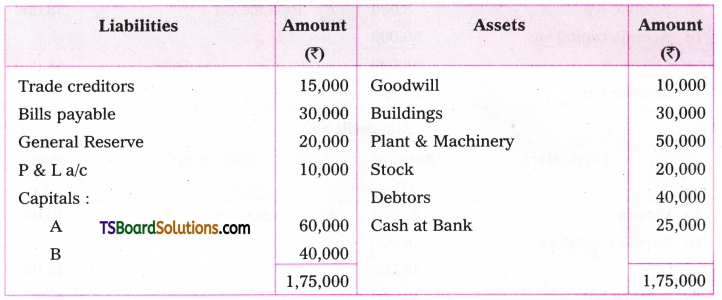
3. The ‘be’ form ‘be’ is introduced.
(Whatever be the subject or the tense form, it is always ‘be’ in imperative sentences.)
Ex : Clean the room. (A.V.)
Let the room be cleaned. (P.V.)
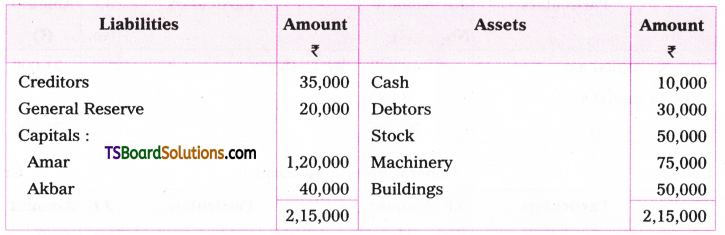
![]()
4. The M.V. is changed into its Past Participle form.
Ex : Paint this chair. (A.V.)
M.V.
Let this chair be painted. (P.V.)
As the subject is not explicit in the imperative sentences, the need to use ‘by’ and its object doesn’t arise, while changing imperative sentences into the passive voice.
CHANGING QUESTIONS INTO PASSIVE
Study carefully the transformation of the interrogative sentences into the passive voice.
Ex : Who brought this book ? (A.V.)
By whom was this book brought ? (P.V.)
All the steps followed here are exactly like those we follow in changing the declarative sentences. But the word order is different.
By whom + be + Subject + M.V in PP + etc ?
Nbw, notice the transformation of Questions with other ‘wh’ words.
Ex : Where did you put my pen ? (A.V.)
Where was my pen put ? (P.V.)
‘Wh’ word + be + subject + MV in PP ?
Observe how ‘yes / no’ Questions are rewritten in the passive voice.
Have you solved the problem ? (A.V.)
Has the problem been solved ? (P.V.)
Helping Verb + Subject + be + MV in pp + etc. ?
EXAMPLES
1. Advertise the post. (A.V.)
Let the post be advertised. (P.V.)
2. America imports Indian tea. (A.V.)
Indian tea is imported by America. (P.V.)
3. The auditors are checking the accounts. (A.V.)
The accounts are being checked by the auditors. (P.V.)
4. They have sent the information. (A.V.)
The information has been sent. (P.V.)
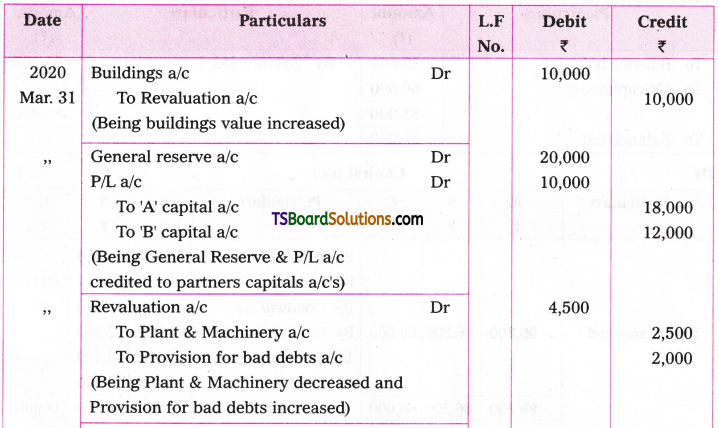
5. Hurry can gain nothing. (A.V.)
Nothing can be gained by hurry. (P.V.)
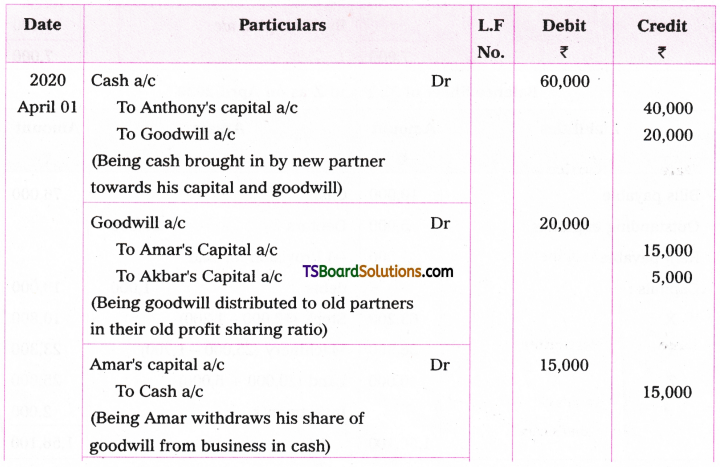
![]()
6. Put the culprit in prison. (A.V)
Let the culprit be put in prison. (P.V.)
7. John teaches us English. (A.V.)
We are taught English by John. (P.V.)
English is taught to us by John. (P.V.)
8. The Manager sent a mail yesterday. (A.V)
A mail was sent by the manager yesterday. (P.V)
9. The conductor has issued tickets to all the passengers. (A.V.)
Tickets have been issued to all the passengers. (P.V.)
All the passengers have been issued tickets. (P.V.)
10. Narayana Murthy started Infosys. (A.V.)
Infosys was started by Narayana Murthy. (P.V.)
Look at the following sentence and observe the changes.
| Tense | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
| Simple present | Floods cause a lot of damage. | am/are/is+v3(past participle) A lot of damage is caused by floods |
| Present continuous | The gardener is watering the plants. | am/are/is+being+v3 The plants are being watered by the gardner. |
| Present perfect | We have organized a special programme for children. | have/has+been+v3 A special programme has been organized for children (by us). |
| Simple past | Raghavendar Rao directed the film ‘Annamayya’. | was/were + v3 The film Annamayya’ was directed by Raghavendar Rao. |
| Past continuous | When they were shifting the patient to the ICU, he died. | Was / were + being v3 When the patient was being shifted to the ICU, he died. |
| Past perfect | The driver had already alerted the passengers before the robbers entered the bus. | had + been + v3 The passengers had already been alerted before the robbers entered the bus. |
| Simple future | I will conduct a spelling – contest tomorrow. | shall/will + be + v3 A spelling – contest will be conducted tomorrow. |
| Future perfect | They will have decorated the hall by evening. | shall / will + have + been + v3 The hall will have been decorated by evening. |
| The future of intention (be going to) | Keeravani is going to compose music this song. | is going to be + v3 Music is going to be composed by Keeravani for this song. |
| Modal veibs (should, must, ought to, can, etc.) | I will type this letter tomorrow. | should/would/must/tought/can + be + v3 ThisletowiBbetypedbyrnetorrKxrcw. |
| It is said (that) or subject+is said to be | Villagers say that there is a ghost in the old building. | It is said that there is a ghost in the old building. |
| Imperative | Check the spelling. | Let…. be + v3 Let the spelling be checked. |
EXERCISES
I. Change the following sentences into the passive voice.
1. We practise yoga every day in the morning.
2. He will make all the arrangements.
3. The judge declared the verdict.
4. They had already announced the results before we entered the hall.
5. Many students sacrificed their precious lives for Telangana.
6. The students borrowed some books from the library.
7. Nobody can save him.
8. How much loan amount has the Bank sanctioned ?
9. One should wear a helmet while riding a two-wheeler.
10. Money alone cannot solve all problems.
11. Switch off the lights.
12. Please maintain silence in the prayer hall.
13. We have to undergo many formalities for getting a visa.
14. The workers called off the strike.
15. The teacher is explaining the lesson.
16. The postman will deliver the letters at noon.
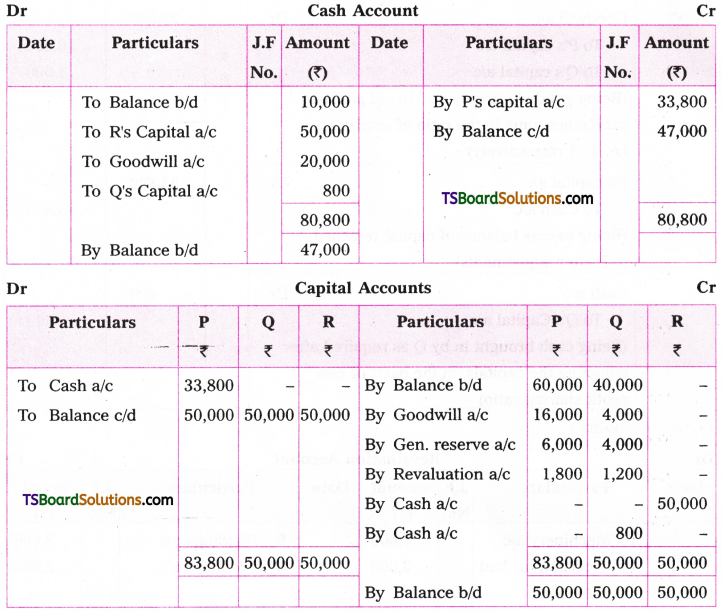
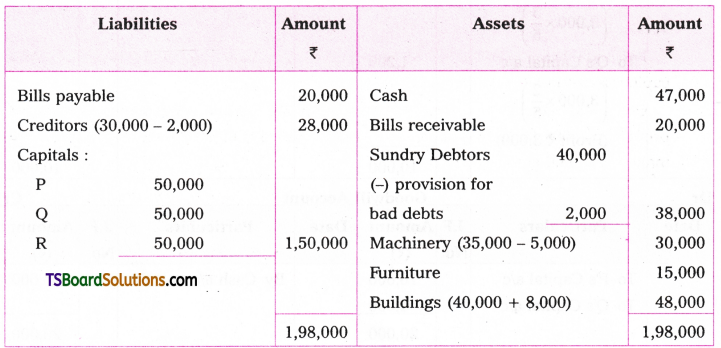
Answers:
1. Yoga is practised by us every day in the morning.
2. All the arrangements will be made by him.
3. The verdict was declared by the judge.
4. The results had already been announced before we entered the hall.
5. Their precious lives were sacrificed by many students for Telangana.
6. Some books were borrowed by the students from the library.
7. He cannot be saved.
8. How much loan amount has been sanctioned by the Bank ?
9. Helmet should be worn while riding a two-wheeler.
10. All problems cannot be solved by money.
11. Let the lights be switched off.
12. Let silence be maintained in the prayer hall.
13. Many formalities have to be undergone for getting a visa.
14. The strike was called off by the workers.
15. The lesson is being explained by the teacher.
16. The letters will be delivered by the postman at noon.
![]()
II. Change the following sentences into the active voice.
1. The parcels will be delivered at any time (by the courier agents)
2. Surya was invited to tea by Chandra.
3. Traffic rules should be followed.
4. Vegetables are washed before cooking.
5. Let the following sentences be changed into the passive voice.
6. How many times were you reminded of the medicine ?
7. Let the dustbin be kept away from the eatables.
8. Hpve all your friends been invited to your birthday ?
9. Every sentence can’t be changed into the passive voice.
10. If the ointment isn’t applied to the wound, it will not heal.
11. My brother has never been beaten at chess by anyone in his school.
12. It is believed that Sammakka and Saralamma are the saviors of their lives in times of crisis by the villagers.
Answers:
1. The courier agents will deliver the parcels at any time.
2. Chandra invited Surya to tea.
3. One (We) should follow traffic rules.
4. We wash vegetables before cocking.
5. Change the following sentences into the passive voice.
6. How many times did I (we) remind you of the medicine ?
7. Keep the dustbin away from the eatables, (food)
8. Have you invited all your friends to your birthday party ?
9. One (We) can’t change every sentence into the passive voice.
10. If you don’t apply the ointment to the wound, it will not heal.
11. No one in his school has ever beaten my brother in chess.
12. The villagers believe that Sammakka and Saralamma are the saviours of their lives in times of crisis.
![]()
III. Change the following sentences into the passive voice.
1. Rainwater fills potholes on roads.
2. He is buying a TV set at the moment.
3. I have been growing plants since 1990.
4. They were reading the newspaper.
5. She had answered it already.
6. I will write an essay tonight.
7. You will have posted it by Monday.
8. Can she play the violin ?
9. They may not telecast it.
10. One must do one’s duty.
11. Gall in the doctor.
12. Close the door.
13. The Government has to do it.
14. Someone has already cast my vote.
15. Who could help him ?
Answers:
1. Potholes on roads are filled with (by) rainwater.
2. A TV set is being bought by him at the moment.
3. Plants have been being grown by me since 1990.
4. TKe newspaper was being read (రెడ్) by them.
5. It had already been answered by her.
6. An essay will be written by me tonight.
7. It will have been posted by you by Monday.
8. Can the violin be played by her ?
9. It may not be telecast, (by them)
10. One’s duty must be done, (by one)
11. Let the doctor be called in.
12. Let the door be closed.
13. It has to be done by the Government.
14. My vote has already been cast, (by someone)
15. By whom could he be helped ?
![]()
IV. Change the following into Active Voice.
1. He was seen crossing the road.
2. You are advised to be careful.
3. Let the picture be seen by me.
4. Her purchases were paid for by me.
5. There are no shops to be let.
6. She has been selected their monitor (by the class)
7. It is said that the earth is round.
8. The road had been repaired.
9. I am surprised at this news.
10. It is hoped that I shall win.
Answers:
1. We saw him crossing the road.
2. We advise you to be careful.
3. Let me see the picture.
4. I paid for her purchases.
5. There are no shops to let (out).
6. The class has selected her their monitor.
7. People say that the earth is round.
8. They had repaired the road.
9. This news surprises me.
10. I hope that I shall win.
![]()
V. Change the following sentences into the passive voice.
1. I have made a mistake.
2. Your students will respect you a great deal more for your frankness and honesty.
3. Call the attention of your near neighbour at the table to the excellence of the coffee.
4. Do you apply Pythagoras Theorem or Newton’s Law of Gravity ?
5. Rahul lost a quarter mark in English.
6. She planted trees; fenced, watered and guarded them.
7. Their hope and encouragement gave me greater strength.
8. Instantly remove that hatter.
Answers:
1. A mistake has been made by me.
2. You will be respected by your students a great deal more for your frankness and modesty.
3. Let the attention of your near neighbour at the table be called to the excellence of the coffee.
4. Is Pythagoras Theorem or Newtons Law of Gravity applied by you ?
5. A quarter mark in English was lost by Rahul.
6. Trees were planted, fenced, watered and guarded by her.
7. I was given greater strength by their hope and encouragement. (OR) Greater strength was given to me by their hope and encouragement.
8. Let that hatter be removed instantly.
![]()
B. DIRECT SPEECH AND INDIRECT SPEECH/REPORTED SPEECH
Sometimes it becomes necessary to report a person’s words. It can be done in two different ways. One -way is to reproduce the actual words of the speaker. The speaker’s actual words are shown in quotation marks in writing. This kind of reporting is called the ‘Direct Speech’.
The other kind is to express the idea of the speaker in the reporter’s words. This type is referred to as the ‘Indirect Speech’.
(ఒక వ్యక్తి అన్న మాటలకు అన్నట్లుగా తిరిగి చెబితే Direct Speech. కేవలం భావం మాత్రమే తిరిగి చెబితే Indirect Speech.)
The sentence in the Direct Speech has two parts. They are (a) the part outside the quotation marks (called the reporting part and (b) the part within the quatation marks (called the reported part).
![]()
The verb in the reporting part is called “the reporting verb.”
“Don’t make a noise,” said the teacher. (Reporting verb)
To change a sentence from the direct speech to the indirect speech, the following steps are to be followed.
1. The reporting part is to be written first. This is applicable only when the reporting part is either in the middle or at the end of the sentence.
Direct Speech :
“Ramu has solved all the problems.” said the teacher (Reporting part at the end)
Indirect Speech :
The teacher said that Ramu had solved all the problems. Reporting part begins the sentence.
![]()
2. The order of the words in the reporting part is arranged as “Subject + Verb.” This is applicable only when this order is not followed in the direct speech sentence.

3. The reporting verb is changed to words like ordered, requested, enquired, told, asked, ad-vised exclaimed, depending on the meaning of the reported part.

4. The quotation marks and the comma between the reporting and reported parts are removed in the indirect speech.
Ex : The boy said,” This plant has grown very tall.” (D.S.)
The boy said that plant had grown very tall. (I.S.)
5. A suitable connecting word is used to connect the reporting and reported parts. The selection of the right connecting word needs careful observation.
The following table will help you to select the right word.
| SI.No. | Sentence in quotation marks | Connecting word |
| 1. | Assertive or Exclamatory | that |
| 2. | Imperative | to |
| 3. | Yes/No type Question | if or whether |
| 4. | ‘Wh’ type Question | No connecting word |

![]()
6. The pronouns in the reported part are to be changed suitably. This depends on the first speaker, the speaker’s listener, the reporter and the reporter’s listener. One has to ensure that the original speaker’s intention is correctly reported. (Indirect speech లోకి మార్చేటప్పుడు, ఎవరు ఎవరితో అన్న మాటలను తిరిగి ఎవరు ఎవరికి చెబుతున్నారు అనే దానిని బట్టి pronouns మారతాయి. మొదట మాట్లాడిన వ్యక్తి ఉద్దేశ్యం మారకుండా సరిగ్గా చెప్పడం అవసరం.)
Now notice the following examples carefully :
a) The teacher said to you, ‘You are late again.” (D.S.)
The teacher told you that you were late again. (I.S.) ‘you’ not changed.
b) The teacher said to me, “You have improved your performance.” (D.S.)
The teacher told me that I had improved my performance.
You → 1 & Your → my
c) The teacher said to Geetha, “You have to submit your assignments tomorrow.” (D.S.)
The teacher told Geetha that she had to submit her assignments the following day. (I.S.)
You → she and you → her
d) The teacher said to Prudhvi, “When will you finish your computer course” ? (D.S.)
The teacher asked Prudhvi when he would finish his computer course. (I.S.)
You → he and your → his
e) The teacher said to the students, “You must consult your parents.” (D.S.)
The teacher told the students that they should consult their parents. (I.S.)
You → they and Your → their
As the examples a, b, c, d and e show you, pronouns change in accordance with the speaker’s reference to a person/persons.
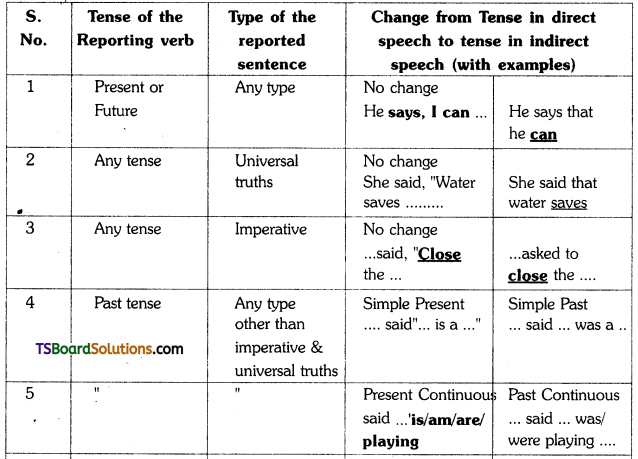
7. In changing sentences into the indirect speech, the tense form of the verbs in the reported part is to be changed. This is the most important part of the transformation. This is done in accor-dance with the concept popularly known as “the sequence of tenses.” (Reported part లోని verbs tenses మార్చడం అతి ప్రధాన భాగము దీనిని ‘Sequence of tenses’ అనే నియమానుసారంగా )
The following table clearly shows when and how to change the tense.

![]()
8. The next step in the transformation from the direct to the indirect is to change the adjectives or adverbs showing ‘nearness to those showing ‘distance as explained in the following table:
| SI. | Ajjective / Adverb | Adjective or Adverb |
| No. | in ‘direct speech’ | in ‘indirect speech’ |
| 1. | this | that |
| 2. | these | those |
| 3. | here | there |
| 4. | now | then |
| 5. | today/tonight | that day/that night |
| 6. | yesterday | the previous day/ the day before |
| 7. | tomorrow | the next day/the following day |
| 8. | ago | before |
9. The transformation from the direct to the indirect involves a change in the word order. This principle is applicable to interrogative and exclamatory sentences only. This is exemplified in the table given below.
| SI. No. | Word order in Direct Speech with examples | Word order in Indirect Speech with examples |
| 1 | … Helping verb+subject+ Main verb … said … “are you coming”… |
subject-1-Helping verb+Main verb asked … you were / coming |
| 2 | Helping verb 4- subject + Main verb said … do you like … |
subject +…… + Main verb
asked … he …. liked |
| 3 | ‘wh’ word+adj/adv+ subject + verb said “How beautiful + the toy is … | subject + verb + intensifier adj/adv exclaimed – the toy was very n beautiful. |
Note that the ‘wh’ word in exclamatory sentences doesn’t have the meaning of a question. It just emphasises the adjective or adverb. Hence this ‘wh’ word in the direct speech becomes the intensifier ‘very’ in the indirect speech.
![]()
10. The last step in this kind of transformation is to change the ‘Question mark’ or the ‘exclamatory mark’ into a full stop in the indirect speech.
You must note that all the Ten steps detailed above are not necessary to follow in the case of all kinds of sentences. You carefully check which steps are necessary and which steps are not necessary to follow in changing a given sentence.
EXAMPLES
1. Direct speech:
Reporter : Are you a vegetarian or non-vegetarian?
Bernard Shaw : I don’t want to make my stomach a burial ground for dead animais.
Reporter : How wonderful your answer is!
Bernard Shaw : Thank you for your compliments.
Indirect speech :
A reporter asked the famous writer Bernard Shaw whether he was a vegetarian or a non-vegetarian. Bernard Shaw replied that he didn’t want to make his stomach a burial ground for dead animals. The reporter responded that it was a wonderful answer. Bernard Shaw thanked him for his compliments.
3. Gandhi said, “I respect all religions.” (D.S)
Gandhi said that he respected all religions. (I.S)
4. He said to me, “Who is your favourite politician ?” (D.S)
He asked me who my favourite politician was (I.S)
5. An American said, “How hard-working Indians are !” (D.S)
An American exclaimed that Indians were hard-working. (I.S)
6. A customer said to the manager, “Can you do me a favour ?” (D.S)
A customer requested the manager to do him/her a favour. (I.S)
7. Abdul Kalam said, “I have come from a poor background.” (D.S)
Abdul Kalam said that he had come from a poor background. (I.S)
8. The teacher said to a student, “Are you confident ?” . (D.S)
The teacher asked a student whether he / she was confident. (I.S)
![]()
9. Amulya says, “I am learning music”. (D.S)
Amulya says that she is learning music. (I.S)
10. The teacher said,’The sun rises in the east.” (D.S)
The teacher said that the sun rises in the east. (I.S)
11. Dr. Rahul said, “1 will try my best to save the patient.” (D.S)
Dr. Rahul said that he would try his best to save the patient. (I.S)
12. Yasoda said to Krishna, “You are mischievous and trouble me a lot. (D.S)
Yasoda told Krishna that he was mischievous and troubled her a lot.” (I.S)
13. They said, “The Minister has at last unveiled the statue today. It has not been unveiled for so many months for reasons unknown.” (D.S)
They said that the Minister had at last unveiled the statue that day and added (that) it had not been unveiled for so many months for reasons unknown. (I.S)
14. A North Indian friend of mine said, “Unlike in Delhi, the climate in Hyderabad is moderate.” (D.S)
A North Indian friend of mine remarked that unlike in Delhi, the climate in Hyderabad was moderate. (I.S)
15. “How is your health ?” said Dr. Charan to a patient. (D.S)
Dr. Charan asked a patient how his/her health was. (I.S)
16. A stranger said to me, “Where is Golconda ?”. (D.S)
A stranger asked me where Golconda was. (I.S)
17. “Dheeraj said to his friend, “Are you interested in teaching ?” (D.S)
Dheeraj asked his friend if/whether he was interested in teaching. (I.S)
18. I said my daughter, “Do you want to do B.Tech. or B.Sc ?” (D.S)
I asked my daughter whether she wanted to do B.Tech or B.Sc. (I.S)
II. Study the following examples and observe how statements are changed into the indirect speech.
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| 1. Simple present He said, “I have many problems.” |
1. Simple past He said that he had many problems. |
| 2. Present continuous “I am reporting her words,” he said. |
2. Past continuous He said that he was reporting her words. |
| 3. Present perfect The cashier in the Bank said, “I have sent a report.” |
3. Past perfect The cashier in die Bank said that he had sent a report. |
| 4. Present perfect continuous A student said, “I have been trying to speak English for two years.” |
4. Past perfect continuous A student said that he had been trying to speak English for two years. |
| 5. Simple past ‘I forgot my hall ticket,” a candidate said. |
5. Simple pastíPast perfect A candidate said that he / she had forgotten his hail ticket. |
| 6. Past continuous “I was watering the plants in the garden,” she said. |
6. Past continuous / Past per.cont. She said that she had been watering the plants in the garden. |
| 7. Simple future “We will move to Hyderabad next year, “Rajitha said. |
7. Rajitha said that they would move to Hyderabad the following year. |
| 8. The English teacher said to the class, “I will tell you the difference between the two sentences.” | 8. The English teacher told the class that he would tell them the difference between the two sentences. |
![]()
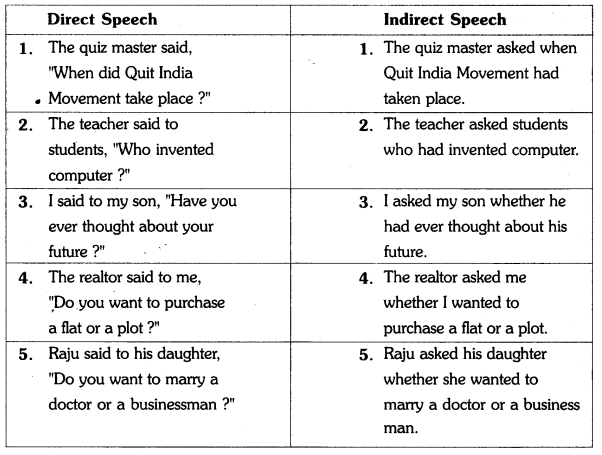
III. Study the following examples and observe how questions are changed into indirect speech.
IV. All the verbs are changed into infinitives [to + verb (v1)] while reporting imperative sentences.
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| 1. Order/Command The Site engineer said to his colleagues : “Don’t deviate from the plan.” |
1. The Site engineer ordered his colleagues not to deviate from the plan. |
| 2. Request A student said to the teacher : “Can you, please, repeat the question, Madam ?” |
2. A student requested the teacher to repeat the question. |
| 3. Advice Ahmad said to his son : “Don’t waste time and money.” |
3. Ahmad advised his son not to waste time and money. |
| 4. Instruction The invigilator said to the candidates in the examination hall:”Write your hall ticket number on the question paper.” |
4. The invigilator instructed the candidates in the examination hall to write their hall ticket number on the question paper. |
| 5. Threat A girl said to a boy : “I will complain to the police, if you tease me.” |
5. A girl warned the boy that she would complain to the police if he teased her. |
| 6. Offer A volunteer said to me : “Can I help you ?” |
6. A volunteer offered to help me. |
| 7. Invitation Praveena said to her friends : “Welcome to my home.” |
7. Praveena invited her friends to her house. |
| 8. Warning Mother said to her son : “Don’t swim in the turbulent river.” |
8. Mother warned her son not to swim in the turbulent river. |
| 9. Promise You said to your mother : Til be careful.” |
9. You promised to your mother to be careful. |
| 10. Apology Raheem said to you : “I am sorry I am unable to help you.” |
10. Raheem apologized to you for not being able to help you. |
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| 1. Keerthi said to us, “Let us have some snacks.” | 1. Keerthi suggested (invited) to us that we should have some snacks. |
| 2. Dev said to us, “Shall we visit the Thousand-Pillar temple today ?” | 2. Dev proposed that we should visit the Thousand- Pillar temple that day. |
![]()
Exclanations :
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| 1. “Oh ! They have lost the match,” he said. | 1. He expressed regret that they had lost the match. |
| 2. “Hurrah ! We have won the match,” said the boys. | 2. The boys exdamed with delight that they had won the match. |
| 3. My brothers said to me, “Better luck next time.” | 3. My brothers wished me better luck next time. |
Some More Examples :
1. He said to me, ‘You are lucky.” (D.S)
He told me (that) I was lucky. (I.S)
2. He said, “My father went to Chennai.” (D.S)
He said (that) his father had gone to Chennai. (I.S)
3. He said, “The sun rises in the east”. (D.S)
He said that the sun rises in the east. (I.S)
4. He said, “Kutub Minar is in Delhi.” (D.S)
He said that Kutub Minar is in Delhi. (I.S)
5. He said, “1 always go to bed early.” (D.S)
He said he always goes to bed earlier (I.S)
6. He said to me, “Do you want coffee ?” (D.S)
He asked me if I wanted coffee. (I.S)
7. He said to me, “Where did you go ?” (D.S)
He asked me where I had gone. (I.S)
8. He said to his son, “Go out and play.” (D.S)
He told his son to go out and play. (I.S)
9. He said, “Don’t disturb me.” (D.S)
He instructed him not to disturb him. (I.S)
10. He said, “What a terrible storm it is !” (D.S)
He exclaimed that it was a terrible storm. (I.S)
![]()
11. He said to her, “How foolish of you !” (D.S)
He exclaimed that she was very foolish. (I.S)
12. He said, “Alas ! What a tragedy.” (D.S)
He exclaimed with sorrow that it was a great tragedy. (I.S)
EXERCISES
I. Report the following statements.
1. Sunil said to his daughter, “I will take care of you.”
2. The M.L.A. said to villagers, ‘You have every right to question me.”
3. The Inspector said to the constable, “I am your boss.”
4. It is better for you to join M.PC.” said Bharath’s mother.
5. The principal said to the lecturers, You should maintain records.”
6. “I have been waiting here for you for one hour, “Vasundhara said to Vandana.
7. Kranthi said to the Inspector, “I met with an accident while taking a turn.”
8. He said, “I have lost my bag.”
9. The girl said, “I can change any given sentence into reported speech.”
10. “I am your fan,” said the boy to Allu Aijun.
Answers:
1. Sunil told his daughter that he would take care of her.
2. Tlje M.L.A told villagers that they had every right to question him.
3. The Inspector told the constable that he was his boss.
4. Bharath’s mother said that it would be better for him to join MPC.
5. The principal told the lecturers that they should maintain records.
6. Vasundhara told Vandana that she had been waiting there for her for an hour.
7. Kranthi informed the Inspector that he had met with an accident while taking a turn.
8. He said that he had lost his bag.
9. The girl said that she could change any given sentence into reported speech.
10. The boy told Allu Aijun that he was his fan.
![]()
II. Match the reported clause of Set n A with each reported statement of the direct speech in Set n B and then change the sentence into the reported speech.

Answers:
1. The palmist told a woman that she would become a good writer.
2. In a press meet, the Union Minister promised that the government would take all precautionary measures regarding cyclone.
3. Dr. Gopal told them that the operation was successful and the patient was out of danger.
4. The lawyer told the client that they could file an appeal in the High Court.
5. The boy came late to the class and told his teacher that his father had been ill for a few days.
III. Report the following questions in indirect speech.
1. A visitor said to me, “Are there any places worth seeing in Warangal ?”
2. The mother said to her son, “When will you have your breakfast ?”
3. The shopkeeper said to the customer, “Shall I show you the latest model ?”
4. I said to the shop assistant, “What is the price of this dress ?”
5. A classmate said to me, “Is your father a businessman ?”
6. Harika said to her friend, “Will you come to my home tomorrow ?”
7. The passenger said to the driver, “Does the bus stop at the crossroads ?”
8. A girl said to the principal, “Do I need to be a postgraduate to become an IAS officer ?”
9. The father said to his daughter, “Who teaches you English, Anitha ?”
10. The teacher said to Kavitha, “What does the word ‘corruption’ mean ?”
Answers:
1. A visitor asked me if there were any worth seeing places in Warangal.
2. The mother asked her son when he would have his breakfast.
3. The shopkeeper asked the customer if he could show him the latest model.
4. I asked the shop assistant what the price of that dress was.
5. A classmate asked me if my father was a businessman.
6. Harika asked her friend if she would come to her home the following day.
7. The passenger asked the driver if the bus would stop at the crossroads.
8. A girl asked the principal if she needed to be a postgraduate to become an IAS officer.
9. The father asked his daughter Anita who would teach them English.
10. The teacher asked Kavitha what the word corruption meant.
![]()
IV. Change the following imperatives into the indirect speech.
1. Hima said, “Get out from here.”
2. Neha said, “Mom, please give me your mobile.”
3. Hardik said to Annu, “Go and study.”
4. Nani said to me, “Exercise daily.”
5. Father said to Swetha, “Switch off the fan.
Answers:
1. Hima ordered him/them to get out from there.
2. Neha requested her mother to give her mobile.
3. Hardik asked Annu to go and study.
4. Nani advised me to exercise daily.
5. Father asked Swetha to switch off the fan
V. Change the following exclamations into the indirect speech.
1. Nivya said to her sister, “How interesting the serial is !”
2. My friend said to me, “What a wonderful opportunity it is !”
3. “Oh ! he is dead,” the doctor said.
4. “Thank goodness ! I’ve passed my exams,” my son said.
5. “Hurray ! I’ve got first rank in the entrance examination !” my friend said.
6. “How awful! She has missed the chance,” Mahesh said.
7. A visitor said, “What sultry weather !”
8. “What a pity ! Many passengers died in the accident,” said an eye witness.
9. Akshay said to his partner, “Bad luck, never mind.”
10. “Oh ! What a beautiful place it is !” he said.
Answers:
1. Nivya exclaimed to her sister that the serial was very interesting.
2. My friend exclaimed to me that it was a wonderful opportunity.
3. The doctor declared sadly that he was dead.
4. My son happily said that he had passed his exams.
5. My friend cheerfully declared that he had got the first rank in the entrance examination.
6. Mahesh rather sadly exclaimed that she had missed the chance.
7. A visitor exclaimed that it was very sultry weather.
8. An eye witness exclaimed sadly that many passengers had died in the accident.
9. Akshay told his partner that it was their bad luck and said better not mind that.
10. He exclaimed that it was a very beautiful place.
![]()
VI. Report the following sentences.
1. A father said to his son. “Ramu, concentrate on your studies now.”
2. “What a wonderful poem it is !” said the teacher.
3. The principal said to the student, “Vinay, can you spell this word ?”
4. “Is there any train to Mumbai now ?” I asked the enquiry clerk.
5. “How much time does a ray of the sun take to reach the earth ?” the quiz master asked the team.
6. “Alas ! India has lost a famous scientist,” said the Prime Minister on the death of Abdul Kalam.
7. “How would you help develop the company ?” the interview board member said to the can-didate.
8. “If I get a job, I will arrange a grand party,” said Spandana.
9. “Stand where you are,” the officer said to the cadets.
10. “Don’t make friends with bad boys,” said the mother to her son.
11. “Hearty welcome to our village !” Radha said to her friends.
12. “Hurrah ! We have defeated Pakistan in T 20 too,” said Kohli.
13. “Please be seated. My father is sleeping,” said the girl to the visitors.
14. “I am a pure vegetarian,” Gandhi said.
15. “How exciting it is to see Telangana as a separate state !” said a hundred-year old man.
16. “Remember, Man is mortal,” said the Swamiji.
17. He said, “We need not wait here for the bus.”
18. “While I was going to see Deepthi, it started raining,” Kiran said.
19. The doctor said, “Sorry, I cannot help it.”
20. “Nothing is in our hands,” said the priest.
Answers:
1. A father advised his son Ramu to concentrate on his studies then.
2. The teacher exclaimed that it was a very wonderful poem.
3. The principal asked Vinay if he could spell that word.
4. I asked the enquiry clerk if there was any train to Mumbai then.
5. The quiz master asked the team how much time a ray of the sun took to reach the earth.
6. The Prime Minister said on the death of Abdul Kalam that India had lost a famous scientist.
7. The interview board member asked the candidate how he would help the company develop.
8. Spandana said that if she got a job she would arrange a grand party.
9. The officer ordered the cadets to stand where they were.
10. The mother advised her son not to make friends with bad boys.
11. Radha extended hearty welcome to her friends to her village.
12. Kohli gladly said that they had defeated Pakistan in T20 too.
13. The girl requested the visitors to be seated and informed them that her father was sleeping.
14. Gandhi said that he was a pure vegetarian.
15. A hundred – year old man exclaimed that it was very exciting to see Telangana as a separate state.’
16. The Swamiji said emphatically that man is mortal.
17. He said that they needed not wait there for the bus.
18. Kiran said that while he was going to see Deepthi, it had started raining.
19. The doctor apologetically said that he couldnot help it.
20. The priest said that nothing was in their hands.
![]()
VII. Change the following sentences into the indirect speech.
1. I said to her, “I had already applied for a job.”
2. You said to me, “She loves you.” * ‘
3. We said to him, “Can we use your phone ?”
4. The teacher said to her, ‘Why did you fail the exam ?”
5. She will say to me, “How do you solve the problem ?”
6. I said to them, “I don’t ever waste my time.”
7. You said to me, “I have not yet met them.”
8. The minister said, “The problem will surely be looked into.”
9. They said to rile, “Have you been working here since 2015 ?”
10. We said to them, ‘We were watching a movie.”
11. She said, “I went to the market yesterday.”
12. They said to us, “We will be waiting for you.”
13. John said to her, “1 will call a doctor for you.”
14. I said to her, “Alas, I am undone !”
15. She said to him, “Please complete the job.”
16. He shouted at them, “Shut up!”
17. The officer said to him, “Don’t repeat this mistake in the future.”
18. The teacher said, “Akbar died in 1605 AD.”
19. She said to her, “Knowledge is power.”
20. A soft voice said, “What a cold day !”
Answers:
1. I told her that I had already applied for a job.
2. You told me that she loved me.
3. We asked him if we could use his phone.
4. The teacher asked her why she had failed the exam.
5. She will ask me how I will solve the problem.
6. I told them that I never wasted my time. (OR) I told them that I never waste my time.
7. You told me that you had not yet met them.
8. The minister said that the problem would surely be looked into.
9. They asked me if I had been working there since 2015.
10. We told them that we had been watching a movie.
11. She said that she had gone to the market the previous day.
12. They told us that they would be waiting for us.
13. John told her that he would call a doctor for her.
14. I exclaimed with sorrow to her that I was undone.
15. She requested him politely to complete the job.
16. He ordered them loudly to shut up.
17. The officer warned him not to repeat that mistake in the future.
18. The teacher said that Akbar had died in 1605 AD.
19. She told her that knowledge is power.
20. A soft voice exclaimed that it was a very cold day.
![]()
VIII. Change the following sentences into the other speech.
1. A good teacher will say frankly and clearly, “I don’t know, 1 cannot answer that question.”
2. I asked my Biology teacher what I should do to save it.
3. I asked my grandmother how she got to be so wise.
4. Thimmakka concludes, “Even one sapling each could make a better place for our children.”
5. Box : Stop ! Can you inform me who the individual is that I invariably encounter going downstairs when I’m coming up, and coming upstairs when I’m going down ?
Answers:
1. A good teacher will say frankly and clearly that he/she doesn’t know. He/She will add that he/ she cannot answer that question. (I.S)
2. I said to my Biology teacher, “What shuld I do to save it ?” (D.S)
3. I said to my grandmother, “How did you get to be so wise” ? (D.S)
4. Thimmakka concludes that even one sapling each could make a better place for our children. (I.S)
5. Box asked (her) to stop. He further asked her if she could inform him who that individual was that he invariably encountered going downstairs when he was coming up and coming upstairs when he was going down. (I.S)
![]()
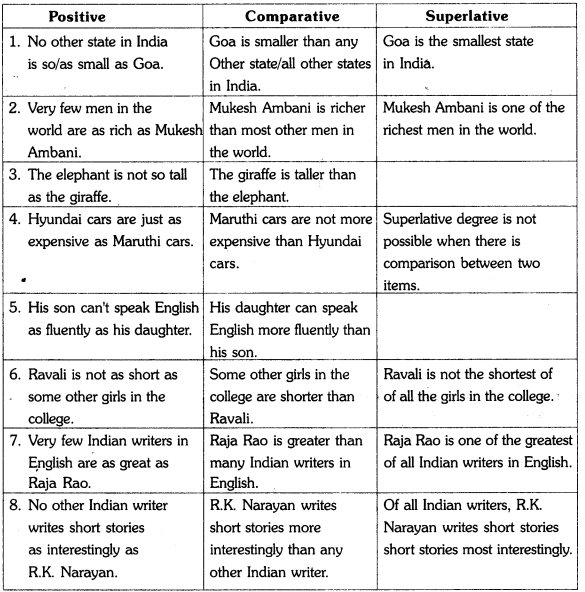
C. DEGREES OF COMPARISON
Man craves for variety. He knows that variety is the spice of life. Hence he tries to express the same idea in various different ways. The result is the tradition of describing the quality, quantity size etc., of some thing or person in three different ways. Most adjectives and some adverbs have three different forms. They are positive, comparative and superlative. They are known as the three degrees of comparision.
(ఒక వ్యక్తి యొక్క వస్తున్న యొక్క గుణ, పరిమాణాలను మూడు భిన్న రూపాలలో వ్యక్తీకరించడం ఆనవాయితీ. ఈ రూపాలనే Degrees of comparison అని పిలుస్తారు)
When the comparison is among a minimum of three persons/things, that can be ex-pressed in all the three degrees. If the compared persons are two only, the superlative degree is not possible. When we talk of the quality, quantity of a single item, only positive degree is possible.
Interchange of Degrees of comparison :
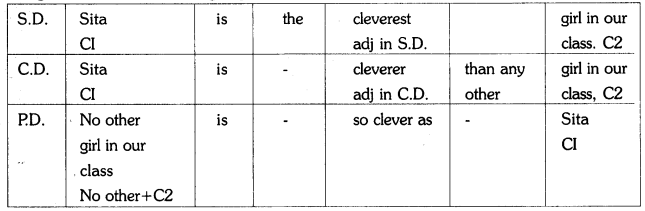
Transforming one sentence from the Superlative Degree to Comparative Degree involves the following steps.
1. First, remove ‘the’ that is used before the superlative adjective, while changing it into the comparative.
2. Write the comparative form of the adjective.
3. Then, add ‘than any other’ after the adjective.
Ex : Praveen is the youngest boy in the class. (S.D.)
Praveen is younger than any other? boy in the class.
To change that sentence into the positive :
1. Begin the sentence with ‘No other’.
2. Secondly, place the phrase after the superlative adjective after ‘No other’.
3. Use ‘so + adj in positive Degree + as’ after the verb.
4. Place the subject in the S.D after ‘as’ in RD.
Ex : He is the richest man in our town. (S.D.)
![]()
Transforming one sentence from the superlative Degree to comparative or positive Degree involves the following steps.
![]()
Sentences with ‘one of phrase in the Superlative degree follow a slightly different wording. This is as explained here under.

Some sentences show the comparison between only two things/persons. In such cases, the superlative is not possible. The interchange is made as shown here.

EXAMPLES
Change the following sentences into other degrees.
Question 1.
Bengaluru is as cool as Ooty. (P.D)
Answer:
Ooty is not cooler than Bengaluru. (C.D)
Question 2.
Australia is the biggest island in the world. (S.D)
Answer:
Australia is bigger than any other island in the world. (C.D)
No other island in the world is so big as Australia. (PD)
Question 3.
The moon is brighter than the stars. (C.D)
Answer:
The stars are not so bright as the moon. (P.D)
Question 4.
There is no vice so bad as drink. (P.D)
Answer:
Drink is worse than any other vice. (C.D)
Question 5.
Kashmir is the most beautiful place in India. (S.D)
Answer:
No other place in India is so beautiful as Kashmir. (P.D)
Kashmir is more beautiful than any other place in India. (C.D)
![]()
Question 6.
Silver is not so precious as gold. (P.D)
Answer:
Gold is more precious than silver. (C.D)
Question 7.
Kumble is one of the ablest bowlers. (S.D)
Answer:
Very few bowlers are so able as Kumble. (P.D)
Kumble is abler them most other bowlers. (C.D)
Question 8.
The lion is more ferocious than any other animal. (C.D)
Answer:
The lion is the most ferocious of all the animals. (S.D)
No other animal is so ferocious as the lion. (P.D)
Question 9.
The sword is not so mighty as the pen. (P.D)
Answer:
The pen is mightier than the sword. (C.D).
Question 10.
Copper is more useful than most other metals. (C.D)
Answer:
Copper is one of the most useful metals. (S.D)
Very few metals are so useful as copper. (P.D)
Question 11.
Mount Everest i.s higher than any other peak in the world. (C.D)
Answer:
Mount Everest is the highest of all the peaks in the world. (S.D)
No other peak in the world is so high as Mount Everest. (P.D)
Question 12.
I like you better than him. (C.D)
Answer:
I didn’t like him as well as I like you. (P.D)
Question 13.
A deer runs faster than a horse. (C.D)
Answer:
A horse does not run so fast as a deer. (P.D)
![]()
Question 14.
Sangeetha is the tallest girl in the class. (S.D)
Answer:
No other girl in the class is so tall as Sangeetha. (P.D)
Question 15.
This is one of the most powerful earthquakes that occurred. (S.D)
Ans. This is more powerful than most other earthquakes that occurred. (C.D)
Very few earthquakes that occurred are as powerful as this earthquake. (P.D)
More Examples :
1. For me, dancing is easier to learn than singing. (C.D)
For me, singing is not as easy to learn as dancing. (P.D)
2. Singing is the best of all art forms. (S.D)
Singing is better than any other art forms. (C.D)
No other art form is as good as singing. (P.D)
3. The sentence is more impressive than the earlier one. (C.D)
The earlier sentence is not so impressive as this one. (P.D)
4. A car, of course, is costlier than a bike. (C.D)
A bike, of course, is not as costly as a car. (P.D)
5. Uttar Pradesh is the largest state in India. (S.D)
Uttar Pradesh is larger than any other state in India. (C.D)
No other state in India is as large as Uttar Pradesh. (P.D)
![]()
6. Bill Gates is the wealthiest man in the world. (S.D)
Bill Gates is wealthier than any other man in the world. (C.D)
No other man in the world is as wealthy as Bill Gates. (P.D)
7. English is the most widely used language in the world. (S.D)
English is more widely used than any other language in the world. (C.D)
No other language in the world is as widely used as English. (P.D)
Types of transformation :
EXERCISES
I. Change the following sentences into other Degrees.
1. LIC is one of the most popular insurance companies in India.
2. The custard apple is better for health than the apple.
3. A computer works faster than the human brain.
4. A Governor is sometimes more powerful than a Chief Minister.
5. The teaching profession is the best of all professions.
6. Laxmi Mittal is one of the most popular industrialists.
7: No other bank in India has as many branches as SBI.
8. Virus infects a person faster than bacteria.
9. Cancer is one of the most dangerous diseases.
10. No other boy in the class is as active as Surya Teja.
11. The Amazon is one of the longest rivers in the world.
12. No other animal lives as long as the turtle.
13. Jupiter is bigger than any other planet.
14. A rainbow is one of the most beautiful sights in nature.
15. Very few English poets are as great as John Keats.
16. The lotus is the most beautiful flower.
![]()
17. Mathematics is more difficult than most other subjects.
18. Shimla is cooler than Ooty.
19. He can’t run as fast as I.
20. Vinay is not as mischievous as some other boys in the college.
21. There are some vegetarian food as healthy as eggs.
22. Of all the Telugu singers S.R Balasubramanyam has the most melodious voice.
23. Health is more important than wealth.
24. I cannot speak as fast as you.
25. Very few TV channels are as popular as E TV.
Answers:
1. Very few insurance companies in India are as popular as LIC. (P.D)
LIC is more popular than many other insurance companies in India. (C.D)
2. The apple is not as good for health as the custard apple. (P.D)
3. The human brain does not work as fast as a computer. (P.D)
4. Sometimes a Chief Minister is not as powerful as a Governor. (P.D)
5. The teaching profession is better than any other profession. (C.D)
No other profession is as good as the teaching profession. (P.D)
6. Very few industrialists are as popular as Laxmi Mittal. (P.D)
Laxmi Mittal is more popular than many other industrialists. (C.D)
7. SBI has the most number of branches. (S.D)
SBI has more branches than any other bank in India. (C.D)
8. Bacteria does not infect a person as fast as virus. (P.D)
9. Cancer is more dangerous than many other diseases. (C.D)
Very few diseases are as dangerous as cancer. (P.D)
10. Surya Teja is more active than any other boy in the class. (C.D)
Surya Teja is the most active boy in the class. (S.D)
![]()
11. The Amazon is longer than many other rivers in the world. (C.D)
Very few rivers in the world are as long as the Amazon. (P.D)
12. The turtle lives longer than any other animal. (C.D)
The turtle lives the longest of all animals. (S.D)
13. No other planet is as big as Jupiter. (P.D)
Jupiter is the biggest planet. (S.D)
14. A rainbow is more beautiful than many other sights in nature. (C.D)
Very few sights in nature are as beautiful as a rainbow. (P.D)
15. John Keats is one of the greatest poets of English. (S.D)
John Keats is greater than many other poets of English. (C.D)
16. The lotus is more beautiful than any other flower. (C.D)
No other flower is as beautiful as the lotus. (P.D)
17. Mathematics is one of the most difficult subjects. (S.D)
Very few subjects are as difficult as Mathematics. (P.D)
18. Ooty is not as cool as Shimla. (P.D)
19. I can run faster than he. (C.D)
20. Vinay is one of the most mischievous boys in the college. (S.D)
Vinay is more mischievous than many other boys in the college. (C.D)
21. Eggs are not healthier than some vegetarian foods. (C.D)
22. No other Telugu singer has a voice as melodious as S.R Balu’s. (P.D)
S.R Balu’s voice is more melodious than that of any other Telugu singer. (C.D)
23. Wealth is not as important as health. (P.D)
24. You can speak faster than I. (C.D)
25. E TV is more popular than many other TV channels. (C.D)
E TV is one of the most popular TV channels (S.D)
![]()
II. Rewrite the following comparisons as directed.
1. The taste of Pizza is more pleasing than that of Burger. (into the other degree)
2. Sheela is getting smarter and smarter than Neela. (into the other degree)
3. Raj is one of the bravest fighters. (into comparative)
4. Radha speaks more fluently than Sudha. (into the other degree)
5. ’ Riding a horse is not as easy as riding a motorbike. (into the other degree)
6. ‘Silence’ is the most potent weapon to win an argument. (into positive)
7. Rachana’s sister is taller than yours. (into the other degree)
8. Dogs don’t look as cute as rabbits. (into the other degree)
9. He is not the worst student in the class. (into comparative)
10. Very few heroes are as great as Gandhiji in the world history. (into superlative)
Answers:
1. The taste of Burger is not so pleasing as that of Pizza. (P.D)
2. Neela is not getting as smart as Sheela. (P.D)
3. Raj is braver than any other fighter. (C.D)
No other fighter is as brave as Raj. (P.D)
4. Sudha does not speak as fluently as Radha. (P.D)
5. Riding a motorbike is easier than riding a horse. (C.D)
6. No other weapon is so potent as silence to win an argument. (P.D)
Silence is more potent than any other weapon to win an argument. (C.D)
7. Your sister is not so tall as Rachana’s sister. (P.D)
8. Rabbits look cuter than dogs. (C.D)
9. He is not worse than most students in the class. (C.D)
Many students in the class are as bad as he. (P.D)
10. Gandhi is one of the greatest heroes in the world history. (S.D)
Gandhi is greater than many other heroes in the world history. (C.D)
![]()
III. Change the following sentences into other degrees of comparison.
1. Bus journey is not as comfortable as train journey.
2. Radhakrishnan is more highly respected than any other teacher.
3. Robert Frost is one of the best American poets.
4. No other road in the world is as long as the Pan American Highway.
5. Kashmir is one of the coolest places in India.
6. A foolish friend can be more dangerous than a wise enemy.
7. Money is not as important as character.
8. Modern culture is not as stable as Traditional culture.
9. For many Indians, cricket gives greater pleasure than football.
10. Natural flowers appeal more to our senses than artificial flowers.
Answers:
1. Train journey is more comfortable than bus journey. (C.D)
2. Radhakrishnan is the most highly respected teacher. (S.D)
No other teacher is so highly respected as Radhakrishnan. (P.D)
3. Robert Frost is better than many other American poets. (C.D)
Very few American poets are as good as Robert Frost. (P.D)
4. Pan American Highway is longer than any other road in the world. (C.D)
Pan American highway is the longest road in the world. (S.D)
5. Kashmir is cooler than many other places in India. (C.D)
Very few places in India are so cool as Kashmir. (P.D)
6. A wise enemy cannot be so dangerous as a foolish friend. (P.D)
7. Character is more important than money. (C.D)
8. Traditional culture is more stable than modern culture. (C.D)
9. For many Indians, football doesn’t give as much pleasure as cricket. (P.D)
10. Artificial flowers do not appeal to our senses as much as natural flowers. (P.D)
![]()
D. QUESTION TAGS
Question tags are short questions added to statements. They seek confirmation or agreement. (ఏకీభావాన్ని లేదా ద్రువీకరణను ఆశిస్తూ, ఒక వాక్యానికి అనుబంధంగా చేర్చబడే చిన్న ప్రశ్నలే Question tags.)
Question tags have a fixed structure. It is represented as : Helping verb + (n’t) + pronoun ? ((n’t) in brackets means it is optioned.)
e.g. She loves her children, doesn’t she?
(Q.T.) does (H.V.) n’t she (pronoun)
1. While constructing a tag, selecting the suitable helping verb is the first and the most important step. If the given sentence has a helping verb, then that helping verb is used in the tag too.
E.g : She has answered all the questions, hasn’t she?
has → Helping Verb in the sentence used in the tag too.
When the sentence doesn’t have a helping verb, the verb is either in the simple present Or in the simple past and in the affirmative. In case of the simple present, the suitable helping verb is “do/does”. If the verb in the sentence is in the simple past, then we must use ‘did’ in the tag.
Eg : a) She hates smokers, doesn’t she ? Simple present, hence ‘does’
b) They grow vegetables, do n’t they ? Simple present
c) He sold his car, didn’t he ? Simple past; hence ‘did’.
2. The second step is to decide whether to use ‘n’t’ or not. The guiding principle is quite simple. If the given sentence doesn’t have ‘rio/not’, use ‘n’t’ is the tag. If the given sentence has ‘no/not’ then the tag doesn’t have ‘n’t’.
Eg : a) He was sleeping in the class, was n’t he ?
‘not’ is not used n’t in the tag
b) They don’t grow paddy, do they?
‘n’t’ in sentence ‘n’t’ not used in tag
Remember to use the short form ‘n’t’ in the tag.
3. The last part of the tag as a pronoun. This corresponds to the subject of the given sentence. If the subject of the sentence is a pronoun, the same pronoun is used in the tag. If the subject is a noun, select a suitable pronoun as shown below.
| SI.No. | Subject in the sentence | Pronoun used in the tag |
| 1. | Name of a man | he |
| 2. | Name of a woman | she |
| 3. | Name of a single thing | it |
| 4. | Name referring to, a group of persons, places, things | they |
Eg : a) Gourav is a good cricketer, isn’t he? ?
b) Sania Mirza played well, didn’t she ?
c) Ooty is a beautiful hill station, isn’t it ?
d) Mangoes aren’t good this season, are they ?
![]()
4. Note that ‘amn’t’ is not used. Instead, aren’t is used.
Eg : lam rather slow, aren’t I ?
5. Imperative sentences take ‘will’ as the helping verb in the tags.
Eg : a) Close the door, Won’t you ? (Will + n’t = won’t)
b) Don’t leave the place, will you ?
6. Sentences expressing proposals with the help of “Let us ……………..” have for their tags “Shall we?”
Eg : Let us walk fast, shall we ?
EXAMPLES
1. Srinivasa Ramanujan is a famous mathematician, isn’t he ?
2. Normally players have a lot of practice, don’t they ?
3. Sania Mirza is not a cricketer, is she ?
4. She can speak English, can’t she ?
5. He should believe us, shouldn’t he ?
6. We must all learn English, mustn’t we ?
7. The Governor administers the oath of office to ministers, doesn’t she / he ?
8. He does not support any one, does he ?
9. Most of the villagers depend on agriculture, don’t they ?
10. They do not seem to lead a happy life, do they ?
11. Children love to play with toys, don’t they ?
12. On their picnic, the children did not have a chance to play in the garden, did they ?
13. The children are not yet back home, are they ?
14. Do me a favour, Raju, can you ?
15. Take a right decision, won’t you ?
16. Don’t waste time, will you ?
17. Let’s understand their problems, shall we ?
18. No one complained against us, did they ?
19. Everyone appreciated his performance, didn’t they ?
20. Someone should take the initiative, shouldn’t they ?
21. Nothing is impossible, is it ?
22. There will be problems in that case, won’t there ?
23. One can achieve anything by faith, can’t one ?
24. I am not disturbing you, am I ?
25. It is used for present actions, isn’t it ?
26. You understand the point, don’t you ?
27. You are attending a job interview tomorrow, aren’t you ?
28. It is clear to you now, isn’t it ?
29. They are ready, aren’t they ?
30. They are not ready, are they ?
31. He did not attend the class, did he ?
32. Oh, you got two prizes, did you ? (Special case. Positive statement, positive tag. Express reaction to a surprising news.)
33. I am going home, aren’t I ? (Note that ‘aren’t is used instead of ‘amn’t.)
![]()
EXERCISES
I. Add an appropriate question tag to each one of the following statements.
1. Sandeep has attended all classes, ……………….. ?
2. We are lucky to be born in India, ………………..?
3. English is an interesting language, ……………….. ?
4. He was very busy yesterday, ……………….. ?
5. I am very happy now, ……………….. ?
6. I can face challenges, ……………….. ?
7. Ravi always thinks positively, ……………….. ?
8. He does not criticize, ……………….. ?
9. Some people always depend on others, ……………….. ?
10. Discipline must be maintained at any cost, ……………….. ?
11. Let us keep to the pavement, ……………….. ?
12. Don’t blame others for everything, ……………….. ?
13. One can do wonders with knowledge, ……………….. ?
14. Nothing is permanent except change, ……………….. ?
15. Students are our best judges, ……………….. ?
Answers:
1. hasn’t he ?
2. aren’t we ?
3. isn’t it ?
4. wasn’t he ?
5. aren’t I ?
6. can’t I ?
7. doesn’t he ?
8. does he ?
9. Don’t they
10. mustn’t it be ?
11. shall we ?
12. will you ?
13. can’t one ?
14. is it ?
15. aren’t they ?
![]()
II. Add an appropriate question tag to each one of the following statements.
1. You don’t lime me, ……………….. ?
2. It is not raining, ……………….. ?
3. You have done your homework, ……………….. ?
4. I am not late, ……………….. ?
5. I am invited to your party, ………………..?
6. You like fast food, ……………….. ?
7. You will come to my party, ……………….. ?
8. You remembered to feed the cat, ……………….. ?
9. Let’s play tennis, ……………….. ?
10. There’s a problem here, ……………….. ?
11. He never says a word, ……………….. ?
12. Nobody came to your party, ……………….. ?
13. Don’t forget, ……………….. ?
14. You think you’re clever, ……………….. ?
15. So you think you’re clever, ……………….. ?
16. We don’t have to go to the party, ……………….. ?
17. It stopped raining, ……………….. ?
18. Have a seat, ……………….. ?
19. Help yourself to some cake, ……………….. ?
20. Children, be quiet, ……………….. ?
Answers:
1. do you
2. is it
3. haven’t you
4. am I (Note . possible tag-am ; negative tag are in the place of ami
5. aren’t I
6. don’t you
7. won’t you
8. didn’t you
9. shall we
10. isn’t there
11. does he (never = not; negative statement; hence positive tag)
12. did they
13. will you
14. don’t you (you think is the main clause)
15. do you (expressing sudden reaction)
16. do we
17. didn’t it
18. won’t you
19. will you
20. will you
![]()
III. Add an appropriate question tag to each one of the following statements.
1. I am unable to answer your question, ………………..?
2. Rahul’s first rank is at stake, ……………….. ?
3. The noise in my ears was that of the faithful Oxford crowd, ……………….. ?
4. The stop-watches held the answer, ……………….. ?
5. It belongs to both of you, ……………….. ?
Answers:
1. am I (unable = not able)
2. isn’t it
3. wasn’t it
4. didn’t they
5. doesn’t it ?