Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 1st Year Economics Study Material 7th Lesson National Income Analysis Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 1st Year Economics Study Material 7th Lesson National Income Analysis
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the various definitions of National Income? Describe the determining factors of National Income.
Answer:
National Income has been defined in a number of ways. National income is the total market value of all goods and services produced annually in a country. In other way, the total income accruing to a country from economic activities in a year’s time is called national income. It includes payments made to all factors of production in the form of rent, wages, interest and profits.
The definitions of national income can be divided into two classes. They are :
i) traditional definitions advocated by Marshall, Pigou and Fisher, and ii) modern definitions.
1) Marshall’s Definition :
According to Alfred Marshall, “the labour and capital of a country acting on its natural resources, produce annually a certain net aggregate of commodities, material and non-material including services of all kinds. This is the true net annual income or revenue of the country”. In this definition, the word ‘net’ refers to deduction of depreciation from the gross national income and to this income from abroad must be added.
2) Pigou’s Definition :
According to A. C.Pigou, “National Income is that part of the objective income of the community including of income derived from abroad which can be measured in money”. He has included that income which can be measured in terms of money. This definition is better than the Marshallian definition.
3) Fisher’s Definition :
Fisher adopted consumption as the criterion of national income. Marshall and Pigou regarded it as the production. According to Fisher, “the national income consists solely of services as received by ultimate consumers, whether from their material or from their human environment. Only the services rendered during this year are income”.
4) Kuznets’ Definition :
From the modem point of view, according to Kuznets, “national income is the net output of commodities and services flowing during the year from the country’s productive system into the hands of the ultimate consumers”.
Determining Factors of National income :
There are many factors that influence and determine the size of national income in a country. These factors are responsible for the differences in national income of various countries.
a) Natural Resources :
The availability of natural resources in a country, its climatic conditions, geographical features, fertility of soil, mines and fuel resources etc., influence the size of national income.
b) Quality and Quantity of Factors of Production :
The national income of a country is largely influenced by the quality and quantity of a country’s stock of factors of production.
c) State of Technology :
Output and national income are influenced by the level of technical progress achieved by the country. Advanced techniques of production help in optimum utilization of a country’s natural resources.
d) Political Will and Stability :
Political will and stability in a country helps in planned economic development and for a faster growth of national income.
![]()
Question 2.
Define national income and explain the various concepts of National Income.
Answer:
National Income means the aggregate value of all the final goods and services produced in the economy in one year.
Concepts of National Income :
1) Gross National Product (GNP) :
It is the total value of all final goods and services produced in the economy in one year.
The main components of GNP are :
- The goods and services purchased by consumers – C.
- Investments made by public and private sectors -1.
- Government expenditure on public utility services – G.
- Income earned through International Trade (x – m).
- Net factor income from abroad.
GNP at market prices = C + I- G + (x-m)+ Net factor income from abroad.
2) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) :
The market value of the total goods and services produced in a country in one particular period usually in a year is the GDP
GDP = C + I + G
3) Net National Product (NNP) :
Firms use continuously machines and tools for the production of goods and services. This result in a loss of value due to wear and tear of fixed capital. The loss suffered by fixed capital is called depreciation. When we substract depreciation from GNP we get NNP.
NNP = GNP – depreciation.
4) National Income at Factor Cost :
The cost of production of a good is equal to the rewards paid to the factors which participated in the production process. So the cost of production of a firm is the rent paid on land, wages paid to labour, interest paid on capital and profits of the entrepreneur.
National Income at factor cost = NNP + Subsidies – Indirect Taxes – Profits of Govt, owned firms.
5) Personal Income :
It is the total of incomes received by all persons from all sources in a specific time period. Personal income is not equal to National Income. Because social security payments. Corporate taxes, undistributed profits are deducted from national income and only the remaining is received by persons.
Personal Income = National Income at factor cost – Undistributed profits – Corporate taxes – Social security contributions + Transfer payments.
6) Disposable Income :
Personal income totally is not available for spending. Income tax is a payment which must be deducted to obtain disposable income.
Disposable Income = Personal income – Personal taxes D.I = Consumption + Savings
7) Per Capita Income :
National Income when divided by country’s population, we get per capita income.
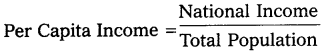
The average standard of living of a country is indicated by per capita income.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the various methods of calculating national income? Explain them. [Mar.’17,’16]
Answer:
There are three methods of measuring National Income.
- Output method or Product method.
- Expenditure method.
- Income method.
‘Carin cross’ says, National Income can be looked in any one of the three ways. As the national income measured by adding up everybody’s income by adding up everybody’s output and by adding up the value of all things that people buy and adding in their savings.
1) Output Method (Product Method) :
The market value of total goods and services produced in an economy in a year is considered for estimating National Income. In order to arrive at the value of the product services, the total goods and services produced are multiplied with their market prices.
Then, National Income = (P1Q1 + P2Q2 + …. PnQn) – Depreciation – Indirect taxes + Net income from abroad.
Where P = Price
Q = Quantity
1, 2, 3 n = Commodities & Services
There is a possibility of double counting. Care must be taken to avoid this. Only final goods and services are taken to compute National Income but not the raw materials or intermediary goods. Estimation of the National Income through this method will indicate the contribution of different sectors, the growth trends in each sector and the sectors which are lagging behind.
2) Expenditure Method :
In this method, we add the personal consumption expenditure of households, expenditure of the firms, government purchase of goods and services net exports plus net income from abroad.
NI = EH + EF + EG + Net exports + Net income from abroad.
Here, National Income = Private final consumption expenditure + Government final consumption expenditure + Net domestic capital formation + Net exports + Net income from abroad
EH = Expenditure of households
EF = Expenditure of firms
EG = Expenditure of Government
Care should be taken to include spending or expenditure made on final goods and services only.
3) Income Method :
In this method, the income earned by all factors of production is aggregated to arrive at the National Income of a country. The four factors of production receives income in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits. This is also national income at factor cost.
NI = W + I + R + P + Net income from abroad
Where, NI = National income
W = Wages
I = Interest
R = Rent
P = Profits
This method gives us National Income according to distribution of shares.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the factors that determine National Income? [Mar. ’17, ’16]
Answer:
National Income is the total market value of all goods and services produced in a country during a given period of time. There are many factors that influence and determine the size of national income of a country.
a) Natural Resources :
The availability of natural resources in a country, its climatic conditions, geographical features, fertility of soil, mines and fuel resources etc., influence the size of National Income.
b) Quality and Quantity of Factors of Production :
The national income of a country is largely influenced by the quality and quantity of a country’s stock of factors of production.
c) State of Technology :
Output and national income are influenced by the level of technical progress achieved by the country. Advanced techniques of production help in optimum utilization of a country’s natural resources.
d) Political Will and Stability :
Political will and stability in a country helps in planned economic development and for a faster growth of National Income.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the differences between gross national product at market prices and gross national product at factor prices.
Answer:
National income is the value of all final goods and services produced in a company in a year.
Gross National Product (GNP) :
Gross National Product is also known as the gross national product at market prices. Gross national product is the current market value of all final goods and services produced in a country during a year including net income from abroad.
The main components of GNP are :
a) The goods and services purchased by consumers (consumption – C).
b) Gross private domestic investment in capital goods (Investment -I)
c) Goods and services consumed by the government (Govt expenditure – G)
d) Net incomes earned through International trade (value of exports – value of imports, i.e., X-M).
GNP = C + I-G + (X-M).
GNP at Factor Cost :
Gross national product at factor cost is the sum of the money value produced by and accruing to the various factors of production in a year in a country. GNP at market prices includes wages, rent, interest, dividends, undistributed corporate profits, mixed incomes (profits of unincorporated business), direct taxes, indirect taxes, depreciation and net income from abroad. GNP at factor cost includes all items mentioned above in GNP at market prices less indirect taxes. GNP at market prices is always higher than GNP at factor cost. If there are any subsidies to the producers, then to get GNP at factor cost, subsidies are added to GNP at market prices.
GNP at factor cost = GNP at market prices = indirect taxes + subsidies.
Question 3.
What are National Income at market prices and National income at factor cost?
Answer:
National Income is the value of all the final goods and services produced in a year of a country.
National Product at Market Prices (NNP) :
The country’s stock of fixed capital undergoes certain amount of wear and tear in producing goods and services over a period of time. This ‘user cost’ or depreciation or charges for renewals and repairs must be substracted from the GNP at market prices to obtain net national product at market prices.
NNP at market prices = GNP at market prices – Depreciation.
National Product at Factor Cost :
It is aslo called as national income. It is the total income received by the four factors of production in the form of rent, wages, interest and profits in an economy during a year. NNP at market prices is not available for distribution among the factors of production. The amount of indirect taxes (which are included in the prices) are paid by the firms to the government and not to the factors of production. Similarly, the government gives subsidies to firms for production of certain types of goods and services and that part of the production cost is borne by the government. Hence, the goods are sold in the market at a lover price than the actual cost of production. Therefore, this volume of subsidies has to broded to the net national income at market prices. Thus,
NNP at factor cost = NNP at market prices – Indirect taxes + Subsidies. In another way,
NNP at factor cost = GNP at market prices – Depreciation – Indirect taxes + Subsidies.
![]()
Question 4.
Discuss the three definitions of National Income.
Answer:
National Income has been defined in a number of ways. National income is the toted market value of all goods and services produced annually in a country. In other way, the total income accruing to a country from economic activities in a year’s time is called national income. It includes payments made to all factors of production in the form of rent, wages, interest and profits.
The definitions of national income can be divided into two classes. They are : i) traditional definitions advocated by Marshall Pigou and Fisher, and ii) modem definitions.
1) Marshall’s Definition :
According to Alfred Marshall, “the labour and capital of a country acting on its natural resources, produce annually a certain net aggregate of commodities, material and non-material including services of all kinds. This is the true net annual income or revenue of the country”. In this definition, the word ‘net’ refers to deduction of depreciation from the gross national income and to this income from abroad must be added.
2) Pigou’s Definition :
According to A.C.Pigou, “National Income is that part of the objective income of the community including of income derived from abroad which can be measured in money”. He has included that income which can be measured in terms of money. This definition is better than the Marshallian definition.
3) Fisher’s Definition :
Fisher adopted consumption as the criterion of national income. Marshall and Pigou regared it as the production. According to Fisher, “the national income consists solely of services as received by ultimate consumers, whether from their material or from their human environment. Only the services rendered during this year are income”.
Fisher definition is better than that of Marshall and Pigou. Because, Fisher’s definition has considered economic welfare which is depending on consumption and consumption represents standard of living.
But the definitions advocated by Marshall, pigou, and Fisher are not flawless. The Marshallian and Pigou’s definitions deal with the reasons for economic welfare. But Fisher’s definition is useful to compare economic welfare in different years.
Question 5.
How the per capita income is calculated? What is the relationship between population and per capita income.
Answer:
The per capita income is the average income of the people in a country in a particular year. It is calculated by dividing national income at current prices by population of the country in that year.
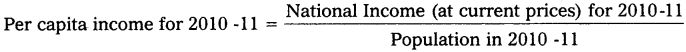
This refers to the measurement of per capita income at current prices. This concept is a good indicator of the average income and the standard of living in a country. But it is not reliable because actual income may be more or may be less when compared to the average income.
This per capita income will also be measured at constant prices and so we get real per capita income. By dividing real national income in a particular year by population of that year we will get real per capita income for that year.
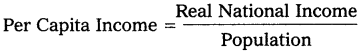
Relationship Between Per Capita Income and Population :
There is a close relationship between national income and population. These two together determine the per capita income. If rate of growth of national income is 6% and rate of growth of population is 3% the rate of growth of per capita income will be 3% and it can be expressed as follows :
gpc = gni – gp
where,
gpc = Growth rate of per capita income
gni = Growth rate of national income
gp = Growth rate of population
A rise in the per capita income indicates a rise in standard of living. The rise in per capita income is possible only when the rate of growth of population is less than the rate of growth of that national income.
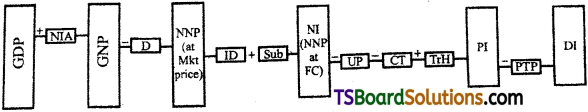
Relationship among National Income Concepts
NIA = Net Income from Abroad
D = Depreciation
ID = Indirect Taxes
Sub = Subsidies
UP = Undistributed Profits
CT = Corporate Taxes
TrH = Transfers received by Households
PTP = Personal Tax Payments
PTP = Gross Domestic Product
GDP = Gross National Product
In fig. we have presented the relation between the various concepts of national income.
![]()
Question 6.
Analyse any two methods of measuring National income.
Answer:
There are three methods of measuring National Income. These are :
- Output method or Product method
- Income method, and
- Expenditure method
CaimCross says, “National Income can be looked in any one of the three ways, as the national income measured by adding up everybody’s output by adding up everybody’s income and by adding up the value of all things that people buy and adding in their savings.
1) Output Method or Product Method :
It is also known as inventory method or commodity service method. In this method we find the the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a year. The entire output of fined goods and services are multiplied by their respective market prices to find out the gross national product.
GNP = (P1Q1 + P2Q2 + …. PnQn) + Net income from abroad.
Where, GNP == gross national product,
P = Price of the goods or services
Q = Quantity of goods or services produced
1,2, 3 n are the various goods and services produced.
The values of the intermediary goods and services should not be included. Only final goods and services should be taken into account. Here, we find out the value of output by the different sectors like agriculture, government, professionals, industry.
2) Income method :
In this method, the incomes earned by all factors of production are aggregated to arrive at the National Income of a country. The four factors of production receives income in the form of wages, rent, interest and profits. Incomes in the form of transfer payment is not included in it. This is also known as national income at factor cost.
NI = R + W + I + P
NI = National income
W = Wages R Rent
I = Interest
P = Profits
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is National Income?
Answer:
National income is the market value of goods and services produced annually in a country.
Question 2.
Mention the factors that determine National Income.
Answer:
There are many factors that influence and determine the size of national income in a country. These factors are responsible for the differences in national income of various countries.
a) Natural Resources :
The availability of natural resources in a country, its climatic conditions, geographical features, fertility of soil, mines and fuel resources etc., influence the size of national income.
b) Quality and Quantity of Factors of Production :
The national income of a country is largely influenced by the quality and quantity of a country’s stock of factors of production. For example, the quantity of agricultural production and hence, the size of National income.
c) State of Technology :
Output and national income are influenced by the level of technical progress achieved by the country. Advanced techniques of production help in optimum utilization of a country’s natural resources.
d) Political Will and Stability :
Political will and stability in a country helps for planned economic development for a faster growth of national income.
Question 3.
Explain the concept of GNP (Gross National Product).
Answer:
It is the total value of all final goods and services produced in the economy in one year.
GNP = C + I + G + (x-m) where,
C = Consumption
I = Gross National Investment
G = Government Expenditure
X = Exports
M = Imports
x – m = Net foreign trade.
![]()
Question 4.
What is Net National Product at factor cost?
Answer:
It is aslo called as national income. It is the total income received by the four factors of production in the form of rent, wages, interest and profits in an economy during a year. NNP at market prices is not available for distribution among the factors of production. The amount of indirect taxes (which are included in the prices) are paid by the firms to the government and not to the factors of production. Similarly, the government gives subsidies to firms for production of certain types of goods and services and that part of the production cost is borne by the government. Hence, the goods are sold in the market at a lower price than the actual cost of production. Therefore, this volume of subsidies has to be added to the net national income at market prices. Thus,
NNP at factor cost = NNP at market prices – Indirect taxes + Subsidies. In another way,
NNP at factor cost = GNP at market prices – Depreciation-Indirect taxes + Subsidies.
Question 5.
What is Personal Income?
Answer:
It is the total of income received by all persons in a year before payment of all direct taxes. The whole of National Income is not availabe to them. Corporate taxes have to be paid by firms. Firms may keep a part of its profits for expansion. Salaried employees may make contributions for social security. Hence,
PI = NI(NNP at factor cost) – (Undistributed corporate profits + Corporate taxes + Social security payments) + Transfer earnings
Question 6.
What are subsidies?
Answer:
A subsidy or government incentive is a form of financial aid or support extended to an economic sector generally with the aim of promoting economic and social policy ………….. consumer/ consumption subsidies. Commonly reduce the price of goods and services to the consumer.
Question 7.
What is Real Per Capita Income ? [Mar. ’17, ’16]
Answer:
Real National Income when divided by country’s population, percapita income is obtained.
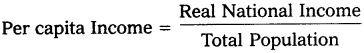
The average standard of living of country is indicated by per capita income.
Question 8.
What are the components of National Income?
Answer:
These are the four components of National Income.
a) Consumption (C) :
It is the total expenditure made by households on goods and services. It depends on the level of income.
b) Investment (I) :
It include expenditure on capital goods and machinery, roadways, bridges etc.
c) Government Expenditure (G) :
It is the expenditure made by the government on infrastructural facilities for the use of society.
d) Net Foreign Income :
It is the income earned by a country through international trade.
![]()
Question 9.
What is income method of measuring National Income?
Answer:
The value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a year is known as National Income.
Difficulties in Measurement National Income :
Following are the some of the difficulties we face while measuring national income.
- Many of the products pass through a number of stages before these are purchased. If these are counted at every stage double counting will be there.
- Goods and services rendered free of charge are not included in the gross national product (GNP). But all these will enhance the welfare of the consumers.
- Income earned through illegal activities is not included in the gross national product (GNP). But this is also the cause for economic welfare.
- Goods meant for self consumption are not included in the national income and its result is under estimation of national income.
- Services of house wives – unpaid services – are not taken into consideration. Therefore, the national income is underestmated.
- In order to get net national product, depreciation is deducted from gross national product. Thus, depreciation lowers the national income.
Question 10.
How National Income is estimated in India?
Answer:
After independence the Government of India appointed a National Income Estimates Committee in the year 1949, Under the chairmanship of Sri PC. Mahalanobis to claculate the national income of India. At present the Central Statistical Organization (CSO) has been entrusted with the responsibility of preparing national income estimates.
The CSO has divided the Indian economy into 13 sectors and grouped them under five heads. They are :
- Primary Sector.
- Secondry Sector.
- Transport, Communication and Trade.
- Finance and Real Estate.
- Community and Personal Services.
Question 11.
Distinguish between Per Capita Income and National Income.
Answer:
Per Capital Income National Income
Per capita income is the average income of people in a country in a particular year. National income is the market value of goods and services produced annually in a country.
Question 12.
What are transfer payments? Give examples.
Answer:
The government may provide social security allowances like pensions, unemployment allowances, scholarships etc. These are incomes for some sections of the society even though no productive services are made by them. These are called transfer payments.
Question 13.
What is the importance of National income estimations?
Answer:
Importance of national income estimations :
- The national income estimates or statistics are very important for preparing economic plans and for framing national economic policies.
- The national income data are useful in research and distribution of income in the country.
- It enables us to assess the performance of each sector in the economy and inter-relationship among the sectors.
- It is more useful in making budgetory allocations.
- It gives us an idea of the standard of living in the country.
![]()
Question 14.
Expand C.S.O. What is its responsibility?
Answer:
C.S.O. is the Central Statistical Organisation and Responsibility for preparing national income estimates.
Question 15.
What is Depreciation?
Answer:
Firms use continuously machines and tools for the production of goods and services. This results in a loss of value due to the wear and tear of fixed capital. This loss suffered by fixed capital is called depreciation.