Learning these TS Inter 2nd Year Maths 2B Formulas Chapter 3 Parabola will help students to solve mathematical problems quickly.
TS Inter 2nd Year Maths 2B Parabola Formulas
→ The locus of a point moving on a plane such that its distance from a fixed point and a fixed straight line in the plane are in a constant ratio ‘e’ is called a conic and e is called the eccentricity of the conic. Fixed point is called focus and the fixed straight line is called the directrix. If e = 1, the conic is called a Parabola.
→ Equation of a parabola in the standard form is y2 = 4ax (a > 0) with focus (a, 0), axis y = 0, equation of directrix is x + a = 0 and length of the latus rectum is 4a.
→ Various different forms of parabola (general)
Table: 1
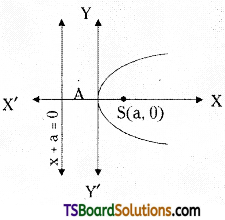
(i) Form: y2 = 4ax
Vertex: (0, 0)
Focus: (a, 0)
Directrix: x + a = 0
Axis: y = 0
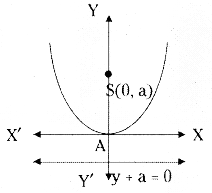
(ii) Form: x2 = 4ay
Vertex: (0, 0)
Focus: (0, a)
Directrix: y + a = 0
Axis: x = 0
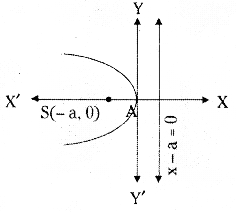
(iii) Form: y2 = -4ax
Vertex: (0, 0)
Focus: (-a, 0)
Directrix: x – a = 0
Axis: y = 0
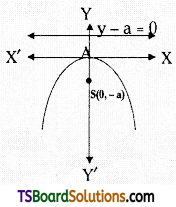
(iv) Form: x2 = -4ay
Vertex: (0, 0)
Focus: (0, -a)
Directrix: y – a = 0
Axis: x = 0
![]()
Table: 2
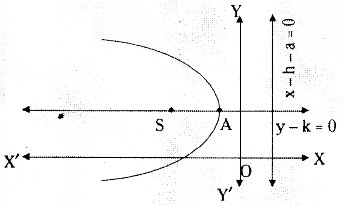
(i) Form:(y – k)2 = 4a(x – h)
Vertex: (h, k)
Focns: (h + a, k)
Axis: y = k
EquaffonotDlrectrlx: x – h + a = 0
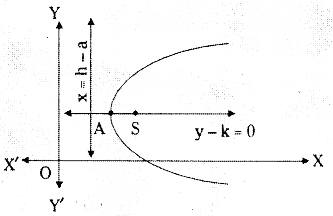
(ii) Form: (y – k)2 = -4a(x – h)
Vertex: (h, k)
Focus: (h – a, k)
Axis: y – k = 0
Equation of Directrix: x – h – a = 0
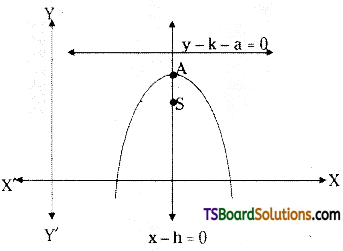
(iii) Form: (x – h)2 = -4a(y – k)
Vertex: (h, k)
Focus: (h, k – a)
Axis: x – h = 0
Equation of Directrix : y – k -a = 0
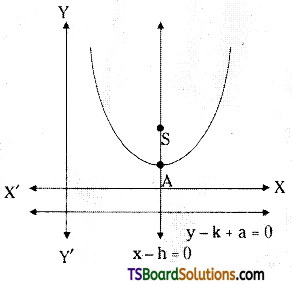
(iv) Form : (x – h)2 = 4a(y – k)
Vertex: (h, k)
Focus: (h, a + k)
Axis: x – h = 0
Equation of Directrix: y – k + a = 0
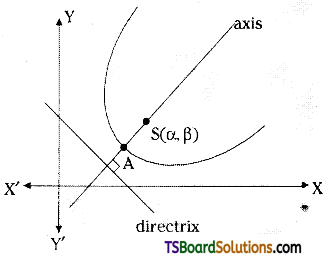
(v) Form: (x – α)2 + (y – β)2 = \(\frac{(l x+m y+n)^2}{l^2+m^2}\)
Vertex : Point A
Focus: (α, β)
Axis: m(x – α) – l(y – β) = 0
Equation of Directrix: lx + my + n = 0
→ The equation of parabola when its axis is parallel to X – axis is x = ly2 + my + n and when axis is parallel to Y- axis is y = lx2 + mx + n.
→ Focal distance of a point (x1, y1) on the parabola y2 = 4ax is x1 + a.
→ Parametric equations of the parabola are x = at2, y = 2at.
→ P(x1, y1) lies outside, on or inside the parabola y2 = 4ax according as S11 \(\frac{\geq}{<}\) 0.
→ y = mx + c (m * 0) is a tangent to the parabola y2 = 4ax when c = a/m.
→ y = mx + a/m (m ≠ 0) is always a tangent to the parabola y2 = 4ax and point of contact is \(\left(\frac{a}{m^2}, \frac{2 a}{m}\right)\)
![]()
→ Equation of the tangent at the point (x1, y1) on the parabola y2 = 4ax is yy1 = 2a (x + x1) or S1 = 0. .
→ Equation of the normal at the point (x1, y1) on the parabola S = 0 is y – y1 = \(-\frac{y_1}{2 a}\) (x – x1).
→ Equation of tangent at a point ‘t’ i.e„ (at2, 2at) on y2 = 4ax is x = yt + at2.
→ Equation of normal at a point ‘t’ on y2 = 4ax is y + xt = 2at + at3.