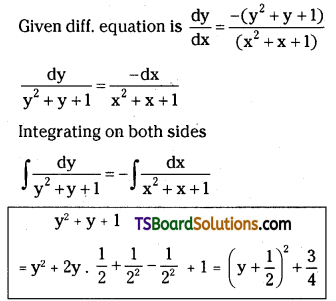
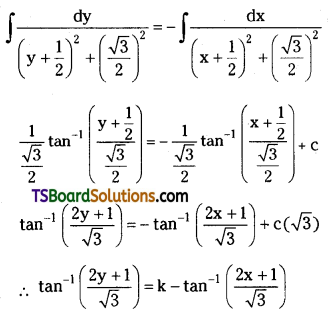
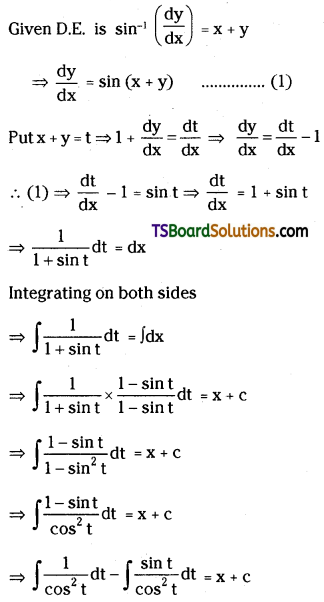
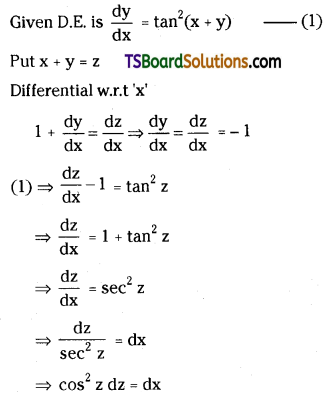
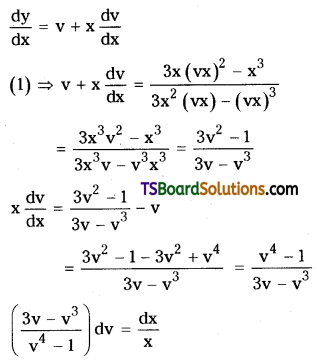
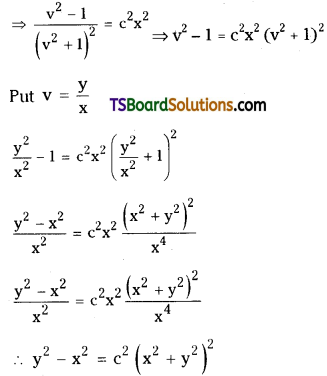
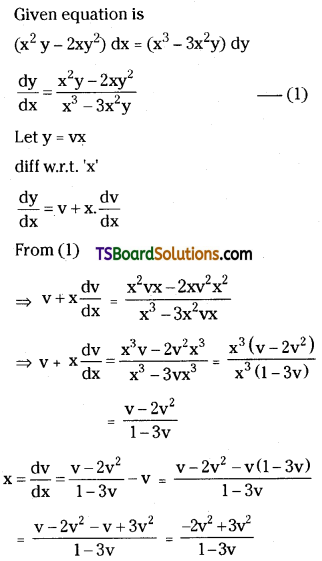
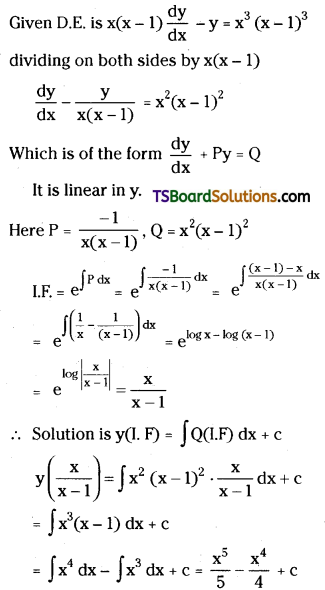
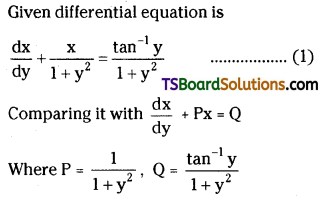
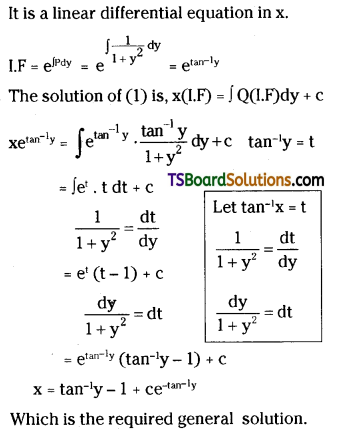
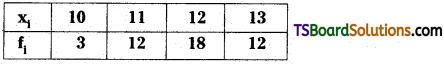
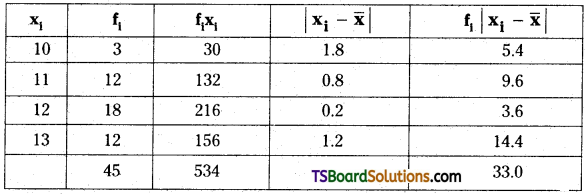
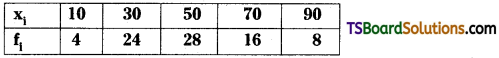
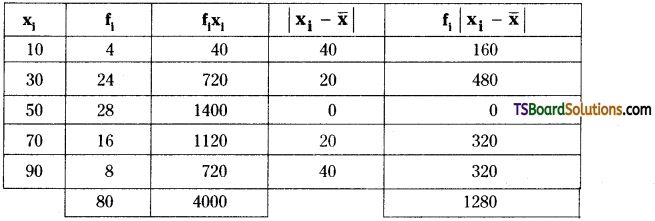
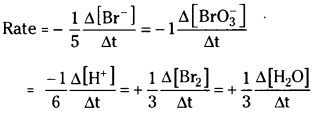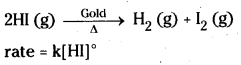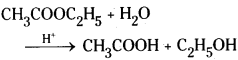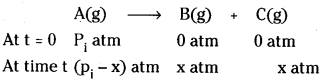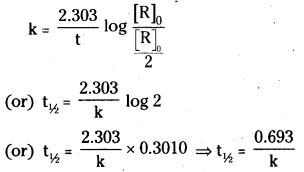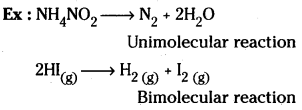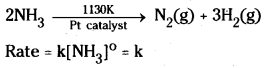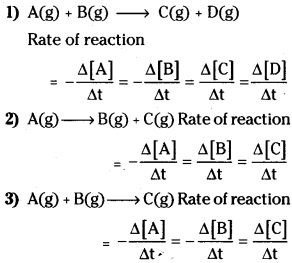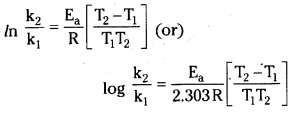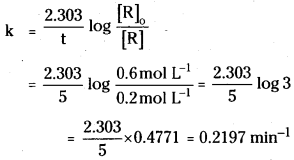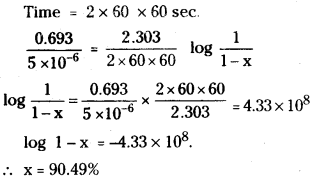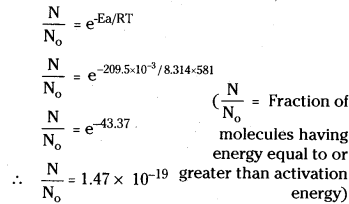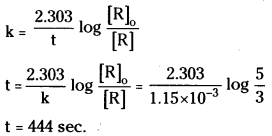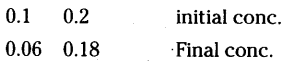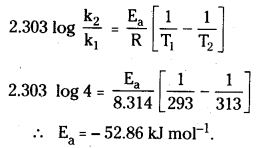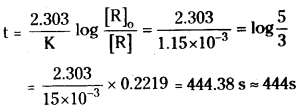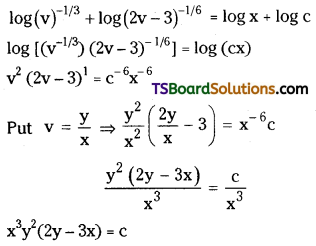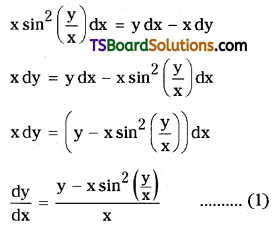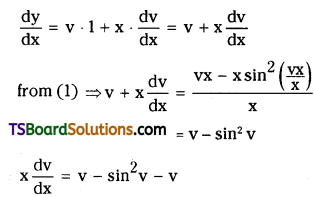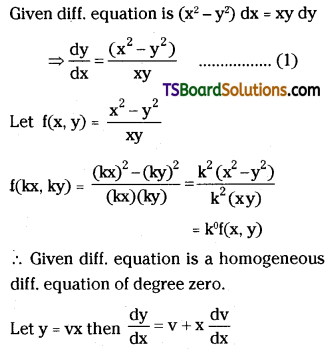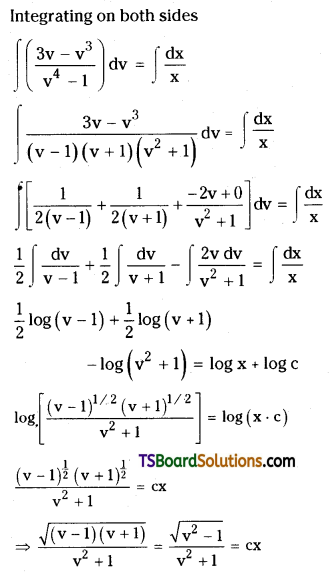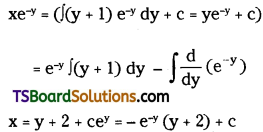Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material Lesson 3(b) Chemical Kinetics Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material Lesson 3(b) Chemical Kinetics
Very Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
Question 1.
Define the speed or rate of a reaction.
Answer:
The rate of a reaction is the change in con-centration of a reactant or product in unit time. It can be expressed in terms of:
- the rate of decrease in concentration of any one of the reactants, or
- the rate of increase in concentration of any one of the products.
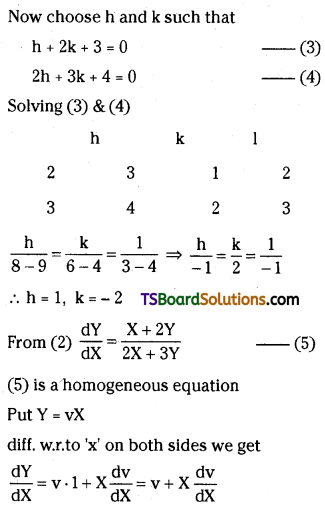
Question 2.
Assuming that the volume of the system is constant, derive the expression for the average rate of the system R → P in terms of R and P. [time = t sec; R = reac-tant, P = product]
Answer:
Considering a hypothetical reaction assuming that the volume of the system remains constant.
R → P
One mole of the reactant R produces one mole of the product P. If [R], and [P], are the concentrations of R and P respectively at time t1 and [R]2 and [P]2 are their concentrations at time t2 then
Δt = t2 – t1 ; Δ[R] = [R]2 – [R]1
Δ[P] = [P]2 – [P]1
Rate of disappearance of R =

Rate of appearance of P =

These equations represent the average rate of a reaction.

Question 3.
What are the units of rate of reaction?
Answer:
The units of rate of reaction are concentration × time-1. If concentration is mol L-1 and time is in seconds then the units will be mol L-1 s-1. For gaseous reaction the units of rate equation are atm s-1.
Question 4.
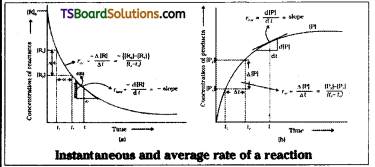
Draw the graphs that relate the concen-tration (C) of the reactants and the reac-tion times (t) and the concentrations of the products (C) and the reaction times (t) in chemical reactions.
Answer:
Question 5.
Write the equation for the rate of the reaction
5Br– (aq) + \(\mathrm{BrO}_3{ }^{-}(\mathrm{aq})\) + 6H+(aq) → 3Br2(aq) + 3H2O(l)
Answer:
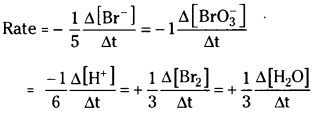
Question 6.
What is rate law? Illustrate with an example.
Answer:
The rate law is the expression in which rea-ction rate is given in terms of molar concen-tration of reactants. Each concentration term is raised to some power, which may or may not be same as the stoichiometric coefficient of the reacting species in balanced chemical equation. Example
2NO (g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
Rate = k [NO]2 [O2]
Question 7.
Mention a reaction for which the exponents of concentration terms are not the same as their stochiometric coefficient in the rate equation.
Answer:
i) Formation of CCl4 from CHCl3?
CHCl3 + Cl2 → CCl4 + HCl
Rate = k[CHCl3] [Cl2]1/2
ii) CH3COO C2H5 + H2O → CH3COOH
+ C2H5OH
Rate = k[CH3COOC2H5]1 [H2O]0
Question 8.
Define order of a reaction. Illustrate your answer with an example. (TS 15)
Answer:
The sum of the powers of the concentration terms of the reactants in the rate law expre-ssion is called the order of that reaction.
Order of reaction can be 0, 1, 2, 3 and even fraction.
Example :
Rate = k[A]1/2 [B]3/2
Order = \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{3}{2}\) = 2. i.e., second order
Question 9.
What are elementary reactions?
Answer:
The reactions taking place in one step are called elementary reactions.
Question 10.
What are complex reactions ? Name one complex reaction.
Answer:
If a reaction takes place in a sequence of elementary reactions called mechanism in which reactants convert into products, it is called complex reaction. These may be consecutive reactions, e.g. Oxidation of ethane to CO2 and H2O proceeds through a series of intermediate steps in which alcohol, aldehyde and acid are formed.
Question 11.
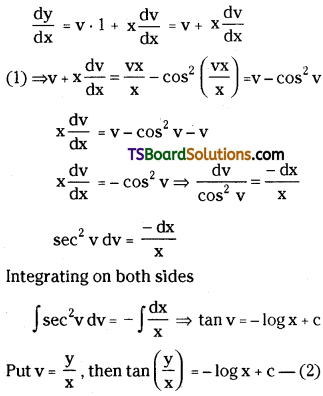
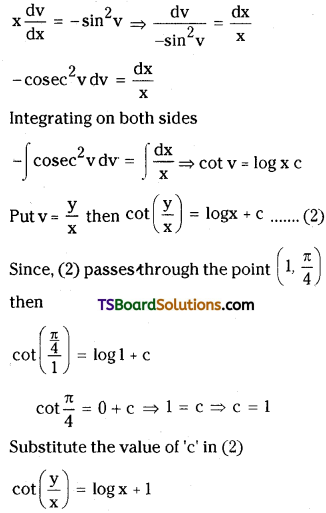
Give the units of rate constants for zero, first order and second order reactions.
Answer:
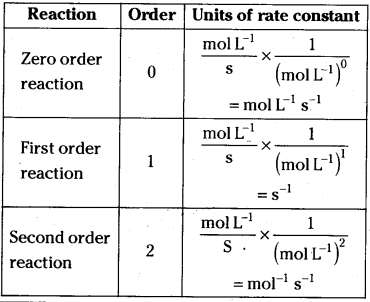
Question 12.
Define molecularity of a reaction. Illustrate with an example.
Answer:
The number of reacting species (atoms, ions, molecules) taking part in an elementary reaction, which must collide simultaneously in order to bring about a chemical reaction is called molecularity of a reaction.
Example:
i) NH4NO2 → N2 + 2H2O
Since only one molecule is involved in the reaction it is unimolecular reaction.
ii) H2 + I2 → 2HI
Since two molecules are involved in the reaction it is a bimolecular reaction.

Question 13.
What is rate determining step in a complex reaction ?
Answer:
Suppose if a reaction proceeds in a sequence of elementary reactions, the overall rate of reaction is controlled by the slowest step and it is called as rate determining step.
Question 14.
Give the mechanism for the decomposition reaction of H2O2 in alkaline medium cata-lysed by I– ion.
Answer:
Decomposition of H2O2 in alkaline medium catalysed by I– ions proceeds in the following steps.
- H2O2 + I– → H2O + IO–
- H2O2 + IO– → H2O + I– + O2
Question 15.
Write the equation relating [R], [R]0 and reaction time ‘t’ for a zero order reaction [R] = concentration of reactant at time ‘t’ and [R]0 = initial concentration of reactant.
Answer:
k = \(\frac{[\mathrm{R}]_0-[\mathrm{R}]}{\mathrm{t}}\) ; Rate = \(\frac{-\mathrm{d}[\mathrm{R}]}{\mathrm{dt}}\) = k[R]0
k = rate constant
[R]0 = initial concentration
[R] = concentration of reactant at time t.
Question 16.
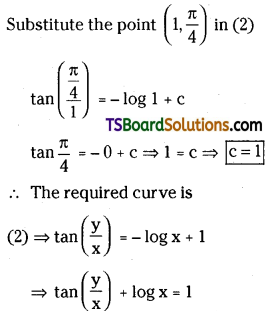
Draw the graph that relates the concentra-tion ‘R’ of the reactant and’t’ the reaction time for a zero order reaction.
Answer:
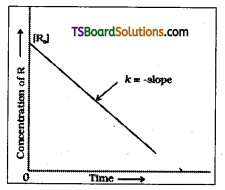
Question 17.
Give two examples for zero order reactions. (TS Mar. ‘ 19 )
Answer:
- The decomposition of gaseous ammonia on a hot platinum surface is a zero order reaction at high pressure.
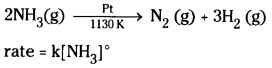
- Thermal decomposition of HI on gold surface is zero order reactions.
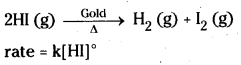
- Photochemical reactions are zero order
Question 18.
Write the Integrated equation for a first order reaction In terms of [R], [R]0 and t.
Answer:
k = \(\frac{2.303}{t}\) log \(\frac{[\mathrm{R}]_0}{[\mathrm{R}]}\)
k = First order rate constant
[R] = Concentration of R at time t
[R]0 = initial concentration R
Question 19.
Give two examples for gaseous first order reactions. (IPE 14)
Answer:
- Hydrogenation of ethane is an example of first order reaction.
C2H4(g) + H2(g) → C2H6(g) - Decomposition of N2O5
N2O5 (g) → 2NO2 + \(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g})\)
Question 20.
For the reaction: A(a) → B(g) + C(g), write the integrated rate equation in terms of total pressure p and the partial pressures PAPBPC.
Answer:
Total pressure Pt = PA + PB + PC
pA, pB and pC are the initial pressures of A, B and C respectively.
pi = initial pressure at time, t = 0.
k = \(\frac{2.303}{t}\)log \(\frac{p_i}{p_A}\) = \(\frac{2.303}{\mathrm{t}}\)log \(\frac{p_i}{2 p_i-p_t}\)
Question 21.
What is half-life of a reaction? Illustrate your answer with an example.
Answer:
The half – life of a reaction is the time in which the concentration of a reactant is reduced to one half of its initial concen-tration. It is represented by t½.
Ex: Half life of C – 14 is 5730 years.
t1/2 = \(\frac{0.693}{\mathrm{k}}\)
For a first order reaction half-period Is constant and is independent of initial con-cent ration.

Question 22.
Write the equation relating the half-life (t1/2) of a reaction and the rate constant ‘K’ for first order reaction.
Answer:
For the first order reaction
k = \(\frac{2.303}{t}\)log \(\frac{[\mathrm{R}]_0}{[\mathrm{R}]}\) at t1/2 [R] = \(\frac{[\mathrm{R}]_0}{2}\)
So the above equation becomes
k = \(\frac{2.303}{t_{1 / 2}}\) log \(\frac{[\mathrm{R}]_0}{[\mathrm{R}]_{0 / 2}}\)
or t1/2 = \(\frac{2.303}{\mathrm{k}}\)log 2 or t1/2 = k
For a first order reaction half-period is constant and is independent of initial con-centration.
Question 23.
Write the equation useful to calculate half-life (t1/2) values for zero and first order reactions.
Answer:
- Half-life for zero order reaction
t1/2 = \(\frac{[\mathrm{R}]_0}{2 \mathrm{k}}\) - Half-life for first order reaction
t1/2 = \(\frac{693}{\mathrm{k}}\) k is rate constant
Question 24.
What are Pseudo first order reactions? Give one example.
Answer:
The reactions which appear to be second order but follow the first order rate equation are called Pseudo first order reactions.
Example :
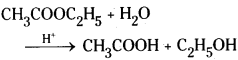
Since the concentration of water is large excess, the change in concentration of water is negligible. So its concentration is taken as constant. Then rate of reaction depend only on the concentration of CH3COOC2H5.
Rate = k[CH3COOC2H5]
Inversion of cane sugar is another example of pseudo first order reaction.
Question 25.
Write the Arrhenlus equation for the rate constant (k) of a reaction.
Answer:
Arrhenius equation for the rate constant (k) is
k = Ae-Ea/RT
A = Arrhenlus frequency factor
R = Gas constant
Ea = Activation energy measured in Joules mol-1
T = Absolute temperature
Question 26.
By how many times the rate constant increases for rise of reaction temperature by 10°C?
Answer:
For a chemical reaction with rise in temperature by 10° the rate constant is nearly doubled.
Question 27.
Explain the term ‘activation energy’ of a reaction with a suitable diagram.
Answer:
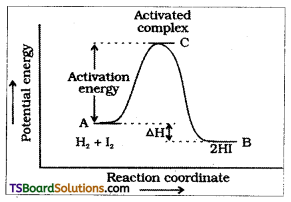
The energy required to form the intermediate called activated complex (C) is known as activatioñ energy Ea.
Question 28.
Write the equation which relates the rate constants k1 and k2 at temperatures T1 and T2 of a reaction.
Answer:
log \(\frac{\mathrm{k}_2}{\mathrm{k}_1}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}}}{2.303 \mathrm{R}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{T}_2-\mathrm{T}_1}{\mathrm{~T}_1 \mathrm{~T}_2}\right]\)
k1 and k2 are the rate constants of a reaction at temperatures T1 and T2 respectively. Ea is activation energy.
Question 29.
What is collision frequency (Z) of a reac-tion? How is rate related to it for the reaction A + B → Products.
Answer:
The number of collisions per second per unit volume of the reactibn mixture is known as collision frequency (Z).
For a bimolecular elementary reaction
A + B → Products
Where ZAB represents the collision frequency of reactants A and B. \(\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{Ea} / \mathrm{RT}}\) represent the fraction of molecules with energies equal to or greater than Ea.
Question 30.
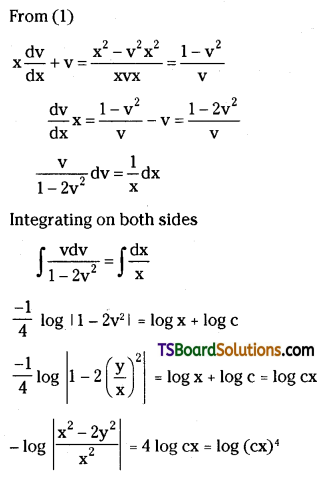
Draw the graphs between potential energy – reaction coordinates for catalysed and uncatalysed reactions.
Answer:
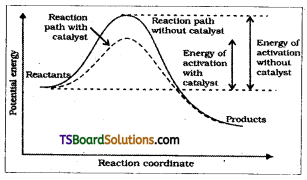
Effect of catalyst on activation energy
Question 31.
What is the effect of temperature on the rate constant?
Answer:
The rate constant of reaction is almost doubled for every rise of 10° in temperature. The temperature dependence of rate of a
chemical reaction is given by Arrhenius equation
k = A. \(\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{Ea} / \mathrm{RT}}\)
A = Arrhenius frequency factor
T = Absolute temperature
R = Gas constant
Ea = Activation energy
Short Answer Questions (4 Marks)
Question 32.
Define average rate of a reaction. How is the rate of reaction expressed in terms of change in the concentration of reactants and products for the following reactions.
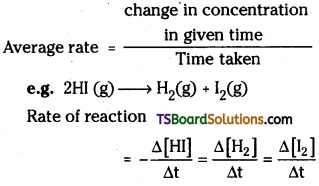
1) 2HI (g) → H2(g) + I2(g)
2) Hg(l) + Cl2 (g) → HgCl2(s)
3) 5Br,sup>- (aq) + \(\mathrm{BrO}_3^{-}(\mathrm{aq})\) + 6H+(aq) → 3Br2(aq) + 3H2O(l)
Answer:
The average rate of a reaction is defined as the rate of change of concentration per unit time.
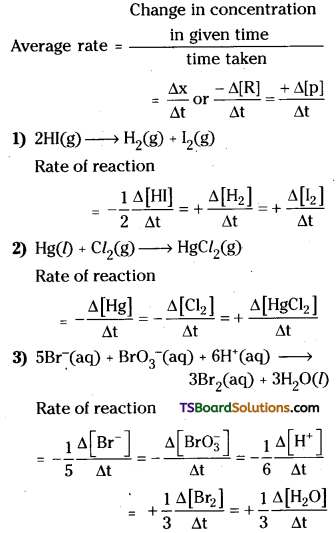
Question 33.
What is rate equation? How is it obtained? Write the rate equations for
1) 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
2) CHCl3 + Cl2 → CCl4 + HCl
3) CH3COOC2H5(l) + H2O(l) → CH3COOH(aq) + C2H5OH(l)
Answer:
The mathematical expression written in terms of concentration of reactants, which actually influence the rate is called rate law or rate equation.
1) 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
Rate = k [NO]2 [O2]
2) CHCl3 + Cl2 → CCl4 + HCI
Rate = k [CHCl3] [Cl2]1/2
3) CH3COOC2H5 + H2O → CH3COOH + C2H5OH
Rate = k [CH3COOC2H5]1 [H2O]0
Experimental data shows that the exponents of the concentration terms may be same as their stoichiometric coefficients in the balance chemical equation as in the example (1) or may not be same as in examples (2) and (3).
Question 34.
Define and explain the order of a reaction. How is it obtained experimentally?
Answer:
The sum of the powers of exponents to which the concentration terms are raised in the rate law expression is called order of reaction.
For a hypothetical reaction
aA + bB → Products
The rate equation is Rate = k[A]x [B]y
Where x + y = n = order of the reaction. The decrease in the concentration of reactants or the increase in the concentration of products are measured experimentally. These values are substituted in rate constant equations of different order of reactions. The equation that gives constant value gives the order of reaction.
Question 35.
What is “molecularity” of a reaction? How is it different from the ‘order’ of a reaction ? Name one bimolecular and one tri- molecular gaseous reactions. (IPE 14)(Mar. 2018 AP)
Answer:
The number of reacting species (atoms, ions or molecules) taking part in an elementary reaction which must collide simultaneously in order to bring about a chemical reaction is called molecularity of a reaction.
- Order of a reaction is an experimental quality. It can be zero and even a fraction but molecularity cannot be zero or non – integer.
- Order is applicable to elementary as well as complex reactions whereas molecularity is applicable only for elementary reactions. For complex reaction molecularity has no meaning.
- For complex reaction, order is given by the slowest step and molecularity of the slowest step is taken as the order of the overall reaction.
Dissociation of hydrogen iodide into H2 and I2 is a bimolecular reaction.
2HI → H2 + I2
Formation of NO2 from NO and O2 is a trimolecular reaction.
2NO + O2 → 2NO2
Question 36.
Derive the integrated rate equation for a zero order reaction.
Answer:
Zero order reaction means that the rate of the reaction is proportional to zero power of the concentration of reactants. Consider the reaction
R → P
Rate = –\(\frac{\mathrm{d}[\mathrm{R}]}{\mathrm{dt}}\) = k[R]°
or Rate = –\(\frac{\mathrm{d}[\mathrm{R}]}{\mathrm{dt}}\) = k × 1( ∵ [R]° = 1)
d[R] = – kdt
Integrating both sides
[R] = – kt +1 (I = integration constant) … (1)
At t = 0, the concentration of the reactant
R0 = [R]0, When [R]0 is initial concentration of the reactant.
Substituting in equation (1)
[R]0 = -k × 0 + 1
[R]0 = I
Substituting the value of I in (1)
[R] = – kt + [R]0 ….. (2)
Further simplifying equation (2) we get the rate constant k as
k = \(\frac{[\mathrm{R}]_0-[\mathrm{R}]}{\mathrm{t}}\)

Question 37.
Derive an Integrated rate equation for a first order reaction.
Answer:
In this type of reactions, the rate of the reaction is proportional to the first power of the concentration of the reactant R. For
example
Rate = –\(\frac{\mathrm{d}[\mathrm{R}]}{\mathrm{dt}}\) = k[R] or \(-\frac{\mathrm{d}[\mathrm{R}]}{\mathrm{R}}\) = kdt
Integrating tuis equation we get
In [R] = -kt + I (I = integration constant) ….. (1)
When t = 0, [R] = [R]0
∴ ln [R]0 = -k × 0 + I
ln [R]0 = I
Substituting the value I in equation (1)
ln[R] = -kt + ln[R]0 or ln \(\frac{[\mathrm{R}]}{\left[\mathrm{R}_0\right]}\) = -kt
or k = \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}} \ln \frac{[\mathrm{R}]_0}{[\mathrm{R}]}\) or k = \(\frac{2.303}{t} \log \frac{[R]_0}{[R]}\)
This is the integrated rate equation for first order reaction.
Question 38.
Derive an integrated rate equation in terms of total pressure [P] and the partial pressures PA, PB, PC for the gaseous reaction
A(g) → B(g) + C(g).
Answer:
The gaseous reaction A(g) → B(g) + C(g)
Let P1 be the initial pressure of A and bt the total pressure at time t. Integrated rate equation for such a react Ion can be derived as
Total pressure Pt = PA + PB + PC
PA, PB and PC are the partial pressures of A, B and C respectively.
If x atm be the decrease in pressure of A at time t and one mole each of B and C is being formed, the increase in pressure of B and C will also be x atm each.
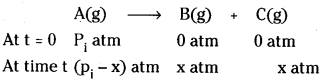
When pi is the intial pressure at time t = 0
Pt = (pi – x) + x + x = pi + x
x = pt – pi
Where PA = pi – x
= pi – (pt – pi)
= 2pi – pt
k = \(\frac{2.303}{t}\)log\(\frac{p_i}{p_A}\)
= \(\frac{2.303}{t}\)log\(\frac{p_i}{2 p_i-p_t}\)
Question 39.
What is half-life (t1/2) of a reaction? Derive the equations for the ‘half-life’ value of zero and first order reactions.
Answer:
The half – life of a reaction is the time in which the concentration of a reactant is reduced to one half of its initial concentra-tion. It is represented as t½.
For the first order reaction
k = \(\frac{2.303}{t}\) log\(\frac{[\mathrm{R}]_0}{[\mathrm{R}]}\) at t1/2[R] = \(\frac{[\mathrm{R}]_0}{2}\)
So the above equation becomes
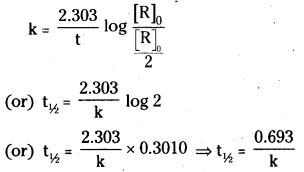
Question 40.
What is Arrhenius equation? Derive an equation which describes the effect of rise of temperature (T) on the rate constant (k) of a reaction.
Answer:
Arrhenius equation explains the temperature dependence of the rate of a chemical reac-tion. Arrhenius equation is
k = Ae-Ea/RT
Where A is the Arrhenius factor, or the frequency factor. R is gas constant and Ea is activation energy in J mol-1.
Taking natural logarithms of both sides
In k = –\(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}}}{\mathrm{RT}}\) + ln A …… (1)
At temperature T1, the equation (1) is
In k1 = –\(\frac{E_a}{R T}\) + ln A …… (2)
At temperature T2, the equation (1) is
In k2 = –\(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}}}{\mathrm{RT}}\) + ln A …… (3)
Subtracting equation (2) from (3) we get
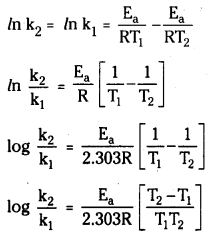
Question 41.
Discuss the effect of catalyst on the kinetics of a chemical reaction with a suitable diagram.
Answer:
A catalyst is a substance which increase the rate of a reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change.
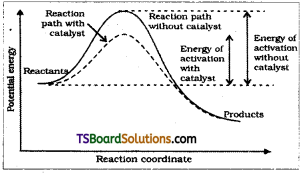
It is believed that the catalyst provides an alternate pathway or reaction mechanism by reducing the activation energy between reactants and products and hence lowering the potential energy barrier as shown in the figure. Lower the value of activation energy faster will be the rate of reaction.
Question 42.
Describe the salient features of the collision theory of reaction rates of bimolecular reactions. (Mar. 2018-TS)
Answer:
Collision theory is based on kinetic theory of gases. According to this theory
- The reactant molecules are assumed to be hard spheres and
- Reaction is postulated to occur when molecules collide with eách other.
- A reaction occurs on collision of two molecules only if they possess a certain minimum amount of energy in excess of the normal energy of molecules.
- The minimum energy which molecules must possess before collision should be equal to or greater than the activation energy.
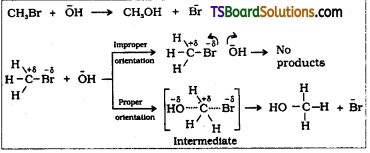
- The collisions in which the reactant molecules have proper orientation only leads to the formation of products.
- Whereas Improper orientation makes them bounce back and no products are formed.
- The collisions in which reactant molecules convert into product molecules are called effective or fruitful collisions.
Question 43.
Explain the terms
a) Activation energy (Ea)
b) ColIsIon frequency (Z)
c) Probability factor (P) with respect to Arrhenius equation.
Answer:
a) Activation energy : According to Arrhenius, a reaction takes place only when reactant molecules collide and form an unstable intermediate which have higher potential energy than reactant or product molecules. The energy required
for the formation of this intermediate or activated complex is called activation energy.
b) Collision frequency : According to collision theory the reactant molecules are assumed to be hard spheres and reaction occurs when molecules collide with each other. The number of collisions per second per unit volume of the reaction mixture is known as collision frequency (Z). For the bimolecular elementary
A + B → Products
Rate = ZAB\(\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}} / \mathrm{RT}}\)
ZAB represents the collision frequency of reactants A and B.
c) Probability factor: To account for effective collisions, a factor known as probability factor or steric factor is introducted. It takes into account the fact that in a collision molecules must be properly oriented.
(ie.,) Rate = P × ZABeEa/RT
Long Answer Questions
Question 44.
Explain the following terms with suitable examples.
(a) Average rate of a reaction
(b) Slow and fast reactions
(c) Order of a reaction
(d) Molecularity of a reaction
(e) Activation energy of a reaction.
Answer:
a) Average rate of a reaction : The average rate of a reaction is defined as the rate of change of concentration per unit time.
b) Slow and fast reactIons : The reactions which takes place instantaneously are called fast reactions. Ionic reactions are fast reactions e.g. Precipitation of silver chloride occurs instantaneously by mixing aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and sodium cholride.
Some reactions takes place slowly e.g. rusting of iron, invension of sugar, hydrolysis of starch. These reactions are called slow reactions.
c) Order of ReactIon : The sum of the powers or exponents to which the concentration terms are raised in the rate law expression is called order of reaction.
For a hypothetical reaction
aA + bB → Products
The rate equation is Rate = k[A]x [B]y
Where x + y = n = order of the reaction.
d) Molecularity of the reaction : The number of reacting species (atoms or ions or molecules) taking part in an elementary reaction which must collide simultaneously in order to bring about a chemical reaction is called molecularity of a reaction.
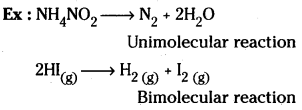
e) Activation energy of a reaction: Accor-ding to Arrhenius, a reaction takes place only when reactant molecules collide and form an unstable intermediate which have higher potential energy than reac-tant or product molecules. The energy required for the formation of this inter-mediate or activated complex is called activation energy.
Ea = ET – ER
Question 45.
Give two examples for each of zero order and first order reactions. Write the equa-tions for the rate of a reaction interms of concentration changes of reactants and products for the following reactions.
1) A(g) + B(g) → C(g) + D(g)
2) A(g) → B(g) + C(g)
3) A(g) + B(g) → C(g)
Answer:
Examples for zero order reaction :
i) The decomposition of gaseous ammonia on a hot platinum surface is a zero order reaction at higher pressure.
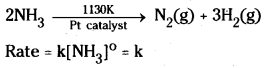
At high pressure, the surface of the metal is completely covered with gas molecules, so unable to alter the ammonia on the surface of the catalyst making the rate of reaction independent of its concentration.
ii) Thermal decomposition of HI on gold surface is another example of zero order reaction.
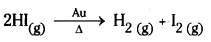
iii) Some enzyme catalysed reactions are zero order reactions.
Examples for first order reactions:
i) Decomposition of N2O5.
N2O5 → 2NO2 + \(\frac{1}{2}\)O2
ii) All natural and artificial radioactive decay of unstable nuclei take place by first order kinetics.
\({ }_{88}^{226} \mathrm{Ra}\) → \({ }_2^4 \mathrm{He}\) + \({ }_{86}^{224} \mathrm{Rn}\)
Rate of reactions:
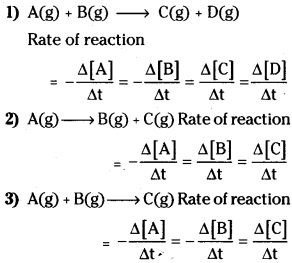

Question 46.
Discuss the effect of temperature on the rate of a reaction. Derive necessary equations in this context.
Answer:
The rate constant of a reaction increases with increase of temperature. This increase is generally two fold to five-fold for 10° rise in temperature. This is explained on the basis of collision theory. The main points of collision theory are as follows.
- For a reaction to occur, there must be collisions between the reacting species.
- Only a certain fraction of total collisions are effective in forming the products.
- For effective collisions the molecules must possess the sufficient energy equal to or greater than activation energy as well as proper orientation.
On the basis of above conclusions, rate of reaction is given by
Rate = f × z where f is the effective collisions and z is total number of collisions per unit volume per second.
Quatitatively the effect of temperature on the rate of reaction and hence on the rate constant k was proposed by Arrhenlus.
k = Ae-Ea/RT —– (1)
Where A is a constant called frequency factor, Ea is the energy of activation R is gas constant and T is the absolute temperature.
The factor e-Ea/RT gives the fraction of molecules having energy equal to or greater than the activation energy, Ea.
Taking logarithms on both sides of equation (1) we get
In k = ln A – \(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}}}{\mathrm{RT}}\)
The value of rate constant at temperatures T1 and T2 are k1 and k2 respectively, then we have
ln k1 = ln A – \(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}}}{\mathrm{RT}_1}\) …. (2)
ln k2 = ln A – \(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}}}{\mathrm{RT}_2}\) …. (3)
Subtracting equation (2) from (3) we get
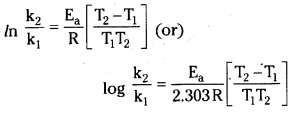
Question 47.
Give a detailed account of the collision theory of reaction rates of bimolecular gaseous reactions. (TS 16: IPE 14)
(TS Mar. 19; (Mar.2018.TS)
Answer:
According to collision theory
- The reactant molecules are assumed to be hard spheres.
- Reaction occur only when molecules collide each other.
- All collisions do not lead to the forma-tion of products.
- The collisions in which the molecules having threshold energy and proper orientation leads to the formation of products.
- Such collisions are called effective collisions.
- The number of collisions per second per unit volume of the reaction mixture is known as collision frequency (Z).
- Activation energy also effects the rate chemical reactions. For a bimolecular elementary reaction.
A + B → Products Rate of reaction is
Rate = ZAB e-Ea/RT
Where ZAB represents the collision frequency of reactants. A and B and e-Ea/RT represents the fraction of molecules with energies equal to or greater than Ea. - If the colliding molecules have improper orientation they bounce back and no reaction takes place.
- To account for effective collisions a new factor ‘p called probability or steric factor is introduced
Rate = PZABe-Ea/RT
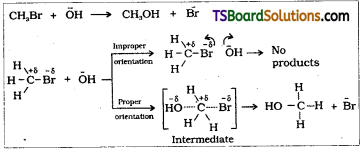
- Thus, in collision theory activation energy and proper orientation of the molecules together determine the criteria for
an effective collision and hence the rate of a chemical reaction.
Numerical Data Based And Concept Oriented Questions
Question 48.
A reaction is 50% completed in 2 hours and 75% completed In 4 hours. What is the order of the reaction?
Answer:
50% completed means half – life.
So for first order reaction t1/2 = 0.
or k = \(\frac{0.693}{k}\) = 0.3465 mol hr-1
In the second experiment 75% completed in 4 hours.
k = \(\frac{2.303}{t} \log \frac{[R]_0}{[R]}\)
[R]0 = 100, [R] = 25
∴ k = \(\frac{2.303}{4}\)log\(\frac{100}{25}\) = \(\frac{2.303}{4}\) log 4
= \(\frac{2.303}{4}\) × 0.6021 = 0.3466
Since k is constant in both experiments, it is first order reaction.
Question 49.
A reaction has a half-life of 10 minutes. Calculate the rate constant for the first order reaction. (TS ’16)
Answer:
For first order reaction
k = \(\frac{0.693}{t_{1 / 2}}\) = \(\frac{0.693}{10}\) = 0.0693 min-1
Question 50.
In a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant is reduced from 0.6 mol/L to 0.2 mol/L m 5 min. Calculate the rate constant (k).
Answer:
Initial concentration [R]0 = 0.6 moL/L
Concentration after 5mn [R] = 0.2 mol /L
First order rate equation
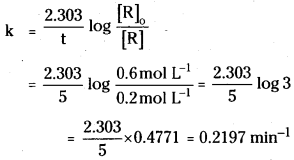
Question 51.
The rate conant for a zero order reaction in A is 0.0030 mol L-1 s-1. How long it will take for the initial concentration of A to fall from 0.10M to 0.075M.
Answer:
For zero order reaction
k = \(\frac{[\mathrm{R}]_0-[\mathrm{R}]}{\mathrm{t}}\) or t = \(\frac{[\mathrm{R}]_0-[\mathrm{R}]}{\mathrm{t}}\)
k = 0.0030 mol L-1 s-1
[R]0 = 0.10M
[R] = 0.075
∴ t = \(\frac{0.10-0.075}{0.0030}\) = 8.33 sec
Question 52.
A first order decomposition reaction takes 40mm for 30% decomposition. Calculate its t1/2 value.
Answer:

Question 53.
Calculate the half-lIfe of first order reaction whose rate constant is 200 s-1.
Answer:
For first order reaction
t1/2 = \(\frac{0.693}{\mathrm{k}}\) = \(\frac{0.693}{200}\) = 0.003465
= 3.465 × 10-3 s
Question 54.
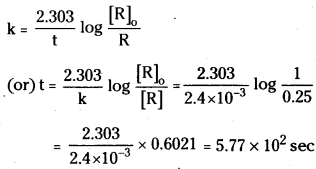
The thermal decomposition of HCOOH is a first order reaction. The rate constant is 2.4 × 10-3 s-1 at a certain temperature. Calculate how long will It take for 3/4 of initial quantity of HCOOH to decompose.
Answer:
Rate constant k = 2.4 × 10-3s-1
[R]0 = 1; [R] = 0.25 ;
Question 55.
The decomposition of a compound is found to follow first order rate law. If it takes 15 minutes for 20% of original material to
react, calculate the rate constant.
Answer:
For a first order reaction
k = \(\frac{2.303}{t} \log \frac{[R]_0}{[R]}\)
[R]0 = 100; [R] =80; t = 15
k = \(\frac{2.303}{15}\)log\(\frac{100}{80}\) = \(\frac{2.303}{15}\) log 1.25
= \(\frac{2.303}{15}\) × 0.0963 = 0.0148 min-1

Question 56.
In a pseudo first order hydrolysis of ester in water, the following results are obtained

Calculate the average rate of reaction between the time Interval 30 to 60 s.
Answer:
i) Average rate of reaction between interval time 30 to 60 seconds is given by
Average rate = \(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{x}}{\Delta \mathrm{t}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{C}_2-\mathrm{C}_1}{\Delta \mathrm{t}}\)
= \(\frac{0.17-0.31}{60}\) = \(-\frac{0.14}{30}\)
= -0.00467 = -4.67 × 10-3 Ms-1
Minus sign indicate that the rate of reaction is decreasing with time as concentration of ester is decreasing with time.
ii)

Question 57.
The half – life for a first order reaction is 5 × 10-6 s. What percentage of the Initial reactant will react in 2 hours?
Answer:
Given that
Half-life for the first order reaction = 5 × 10-6 s
First order rate constant, k = \(\frac{0.693}{5 \times 10^{-6} \mathrm{~s}}\)
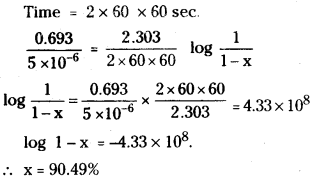
Question 58.
H2O2 (aq) decomposes to H2O(l) and O2(g) in a first order reaction w.r.t. H2O2. The rate constant is k = 1.06 × 10-3 min-1. How long it will take 15% of the sample to de-compose ?
Answer:
Given that
Rate constant k = 1.06 × 10-3 min-1
Initial concentration of reactant [R]0 = 100
Concentration of reactant at time
t[R]t = 100 – 15 = 85
First order rate constant
k = \(\frac{2.303}{t} \log \frac{\left[R_o\right]}{[R]}\);
t = \(\frac{2.303}{1.06 \times 10^{-3}} \log \frac{100}{85}\) ; t = 153 min
Question 59.
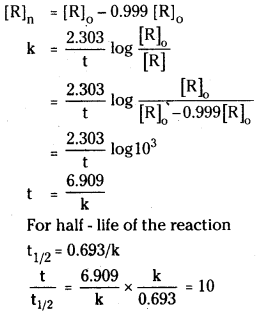
Show that in the case of first order reaction, the time required for 9999% completion of the reaction is 10 times that required for 50% completion. (log 2 = 3010)
Answer:
When the reaction has completed 99.9%
Question 60.
The rate constant of a reaction is doubled when the temperature is raised from 298K to 308K. Calculate the activation energy.
Answer:
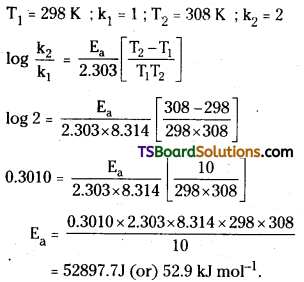
Question 61.
The first order rate constant k for the reaction C6H5I(g) → C2H4(g) + HI(g) at 600K is 1.60 × 10-5s-1. The energy of activation is 209 kJ mol. Calculate k at 700 K.
Answer:
Given that
Rate constant at 600 K = 1.60 × 10-5 s-1
Rate constant at 700 K =?
R = 8.314 J kJ mol-1
T1 = 600K T2 = 700K
Activation energy Ea = 209 kJ mol-1 = 209000 J
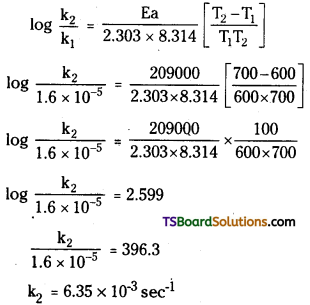
Question 62.
The activation energy for the reaction 2HI(g) → H2(g) + I2(g) at 581K is 209.5 kJ/mol. Calculate the fraction of molecules having energy equal to or greater than activation energy. (R = 8.31 JK-1 mol-1]
Answer:
Temperature T = 581K
Activation energy Ea = 209.5 JK mol-1
R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
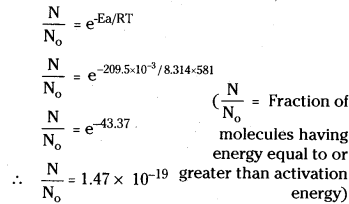
Question 63.
For the reaction R → p, the concentration of a reactant changes from 0.03M to 0.02M in 25 minutes. Calculate the average
rate of reaction using units seconds.
Answer:
Given that
[R]0 = 0.03M
[R] = 0.02M
[R]0 – [R] = 0.03 – 0.02 = 0.01M
Time = 25 mm = 25 × 60 sec.
Average rate of reaction = \(\frac{[R]_0-[R]}{t}\)
= \(\frac{0.01}{25 \times 60}\) = 6.66 × 10-6 Ms-1
Question 64.
In a reaction 2A → Products, the concentration of A decreases from 0.5 mol L-1 to 0.4 moL-1 in 10 minutes. Calculate the rate during this Interval.
Answer:
2A → Products
Rate \(\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{dt}}\) = \(-\frac{1}{2} \frac{\Delta[\mathrm{A}]}{\Delta \mathrm{t}}\)
Δ[A] = 0.5 – 0.4 = 0.1 mol-1
Rate = \(-\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{0.1}{10}\) = 5 × 10-3 mol-1 L-1 min-1
Question 65.
For a reaction, A + B → product : the rate law is given by r = k[A]1/2[B]2. What is the order of reaction?
Answer:
Order of reaction Is the sum of the powers of concentration terms in rate equation.
Rate equation r = k[A]1/2 [B]2
∴ order = 0.5 + 2 = 2.5
Question 66.
The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased by three times, how will it affect the rate of formation of Y.
Answer:
Since the reaction follows second order kinetics r = k(x)2
x increases by 3 times
∴ r = k(3)2
So rate increases by nine times.

Question 67.
A first order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10-3s-1. How long will 5g of this reactant take to reduce to 3g ?
Answer:
Rate constant k = 1.15 × 10-3s-1
Initial cone. [R]0 = 5
Conc. at time t [R] = 3
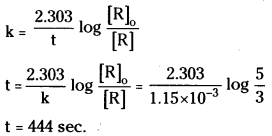
Question 68.
Time required to decompose SO2Cl2 to half of its initial amount is 60 minutes. If the decomposition is a first order reaction, calculate the rate constant of the reaction.
Answer:
For first order reaction
k = \(\frac{0.693}{t_{1 / 2}}\) = \(\frac{0.693}{60 \times 60}\) = 1.925 × 10-4 sec-1
(or) 1.155 × 10-2 min-1
Question 69.
From the rate expression for the following reactions, determine their order of reaction and the dimensions of the rate constants.
i) 3NO(g) → N2O(g)
Rate = k[NO]2
ii) H2O2(aq) + 3I–(aq) + 2H+ → 2H2O(l) + \(I_3^{-}\)
Rate = k[H2O2] [I–]
iii) CH3CHO(g) → CH4(g) + CO(g)
Rae = k[CH3CHO]3/2
iv) C2H5Cl (g) → C2H4 (g) + HCl(g)
Rate = k[C2H5Cl]
Answer:
i) 3NO(g) → N2O (g)
Rate = k[NO]2
Order w.r.t NO = 2
Overall order = 2
Units of k = (mol L-1)1-2 s-1
= mol-1 L s-1
ii) H2O2 + 3l– + 2H+ → 2H2O + \(I_3^{-}(\mathrm{aq})\)
rate = k[H2O2] [I–]
Order w.r.t. H2O2 = 1
Order w.r.t. I– = 1
Overall order =2
Units of k = (mol L-1)1-2 s-1
= mol-1 L s-1
iii) CH3 CHO(g) → CH4(g) + CO(g)
rate = k[CH3CHO]3/2
Order w.r.t. CH3CHO = 1.5
Overall order = 1.5
Units of k = (mol L-1)1-1.5s-1
= mol1/2 L1/2 s-1
iv) C2H5Cl(g) → C2H4(g) + HCl (g)
rate = k[C2H5Cl]
order w.r.t. C2H5Cl = 1
overall order = 1
Units of k = (mol L-1)1-1 s-1
= s-1
Question 70.
For the reaction 2A + B → AB, the rate = k[A][B]2 with k = 2.0 × 106 v mol-2 L2s-1. Calculate the Initial rate of the reaction when [A] = 0.1mol L-1, [B] = 0.2 mol L-1. Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 0.06 mol L-1.
Answer:
Given that
k = 2.0 × 10-6 mol-2 L2 s-1
[A] = 0.1 mol L-1
[B] = 0.2 mol L-1
i) Initial rate = k[A] [B]2
= 2 × 10-6 × 0.1 × (0.2)2
∴ Rate of reaction = 8 × 10-9 mol L-1sec-1
ii) 2A + B → AB
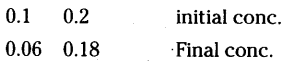
r = 2 × 10-6 × 0.06 × (0.18)2
∴ Rate of reaction = 3.89 × 10-9 mol L-1sec-1
Question 71.
The decomposition of NH3 on platinum surface is zero order reaction. What are the rates of production of N2 and H2 if k = 2.5 × 10-4 mol-1 Ls-1.
Answer:
Since the decomposition of NH3 on platinum surface is zero order.
So rate of reaction k = 2.5 × 10-4 mol L-1 sec-1.
2NH3 → N2 + 3H2
\(\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{dt}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{dN}_2}{\mathrm{dt}}\) = \(\frac{1}{3} \frac{\mathrm{dH}_2}{\mathrm{dt}}\)
Rate production of N2 = \(\frac{\mathrm{dN}_2}{\mathrm{dt}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{dt}}\)
= 2.5 × 10-4 mol-1 L-1 sec-1
Rate production of H2 = \(\frac{\mathrm{dH}_2}{\mathrm{dt}}\) = \(\frac{3 \mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{dt}}\)
= 7.5 × 10-4 mol L-1 sec-1
Question 72.
The rate expression for the decomposition of dimethyl ether in terms of partial pressures is given as Rate = k(pCH3 O CH3)3/2. If the pressure is measured in bar and time in minutes, then what are the units of rate and rate constant ?
Answer:
Units of rate = bar min-1
r = k p3/2
bar min-1 = k (bar)3/2
∴ k = bar-1/2 min-1
Question 73.
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction is affected if the concentration of the reactant is
(i) doubled
(ii) reduced to half.
Answer:
Ratio of second order reaction = k[Reactant]2
When the concentration is doubled Rate = k[2]2
∴ Rate increases by 4 times.
When concentration is reduced to half.
rate = k\(\left[\frac{1}{2}\right]^2\)
∴ Rate decreases to \(\frac{1}{4}\) times.
Question 74.
A reaction is first order in A and second order in B.
i) Write the differential rate equation,
ii) How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of B three times ?
iii) How is the rate affected when the concentration of both A and B are doubled ?
Answer:
The reaction is first order in A and second order in B.
∴ The differential rate equation r = k [A]1 [B]2
When the concentration of B is increased three times r = k[A][B]2
∴ rate increases by 9 times
When the concentration of both A and B are doubled
r = k[2][2]2
∴ Rate increases by 8 times.
Question 75.
In a reaction between A and B, the initial rate of reaction (r0) was measured for different initial concentrations of A and B as given below :

What is the order of the reaction with respect to A and B ?
Answer:
Rate of reaction r = kAm Bn
5.07 × 10-5 = k(0.2)m (0.3)n
5.07 × 10-5 = k(0.2)m (0.1)n
1.43 × 10-5 = k(0.4)m (0.05)n
∴ order of reaction with respect to A = 1.5
∴ r = k A1.5 B0
order of reaction with respect to B = 0
Question 76.
The following results have been obtained during the kinetic studies of the reaction:
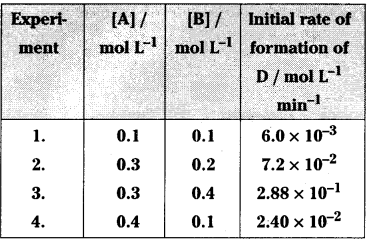
Determine the rate law and rate constant for the reaction.
Answer:
When [A] = [B] the intial rate of formation of D is 6.0 × 10-3 mol L-1 min-1
From the experiment no.4 when the concentration of A is increased four times keeping the concentration B. Constant the rate increases by 4 times i.e.
6.0 × 10-3 × 4 = 2.4 × 10-2
So the order of reaction with respect to A is 1
From the experiments 2 and 3, when the concentration of B is doubled keeping the concentration of A constant the rate increases by 4 times i.e.,
7.2 × 10-2 × 4 = 2.88 × 10
∴ The order of reaction w.r.t B = 2
Rate law = k[A][B]2
Rate = k[A][B]2
6.0 × 10-3 = k[0.1] [0.1]2
6.0 × 10-3 = k × 1 × 10-3
k = \(\frac{6.0 \times 10^{-3}}{10^{-3}}\) = 6.0 Mol-1 L2 min-1
Question 77.
The rate constant for a first order is 60 s-1. How much time will It take to reduce the initial concentration of the reactant to its 1/16th value.
Answer:
Rate constant = 60 s-1
For first order reaction
t1/2 = \(\frac{0.693}{k}\) = \(\frac{0.693}{60}\) = 0.01155 sec.
t = 4t1/2 = 4 × 0.01155 = 4.62 × 10-2 sec.
Question 78.
For a first order reaction, show that the time required for 99% completion is twice the time required for completion of 90% of reaction.
Answer:
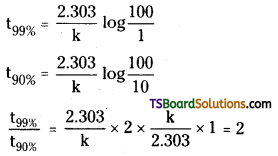
∴ The time required for 99% completion is twice the time required for completion of 90% reaction.

Question 79.
For the decomposition of azoisopropane to hexane and nitrogen at 543 K, the following data are obtained.
| t(sec) | p(mm of Hg) |
| 0 | 35.0 |
| 360 | 54.0 |
| 720 | 63.0 |
Answer:
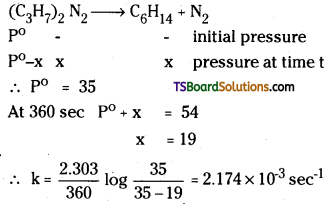
Question 80.
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at a constant volume.
SO2Cl2(g) → SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
| Experiment | Time/s-1 | Total Pressure / atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.6 |
Calculate the rate of reaction when total pressure is 0.65 atm.
Answer:

Pressure of SO2Cl2 = 0.35
∴ r = k[SO2Cl2] = (2.23 × 10-3) (0.35)
= 7.8 × 10-4 atm sec-1
Question 81.
The rate constant for the decomposition of hydrocarbons is 2.418 × 10-5 s-1 at 546K. If the energy of activation is 179.9 kJ / mol. What will be the value of pre – exponential factor?
Answer:
Rate constant for the decomposition of hydrocarbon = 2.418 × 10-5s-1
Temperature T = 546 K
Energy of activation Ea = 179.9 kJ / mol.
The value of pre-exponential factor ?
k = Ae-Ea/RT
2.418 × 10-5 = A.e-179.103/8.314 × 546
∴ A = 3.9 × 1012 sec-1.
Question 82.
Consider a certain reaction A → Products with k = 2.0 × 10-2 s-1. Calculate the concentration of A remaining after 100s if the initial concentration of A is 1.0 mol L-1.
Answer:
Rate constant k = 2.0 × 10-2 sec-1
Initial concentration [R]0 = 1.0 mol L-1
Time t = 100 s
Concentration after time T = [R] =?
k = \(\frac{2.303}{t} \log \frac{[R]_0}{[R]}\)
2 × 102 = \(\frac{2.303}{100} \log \frac{1}{1-x}\)
log \(\frac{1}{1-x}\) = 0.868
∴ 1 – x = 0.135M
Question 83.
Sucrose decomposes in acid solution into glucose and fructose according to the first order rate law, with t1/2 = 3.00 hours. What fraction of sample of sucrose remains after 8 hours ?
Answer:
Decomposition of sucrose in acid solution follows first order kinetics
Half – life t1/2 = 3.00 hours
For first order
k = \(\frac{0.693}{3} \mathrm{hr}^{-1}\)
∴ \(\frac{0.693}{3}\) = \(\frac{2.303}{8} \log \frac{1}{1-x}\)
1 – x = 0.157
Question 84.
The decomposition of hydrocarbon follows the equation
K = (4.5 × 1011 s-1) e-28000k/T. Calculate Ea.
Answer:
K = Ae-Ea/RT
\(\frac{E_a}{R}\) = 28000
Ea = 232.79 kJ/mole
Question 85.
The rate constant for the first order de-composition of H2O2 is given by the following equation: log k = 14.34 – 1.25 × 104 K/T. Calculate Ea for this reaction and at what a temperature will its half – life period be 256 minutes ?
Answer:

Question 86.
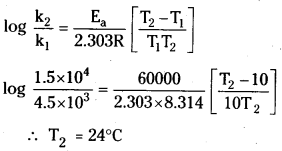
The decomposition of A into product has value of k as 4.5 × 103 S-1 at 10°C and energy of activation 60 kJ mol-1. At what temperature would k be 1.5 × 104 s-1?
Answer:
Question 87.
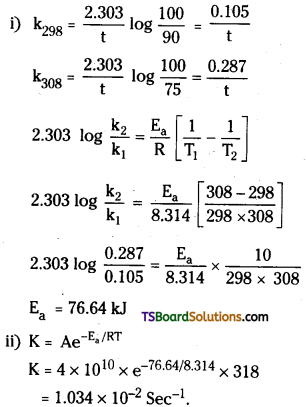
The time required for 10% completion of a first order reaction at 298 K is equal to that required for Its 25% completion at 308K. If the value of A is 4 × 1010 s-1, cal-culate k at 318 K and Ea.
Answer:

Question 88.
The rate of a reaction quadruples when the temperature changes from 293 K to 313 K. Calculate the energy of activation
of the reaction assuming that it does not change with temperature.
Answer:
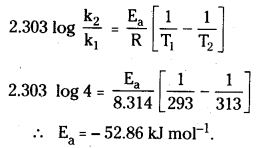
Intext Questions – Answerš
Question 1.
For the reaction R → P, the concentration of a reactant changes from 003M to 002M in 25 minutes. Calculate the average rate of reaction using units of time both in minutes and seconds.
Answer:
The average rate of reaction will be
= \(-\frac{\Delta R}{\Delta t}\) = –\(\frac{[R]_2-[R]_1}{t_2-t_1}\)
Now [R]2 = 0.02M, [R]1 = 0.03M, Δt = 25mm
∴Average rate = –\(\frac{0.02-0.03}{25}\) = –\(\frac{(-0.01)}{25}\)
= 4 × 10-4M min-1
= \(-\frac{(0.01)}{25 \times 60}\) = 6.66 × 10-6Ms-1
Question 2.
In a reaction 2A → products, the concentration of A decreases from 0.5 mol L-1 to 0.4 mol L-1 in 10 minutes. Calculate the rate during this Interval.
Answer:
Average rate = \(-\frac{1}{2} \frac{0.4-0.5}{10}\) = \(-\frac{1}{2} \frac{(-0.1)}{10}\)
= 5 × 10-3 M min-1
Question 3.
For a reaction A + B → product; the rate law is given by, r = k[A]1/2 [B]2. What is the order of the reaction?
Answer:
The order of reaction ¡s sum of powers of concentration terms.
Order = \(\frac{1}{2}\) + 2 = 2.5
Question 4.
The conversion of molecules x to y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of x is increased to threetlmes, how will it
effect the rate of formation of y?
Answer:
The reaction x → y follows second order Kinetics. Therefore, the rate equation for this reaction will be Rate = K[x]2
Let [x] = a mol L-1, then equation (1) can be written as
Rate = K. (a)2 = Ka2
If the concentration of x is Increased to three times then [x] = 3a mol L–
Now the rate equation will be
Rate = K(3a)2 = 9(Ka)2
Hence the rate of formation will increase by 9 times.
Question 5.
A first order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10-3s-1. How long will 5gm of this reactant take to reduce 3g?
Answer:
Given, Initial amount = 5g
Rate constant = 1.15 × 10-3 s-1
We know that for a 1st order reaction
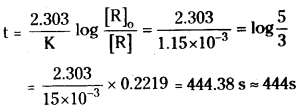
Question 6.
Time required to decompose SO2Cl2 to half of its initial amount is 60 minutes. If the decomposition is a first order reaction. Calculate the rate constant.
Answer:
We know that for a ¡st order reaction

Question 7.
What will be the effect of temperature on rate constant?
Answer:
The rate constant of reaction is almost doubled for every rise of 100 in temperature. The temperature dependence of rate of a chemical reaçtion is given by Arrhenius equation
k = A.e-Ea/RT
A = Arrhenius frequency factor
T = Absolute temperature
R = Gas constant
Ea = Activation energy
Question 8.
The rate of the chemical reaction doubles for an increase of 10K in absolute temperature from 298 K. Calculate Ea.
Answer:
Given that T1 = 298 K
T2 = 298 + 10 = 308K
The rate of reaction will be doubled when temperature is raised by 100.
∴If the value of k1 = k; k2 = 2k
Substituting these values in Arhenious equation
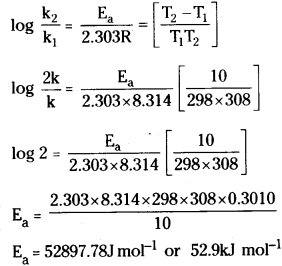

Question 9.
The activation energy for the reaction
2HI (g) → H2(g) + I2(g) is 209.5kJ mol-1 at 581 K. Calculate the fraction of molecules of reactants having energy equal to or greater than activation energy.
Answer:
Here
Ea = 209.5kJ mol-1 = 209500 J mol-1
T = 581K; R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
The fraction of molecules having energy equal or more than activation energy is given by
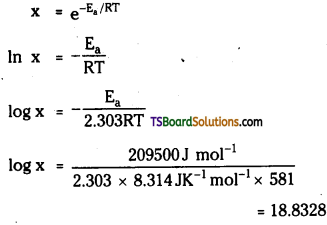
Now x = Anti log of 18.8323
= Anti log 19.1677 = 1.471 × 10-19
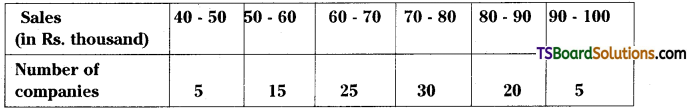
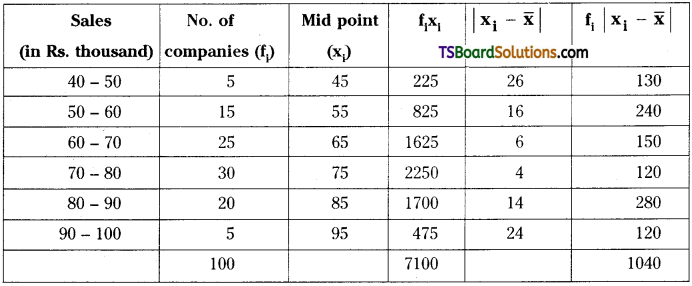
![]()
![]()

![]()


![]()


![]()

![]()
![]()

![]()