Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material Lesson 12(a) Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material Lesson 12(a) Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
Very Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
Question 1.
Explain why propanol has higher boiling point than that of the hydrocarbon butane.
Answer:
Propanol and butane are of comparable molecular mass. However, the boiling point of propanol is higher than that of butane, due to the presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Question 2.
Alcohols are comparatively more soluble in water than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses. Explain this fact.
Answer:
Alcohols are comparatively more soluble in water than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses, due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
![]()
Question 3.
Give the structures and 1UPAC names of monohydric phenols of molecular formula, C7H8O.
Answer:
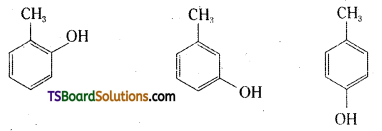
Common Name:
o – Cresol
m – Cresol
p – Creol
IUPAC Name:
2 – Methylphenol
3 – Methylphenol
4 – Methylphenol
Question 4.
Give the reagents used for the preparation of phenol from chlorobenzene.
Answer:
- NaOH
- HCl.
Question 5.
Preparation of ethers by acid dehydration of secondary or tertiary alcohols is not a suitable method. Give reason.
Answer:
This is because elimination competes over substitution and as a consequence, alkenes are easily formed.
![]()
Question 6.
Write the mechanism of the reaction of HI with methoxymethane.
Answer:
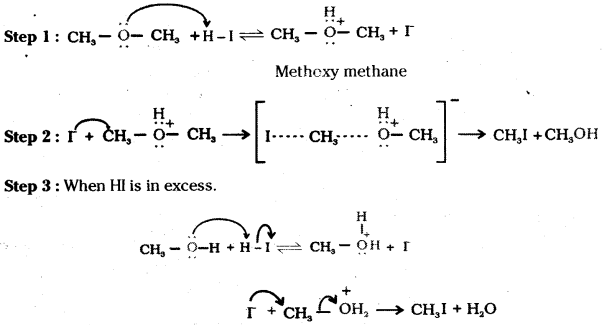
Question 7.
Name the reagents used in the following reactions.
- Oxidation of primary alcohol to carboxylic acid.
- Oxidation of primary alcohol to aldehyde.
Answer:
- Acidified potassium permanganate.
- Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) or CrO3 in anhydrous medium.
Question 8.
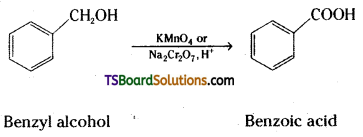
Write the equations for the following reactions.
i) Bromination of phenol to 2, 4, 6-tribromophenoI.
ii) Benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid.
Answer:
i) A white precipitate of 2,4,6 – tribromophenol is formed when phenol is treated with bromine water.
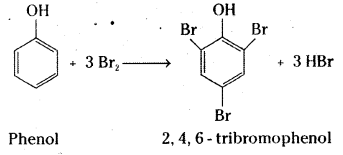
ii) Benzyl alcohol is oxidised to benzoic acid by acidified KMn04 or acidic solution of sodium dichromate.
Question 9.
Identify the reactant needed to form t-butyl alcohol from acetone.
Answer:
Methyl magnesium halide (Grignard reagent) is needed to form t-butyl alcohol from acetone.
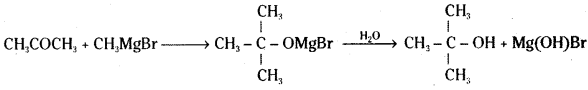
![]()
Question 10.
Write the structures for the following compounds.
i) Ethoxyethane
ii) Ethoxybutane
iii) Phenoxyethane
Answer:
i) C2H5OC2H5 – Ethoxyethane
ii) CH3CH2CH2CH2OCH2CH3 – Ethoxybutane
iii) C2H5OC6H5 – Phenoxyethane
Short Answer Questions (4 Marks)
Question 11.
Draw the structures of all isomeric alcohols of molecular formula C5H12O and give their IUPAC names and classify them as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Answer:
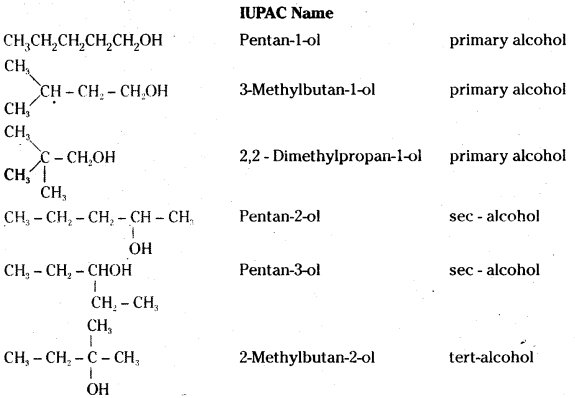
![]()
Question 12.
While separating a mixture of ortho and para nitrophenols by steam distillation, name the isomer which will be steam volatile. Give reason.
Answer:
O-nitrophenol will be steam volatile due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding while p-nitro- phenol will be less volatile due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding which causes association of molecules.
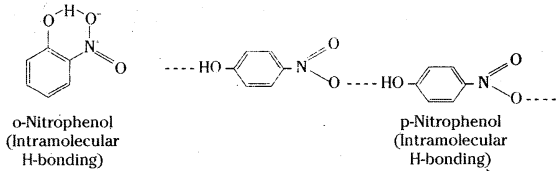
Question 13.
Give the equations for the preparation of phenol from Cumene.
Answer:
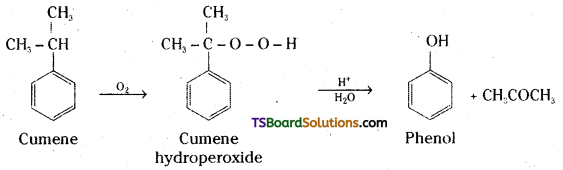
Question 14.
Write the mechanism of hydration of ethene to yield ethanol.
Answer:
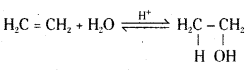
Mechanism : The mechanism of the reaction involves three steps.
Step 1: Protonation of the alkene (ethene) to form carbonation by electrophilic attack of H3O+.
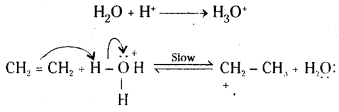
Step 2 : Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
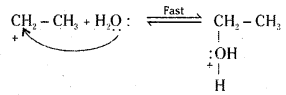
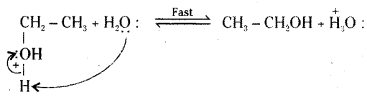
Step 3 : Deprotonation to form an alcohol.
![]()
Question 15.
Explain the acidic nature of phenols and compare with that of alcohols.
Answer:
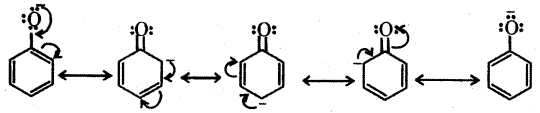
The reactions of phenol with metals (e.g. : Na, Al) and NaOH indicate its acidic nature. The hydroxyl group, in phenol is directly attached to the sp2 hybridised carbon of benzene ring which acts as an electron withdrawing group. The charge distribution in phenol molecule as depicted in its resonance structures, causes the oxygen of – OH group to be positive.
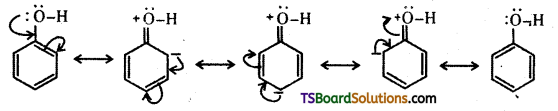
The reaction of phenol with NaOH solution indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Let us compare the acidic nature of phenol with that of alcohol.
The ionisation of an alcohol and a phenol takes place as shown below.
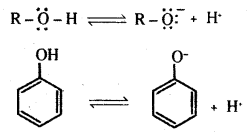
Owing to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which – OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of – OH bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols.
The relative stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions should be considered. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen whereas in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol. There is delocalisation in unionised phenol also but the resonance structures have charge separation. Hence, phenol molecule is less stable them phenoxide ion.
Question 16.
Write the products formed by the reduction and oxidation of phenol. [IPE 14]
Answer:
Reduction of phenol: Phenol is converted to benzene when heated with zinc dust.
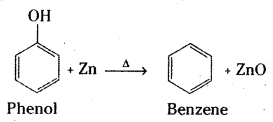
Oxidation : Phenol gives benzoquinone on oxidation with chromic acid.
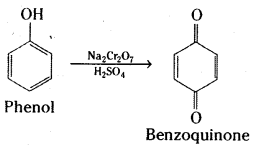
In the presence of air, phenols are slowly oxidised to dark coloured mixtures containing quinones.
![]()
Question 17.
Ethanol with H2SO4, at 443K forms ethane while at 413 K it forms ethoxy ethane. Explain the mechanism.
Answer:
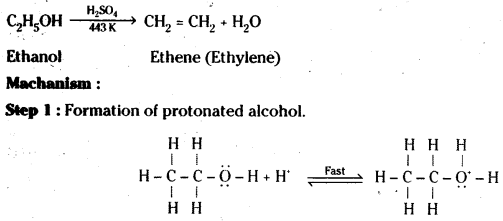
Step 2 : Formation of carbocation.
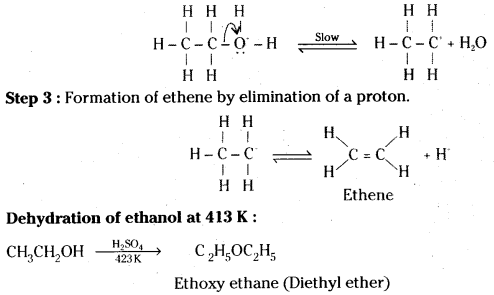
Mechanism : The formation of ether is a nucleophilic bimolecular reaction (SN2) involving the attack of alcohol molecule on a protonated alcohol.
Question 18.
Account for the statement: Alcohols boil at highest temperature than hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular masses.
Answer:
The higher boiling points of alcohols are mainly due to the presence of inter molecular hydrogen bonding in them which is lacking in ethers and hydrocarbons.
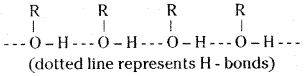
![]()
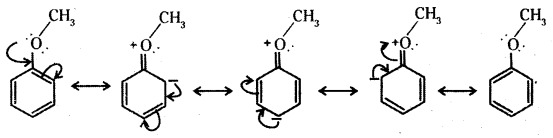
Question 19.
Explain why in anisole electrophilic substitution takes place at ortho and para positions and not at meta position.
Answer:
In benzene derivatives the electrophile is most likely to react at the position of highest electron density. The methoxy group ih anisole is an electron releasing group. It increases the relative electron density at ortho and para positions and hence electrophilic substitution takes place at these positions and not at the meta position.
Question 20.
Write the products of the following reactions:
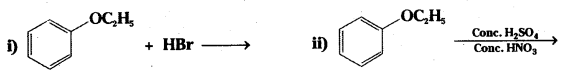
Answer:
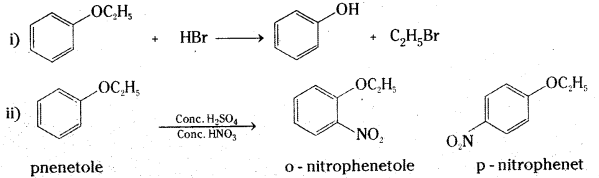
Long Answer Questions (8 Marks)
Question 21.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
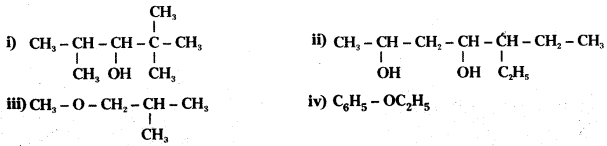
Answer:
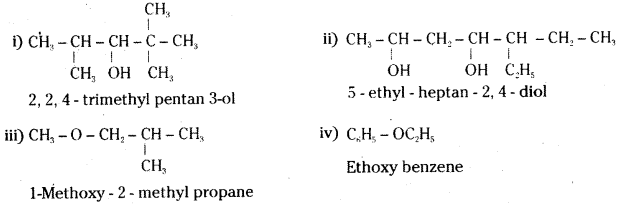
![]()
Question 22.
Write structures of the compounds whose IUPAC names are as follows: [IPE 14]
i) 2- Methyl butan-1- ol
ii) 1-Phenylpropan-2-ol
iii) 3, 5-Dimethythexane- 1, 3, 5- triol
iv) 2, 3- Dlethylphenol
v) 1 – Ethoxypropane
vi) 2- Ethoxy -3- methylpentane
vii) Cyclohexylmethanol
viii) 3- Chloromethylpentan – 1 – ol
Answer:

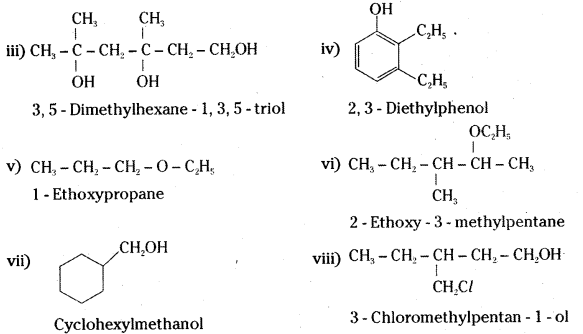
Question 23.
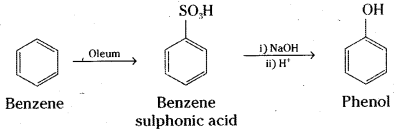
Write the equations for the preparation of phenol using benzene, Cone. H2SO4 and NaOH.
Answer:
Benzene is sulphonated with oleum and benzene sulphonic acid so formed is converted to sodium phenoxide on heating with molten sodium hydroxide. Acidification of the sodium salt gives phenol.
Question 24.
Illustrate hydroboration-oxidation reaction with a suitable example.
Answer:
Diborane B2H6 [or (BH3)2] reacts with aikenes to give trialkyl boranes as addition product. This is oxidised to alcohol by hydrogen peroxide in the presence of aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Ex : Propene gives Propan-1-ol on hydroboration – oxidation reaction.
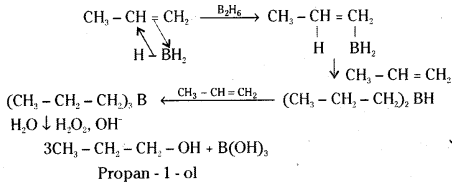
![]()
Question 25.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
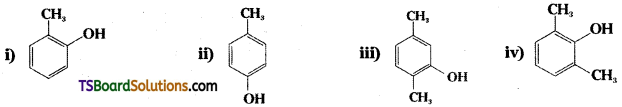
Answer:
i) 2-methyl phenol
ii) 4 – methyl phenol
iii) 2, 5 – dimethyl phenol
iv) 2, 6 – dimethyl phenol
Question 26.
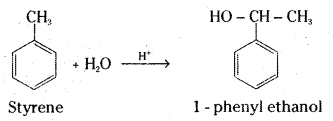
How will you synthesise :
i) 1 – Phenylethanol from a suitable alkene ?
ii) Cyclohexylmethanol using an alkyl halide by an SN2 reaction ?
iii) Pentan-1-ol using a suitable alkyl halide ?
Answer:
i) Styrene on acid catalysed hydration gives 1-phenyl ethanol.
ii) Cyclohexyl chloromethane reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution to give cyclohexyl methanol.
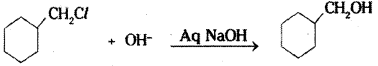
iii) Pentan-1-ol is obtained by the reaction of 1-chloropentane with aqueous NaOH solution.
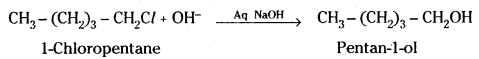
Question 27.
Explain why –
i) Ortho nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho methoxyphenol.
ii) OH group attached to benzene ring activates it towards electrophilic substitution.
Answer:
i) Electron withdrawing groups enhance the acidic strength of phenol. This effect is more pronounced if these groups are present in ortho and para positions. It is due to the effective delocalisation of negative charge in phenoxide ion. On the other hand electron releasing
‘ groups do not favour the formation of phenoxide ion resulting in decrease in acid strength.
Nitro group is an electron withdrawing group. It increases the acidic strength of phenol. Methoxy group is an electron releasing group. It decreases the acidic strength of phenol. Hence o-nitrophenol is more acidic than orthomethoxyphenol.
ii) The – OH group attached to the benzene ring activates it towards electrophilic substitution. Further, it directs the incoming group to ortho and para positions in the ring as these positions become electron rich due to the resonance effect caused by – OH group.
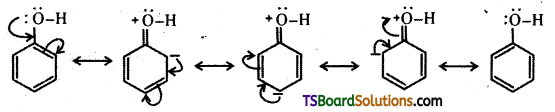
Question 28.
With a suitable example write equations for the following:
i) Kolbe’s reaction.
ii) Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
iii) Willamson’s ether synthesis.
Answer:
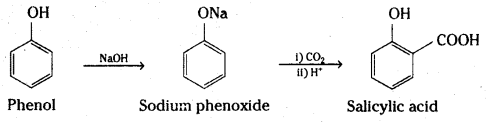
i) Kolbe’s synthesis: When sodium salt of phenol (sodium phenoxide) is heated with carbon dioxide under pressure, a carboxylic group is introduced in the aromatic ring preferably at ortho position with respect to phenolic group. The sodium salt of o-hydroxybenzoic acid (sodium salicylate) formed, when treated with acid yields salicylic acid.
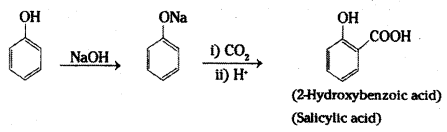
ii) Reimer-Tiemann reaction : When phenol is heated with chloroform in the presence of sodium hydroxide at 60°C, a – CHO group is introduced at the ortho position with respect to the phenolic group. This reaction is known as Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
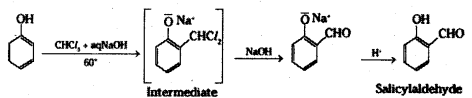
iii) Willamson’s ether synthesis: It is an important method for the preparation of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. In this method, an alkyl halide is allowed to react with sodium alkoxide.
![]()
Ethers containing substituted alkyl groups (2° or 3°) may also be prepared by this method. The reaction involves SN2 attack of an alkoxide ion on primary alkyl halide.
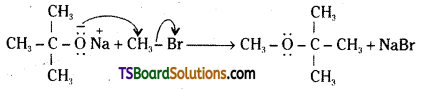
In case of secondary and tertiary alkyl halides, elimination competes over substitution. If a tertiary alkyl halide is used, an alkene is the only reaction product and no ether is formed.
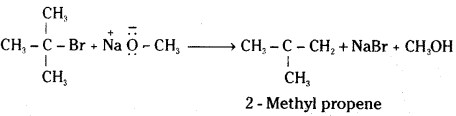
![]()
Question 29.
How are the following conversions carried out ?
i) Benzyl chloride to Benzyl alcohol
ii) Ethyl magnesium bromide to Propan-1-ol
iii) 2-butanone to 2-butanol
Answer:
i) Benzyl chloride is converted to benzyl alcohol by hydrolysis with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
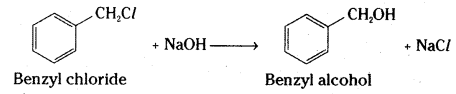
ii) Ethyl magnesium bromide reacts with formaldehyde to form an adduct. Hydrolysis of the adduct yields an propan-1-ol.
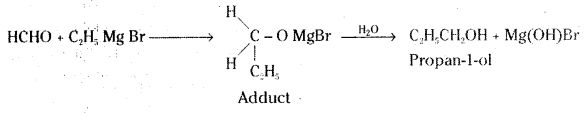
iii) 2-butanone bn reduction with sodium borohydride (NaBH4) gives 2-butanol.
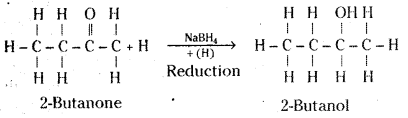
Question 30.
Write the names of the reagents and equations for the preparation of the following ethers by Williamson’s synthesis:
i) 1-Propoxypropane
ii) Ethoxybenzene
iii) 2-Methoxy-2-methylpropane
iv) 1-Methoxyethane
Answer:
i) Sodium propoxide and propyl bromide.
CH3CH2CH2ONa + CH3CH2CH2 – Br → CH3CH2CH2OCH2CH2CH3 + NaBr
ii) Chlorobenzene and sodium ethoxide.

iii) Sodium tertiary butoxide and methylbromide.
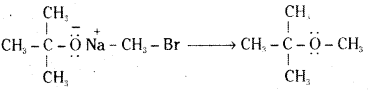
iv) Sodium ethoxide and methyl bromide.
![]()
Question 31.
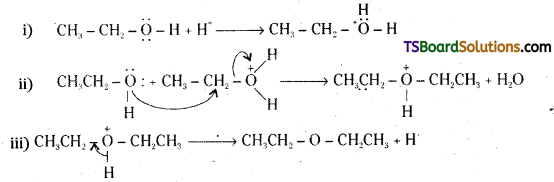
How is 1-propoxypropane synthesized from propan-1-ol ? Write mechanism of this reaction.
Answer:
1-rpropoxypropane is synthesised from propan-1-ol by dehydration in the presence of sulphuric acid.
Mechanism :
The formation of 1-propoxypropane is an SN2 reaction involving the attack of alcohol molecule on a protonated alcohol.
![]()
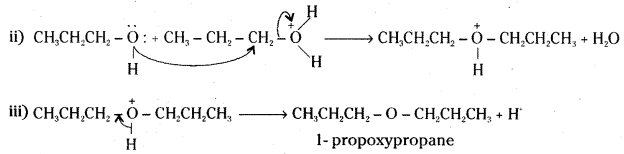
![]()
Question 32.
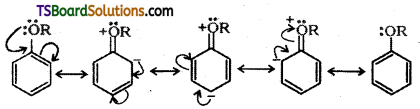
Explain the fact that in aryl alkyl ethers the alkoxy group activates the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution.
Answer:
Alkoxy group ![]() is an electron releasing group. When attached to benzene ring alkoxy group activates the ring towards electrophilic substitution. Further, it directs the incoming group to ortho and para positions in the benzene ring as these positions become electron rich due to the resonance effect caused by the – OR group.
is an electron releasing group. When attached to benzene ring alkoxy group activates the ring towards electrophilic substitution. Further, it directs the incoming group to ortho and para positions in the benzene ring as these positions become electron rich due to the resonance effect caused by the – OR group.
Question 33.
Write equations of the below given reactions :
i) Alkylation of anisole
ii) Nitration of anisole
iii) Friedel-Crafts acylation of anisole
Answer:
i) Alkylation of anisole: Anisole undergoes Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction with alkyl halide in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 as catalyst. The alkyl group is introduced in the ortho and para positions.
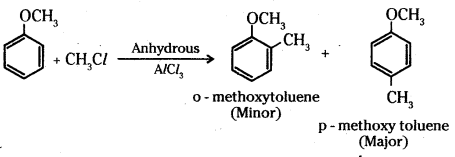
ii) Nitration of anisole : Anisole on nitration with a mixture of concentrated H2SO4 and HNO3 yields a mixture of ortho and para nitroanisole.
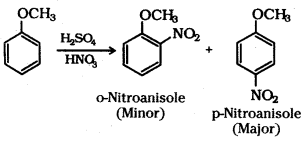
iii) Friedel-Crafts acylation of anisole : Anisole undergoes Friedel-Crafts acylation with acyl halide in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3.
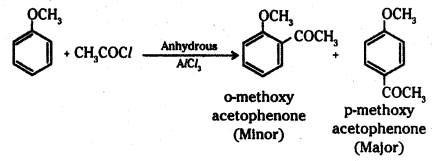
The acyl group is introduced in the ortho and para positions.
![]()
Question 34.
Show how you would synthesize Hie following alcohols from appropriate aikenes ?
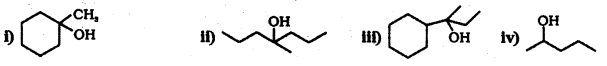
Answer:
By acid – catalysed hydration
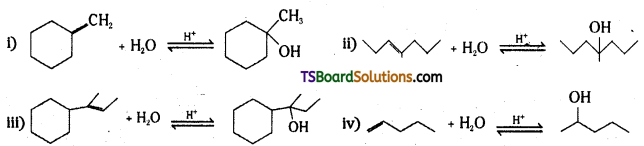
Question 35.
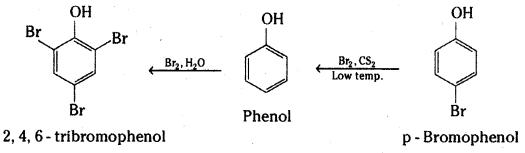
Explain why phenol with bromine water forms 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol while on reaction with bromine in CS2 at low temperatures forms para-bromophenol as the major product.
Answer:
The hydroxyl group (- OH) is a very powerful activating substituent, and electrophilic substitution in phenols occurs faster, and under milder conditions, than in benzene.
Bromination of phenol occurs readily even in the absence of a catalyst at low temperature; Substitution occurs primarily at the para position to the hydroxyl group. When the para position is blocked, ortho substitution is observed. The reaction is carried out in a non-polar solvent CS2 or ClCH2CH2Cl. In polar solvents such as water it is difficult to limit the bromination of phenols to monobromination. With bromine water all three positions that are ortho or para to the hydroxyl undergo rapid substitution.
Intext Questions – Answers
Question 1.
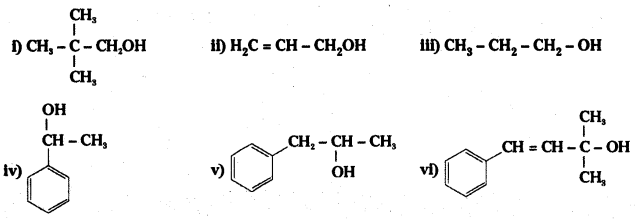
Classify the following as primary, secondary and teritary alcohols :
Answer:
i) Primary alcohol
ii) Primary alcohol
iii) Primary alcohol
iv) Secondary alcohol
v) Secondary alcohol
vi) Tertiary alcohol
![]()
Question 2.
Identify allylic alcohols in the above examples.
Answer:
In the examples given above (under question 1), (ii) and (vi) are allylic alcohols.
Question 3.
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system.
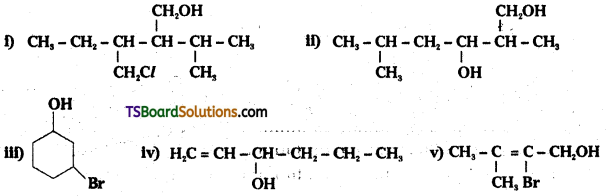
Answer:
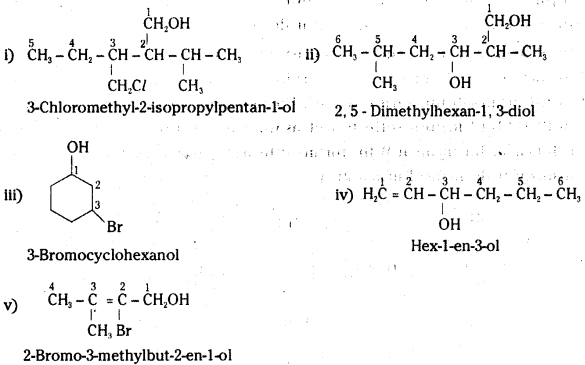
![]()
Question 4.
Show how the following alcohols are prepared by the reaction of a suitable Grignard reagent on methanal ?
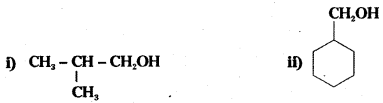
Answer:
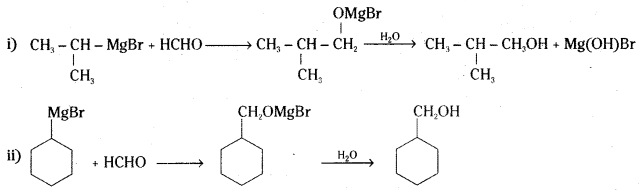
Question 5.
Write structures of the products of the following reactions.
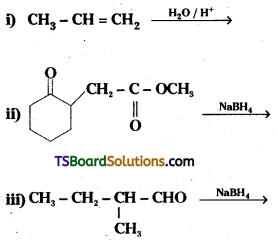
Answer:
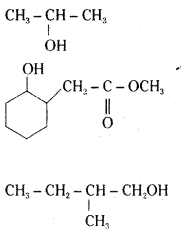
Question 6.
Write the structures of the major products expected from the following reactions :
a) Mononitration of 3-methylphenol
b) Dinitration of 3-methylphenol
c) Mononitration of phenyl methanoate.
Answer:
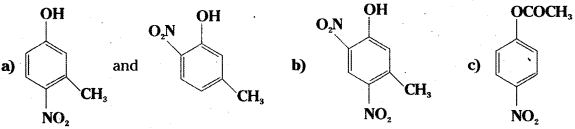
![]()
Question 7.
Give structures of the products you would expect when each of the following alcohol reacts with
a) HCl – ZnCl2,
b) HBr and
c) SOCl2.
i) Butan-1-ol
ii) 2-Methylbutan-2-ol
Answer:
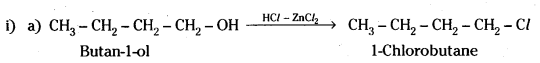
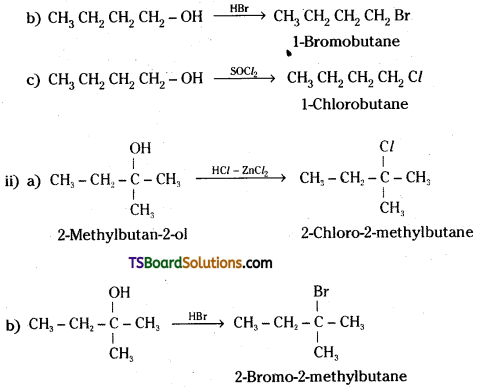
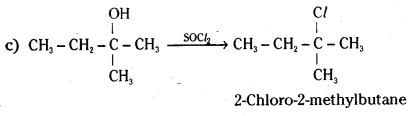
Question 8.
Predict the major product of acid catalysed dehydration of
i) 1-methylcyclohexanol and
ii) butan-1-ol
Answer:
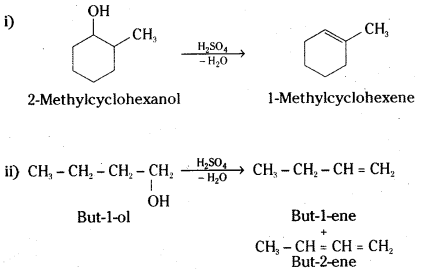
A mixture of but-l-ene and but-2-ene will be obtained. The 1 ° carbocation formed as intermediate will undergo rearrangement to give a more stable 2° carbocation. Loss of proton results in the mixture of but-1-ene and but-2-ene. However, but-l-ene will be the major product.
![]()
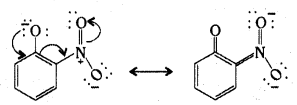
Question 9.
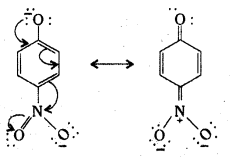
Ortho and para nitrophenols are more acidic titan phenol. Draw the resonance structures of the corresponding phenoxide ions.
Answer:
Electron delocalization in o-nitrophenoxide ion.
Electron delocalization in p-nitrophenoxide ion.
Question 10.
Write the equations involved in the following reactions:
i) Reimer – Tiemann reaction
ii) Kolbe’s reaction
Answer:
i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction :
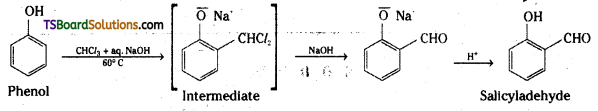
ii) Kolbe’s reaction
Question 11.
Write the reactions of Williamson synthesis of 2-ethoxy-3-methylpentane starting from ethanol and 3-methylpentan-2-ol
Answer:
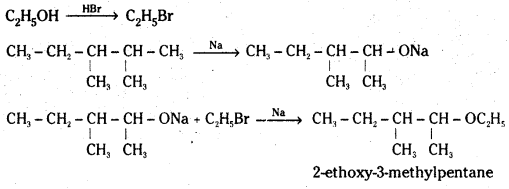
![]()
Question 12.
Which of the following is an appropriate set of reactants for the preparation of 1-methoxy- 4-nitrobenzene and why ?

Answer:
Set (ii) is appropriate.
Question 13.
Predict the products of the following reactions:
i) CH3-CH2-CH2-O-CHS + HBr →
Answer:
CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – OH + CH3Br
ii)
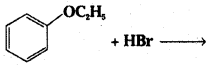
Answer:
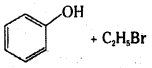
iii)

Answer:
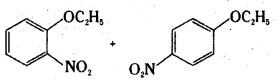
iv)
![]()
Answer:
(CH3)3C – I + C2H5OH