Here students can locate TS Inter 1st Year Physics Notes 1st Lesson Physical World to prepare for their exam.
TS Inter 1st Year Physics Notes 1st Lesson Physical World
→ Physics: Physics is the study of nature and natural phenomena.
→ Fundamental forces in nature : In physics
- Gravitational force
- Electromagnetic force
- Strong nuclear force
- Weak nuclear force.
→ Gravitational force : It is the force of attraction between any two objects by virtue of their masses.
These are very weak forces. They are very long distance forces. For heavy bodies like planets and stars etc. the magnitude of these forces is high. These forces are very important in planetary motion, and in formation of Stars and Galaxies.
→ Electromagnetic forces : It is the force between two charged particles.
Between like charges they are “repulsive forces” and between unlike charges they are “attractive forces”. These forces are very strong forces. These are long distance forces.
→ Strong nuclear forces: Strong nuclear forces bind protons and neutrons in a nucleus.
These are very strong attractive forces. They are 100 times stronger than electromagnetic forces. They are short range forces. Their effect is upto very few fermi.
→ Weak nuclear forces: Weak nuclear forces will appear only in certain nuclear processes such as β – decay of nucleus where nucleus emits electron and neutrino. These are weak forces, their range is upto few fermi.
→ Conserved quantities: In physics any physical phenomenon is governed by certain forces. Si.oeral physical quantities will change with time but some special physical quantities will remain constant with time. Such physical quantities are called conserved quantities of nature.
Ex : For motion under an external conser-vative force such as gravitational field the total mechanical energy (i.e., P.E + K.E) is constant or energy is conserved.
![]()
→ Some physicists and their major contributions
| Name | Major contribution/ Discovery |
| 1. Archimedes | Principle of buoyancy, Principle of the lever |
| 2. Galileo Galilei | Law of inertia |
| 3. Isaac Newton | Universal law of gravitation; Laws of motion, Corpuscular theory of light; Reflecting telescope. |
| 4. C.V.Raman | Inelastic scattering of light by molecules. |
| 5. Edwin Hubble | Expanding universe |
| 6. Hideki Yukawa | Theory of nuclear forces |
| 7. S. Chandrasekhar | Chandrasekhar limit, structure and evolution of stars |
| 8. Michael Faraday | Electromagnetic induction laws |
| 9. James Clark Maxwell | Electromagnetic theory – light – electromagnetic waves |
| 10. J.J.Thomson | Electron |
| 11. Albert Einstein | Explanation of photoelectric effect and theory of relativity |
| 12. R.A.Millikan | Measurement of charge of electron. |
| 13. Ernest Rutherford | Nuclear model of atom |
| 14. John Bardeen | Transistors; Theory of super conductivity. |
→ Fundamental forces of nature
| Name | Relative strength (N) |
| l. Gravitational force | 10-39 |
| 2. Weak nuclear forces | 10-13 |
| 3. Electromagnetic forces | 10-2 |
| 4. Strong nuclear forces | 1 |
→ Fundamental constants of Physics
| Physical constant | Symbol | Value |
| 1. Speed of light in vacuum | c | 3 × 108 meter/sec |
| 2. Planck’s constant | h | 6.63 × 10-34 joule.sec |
| 3. Molar gas constant | R | 8.31 joule/mole.K |
| 4. Avogadro’s number | NA | 6.02 × 1023/ mol |
| 5. Boltzmann’s constant | K | 1.38 × 10-23/mol |
| 6. Gravitational constant | G | 6.67 × 10-11 Newton.m2/kg2 |
| 7. Mechanical equivalent of heat | J | 4.185 joule/cal. |
| 8. Triple point of water | Ttr | 273.16 K |
| 9. Density of water at 20° C | dw | 103kg/m3 |
| 10. Density of mercury | dm | 13.6 × 103 kg/m3 |
| 11. Density of dry air at N.T.P. | da | 1.293 kg /m3 |
| 12. Specific heat of water | sw | 1 cal./gm/°C |
| 13. Latent heat of ice | Lf | 80 cal./gm |
| 14. Latent heat of steam | Lv | 540 cal/gm (or 539) |
| 15. √5 = 2.236, √3 = 1.732, √10 = 3.162, loge 10 = 2.3026 | ||
| 16. π = 3.14, π2 = 9.87, √π = 1.7772, √2 = 1.414 | ||
→ Conversion factors:
| 1 metre | 100 cm |
| 1 millimeter | 10-3m |
| 1 inch | 2.54 × 102 m |
| 1 micron (p) | 10-4cm |
| 1 Angstrom (A0) | 10-8cm |
| 1 fermi (f) | 10-13 cm |
| 1 kilometer | 103 m |
| 1 light year | 9.46 × 1015 m |
| 1 litre | 103 cm3 |
| 1 kilogram | 1000 gm |
| 1 metric ton | 1000 kg |
| 1 pound | 453.6 gm |
| 1 atomic mass unit (a.m.u) | 1.66 × 10-27 kg |
| 1 a.m.u | 931 MeV |
| 1 day | 8.640 × 104 seconds |
| 1 km/hour | \(\frac{5}{8}\)m/sec (or) 0.2778 meter/sec |
| 1 Newton | 105 dynes |
| 1 gm wt | 980.7 dynes |
| 1 kg.wt | 9.807 Newton |
| 1 Newton/meter2 | 1 pascal |
| 1 atmospheric | 1.0133 × 105 |
| pressure | pascal (N/m2) |
| 1 atmospheric | 76 cm of Hg |
| pressure | |
| 1 Pascal | 10 dyne/cm2 |
| 1 Joule | 107erg |
| 1 kilo watt hour | 3.6 × 106 joule |
| 1 electro volt (ev) | 1.602 × 10-19 joule |
| 1 watt | 1 joule / sec |
| 1 horse power (HP) | 746 watt |
| 1 degree (° ) | 60 minute (‘) |
| 1 Radian | 57.3 degree ( ° ) |
| 1 Poise | 1 dyne . sec / cm2 |
| 1 Poiseuille | 10 poise |
| (Newton, sec/m2 (or) Pascal sec.) | |
![]()
→ Important Prefixes:
| Prefix | Symbol | Multiplier |
| Exa | E | 1018 |
| Peta | P | 1015 |
| Tera | T | 1012 |
| Giga | G | 109 |
| Mega | M | 106 |
| Kilo | k | 103 |
| Hecto | h | 102 |
| Deca | da | 101 |
| deci | d | 10-1 |
| centi | c | 10-2 |
| milli | m | 10-3 |
| micro | 0 | 10-6 |
| nano | n | 10-9 |
| pico | P | 10-12 |
| femto | f | 10-15 |
| atto | a | 10-18 |
→ The Greek Alphabet:
| Alpha | α |
| Beta | β |
| Gamma | γ |
| Delta (A) | δ |
| Epsilon | ε |
| Rho | ρ |
| Lambda | λ |
| Mu | μ |
| Nu | ν |
| Xi | ξ |
| Pi | π |
| Theta | θ |
| Tau | τ |
| Chi | χ |
| Psi | Ψ |
| Omega | ω |
| Eta | η |
| Sigma(Σ) | σ |
→ Formulae of geometry :
- Area of triangle = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × base × height
- Area of parallelogram = base × height
- Area of square = (length of one side)2
- Area of rectangle = length × breadth
- Area of circle = πr2 (r = radius of circle)
- Surface area of sphere = πr2 (r = radius of sphere)
- Volume of cube = (length of one side of cube)3
- Volume of parallelopiped = length x breadth x height
- Volume of cylinder = πr2l
- Volume of sphere = \(\frac{4}{3}\)πr3
- Circumference of square = 41
- Volume of cone = \(\frac{1}{3}\)πr2h
- Circumference of circle = 2πr
→ Formulae of algebra:
- (a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab
- (a – b)2 = a2 + b2 – 2ab
- (a2 – b2) = (a + b) (a – b)
- (a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab (a + b)
- (a – b)3 = a3 – b3 – 3ab (a – b)
- (a + b)2 – (a – b)2 = 4ab
- (a + b)2 + (a – b)2 = 2(a2 + b2)
![]()
→ Formulae of differentiation:
- \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (constant) = 0 differentiation with respect to x = \(\frac{d}{d x}\)
- \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (xn) = n xn-1
- \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (sin x) = cos x
- \(\frac{d}{d x}\)(cos x) = – sin x dx
→ Formulae of Integration:
Integration with respect to x = ∫dx
- ∫dx = x
- ∫xn dx = \(\frac{x^{n+1}}{n+1}\)
- ∫sin x dx = cos x + c
- ∫cos x dx = sin x + c
→ Formulae of logarithm :
- log mn = (log m + log n)
- log(\(\frac{m}{n}\)) = (log m – log n)
- log mn = n log m
→ Value of trigonometric functions :
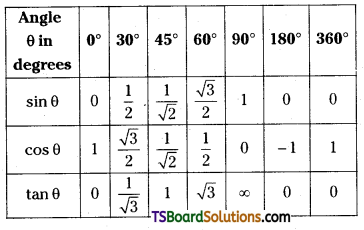
→ Signs of trigonometrical ratios :
- sin (90° – θ) = cos θ ; sin (180° – θ) = sin θ
- cos (90° – θ) = sin θ ; cos (180° – θ) = – cos θ
- tan (90° – θ) = cot θ ; tan (180° – θ) = – tan θ
→ According to Binomial theorem :
(1 + x)n ≈ (1 + nx) if x < < 1
→ Quadratic equation:
ax2 + bx + c = 0
x = \(\left(\frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-4 a c}}{2 a}\right)\)