Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 2nd Year Economics Study Material 9th Lesson Environmental Economics Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 2nd Year Economics Study Material 9th Lesson Environmental Economics
Essay Questions
Question 1.
Explain different types of pollution and examine their effects.
Answer:
Pollution :
Environmental pollution refers to the presence of mater (gas, liquid, solid) or energy (heat, noise, radiation) whose nature, location of quality directly or indirectly alters characteristics or processes of any part of environment, and causes (of has the potential to cause) damage to the condition, health, safety or welfare of animals, humans, plants or property. In short it is a term that refers to all the ways by which people pollute their surroundings.
1. Air Pollution :
Air pollution is a mixture of solid particles and gases in the air. The sources of air pollution are :
- agricultural activities
- Combustion
- manufacturing processes
- solvent usage; and
- nuclear energy programmes.
Air pollution affects the respiratory system of humans, animals and birds. It causes diseases like T.B. and asthma. Air pollution affects food items, vegetables and fruits. Plants, crops and grazing lands are covered with layers of dust and land productivity decreases. Its effects are felt on monuments, buildings and art forms as particles of acid are spread out.
It damages the green house and there by the temperature on the earth increases, icy glaciers and polar regions melt down. Life of the living organisms become vulnerable. Acid rains are also due to air pollution and they damage the earth’s surface, buildings, trees, plants and wild life.
2. Water Pollution :
The process of altering the properties of water which makes it useless or harmful is called water pollution. It is defined as the addition of excess materials to water, which are harmful to living organisms. It is a change in the quality of water due to which it is unusable or dangerous. Fresh water contains dissolved materials like phosphates, oxygen, hydrogen, organic compounds, silt and micro organisms. Lack of balance between them is due to pollution. Main water pollutants are :
- sewage and other oxygen demanding wastes infectious agents
- exotic organic chemicals and
- inorganic mineral and compounds.
- radioactive waste
- plastic pollution .
- chemical fertilisers and pesticides.
Water-born diseases like cholera, typhoid and dysentry affect human health, especially, in the rural areas where safe drinking water is a problem. Water pollution decreases the agricultural productivity and degrades the natural fertility of the soil. Cost of production of some industries increases as they have to spend huge amounts to purify water they need. Water pollution kills the fish and thus damages the aquatic food reserves.
3. Noise Pollution :
Noise pollution refers to the physiological or psychological harm created by sound. Traffic, railways, industries, construction works, public gatherings, use of loud speaker, crackers, drums etc. are the sources of noise pollution. Loud or disagreeable sound is noise. Noise is a pollution component and it deteriorates the environment. Noise pollution affects human beings, animals and birds also. It damages the ear and causes temporary or permanent hearing loss, Prolonged exposure to noise pollution causes deafness. Some times noise pollution creates physiological disorders. It creates irritation and affects the brain and nervous system. Mental fatigue, lack of concentration and inability to think and act properly are the other effects. The efficiency of labour and their occupational performances decrease due to continuous exposure to noise.
![]()
Question 2.
In what way environmental degradation effects the economy? Suggest remedial measures to overcome this problem.
Answer:
Environmental degradation means the disintegration of the earth or the deterioration of the natural assets in the environment. It is any change or aggravation to nature’s turf which is undesirable. It occurs when earth’s natural resources are depleted as result of which extinction of some species, pollution in air, water and soil take place. Environmental degradation has become one of the largest threats to the world.
Effects of Environmental Degradation :
- Human health is at the receiving end. Pollution has increased. Diseases like asthma, pneumonia and diarrhea. These are bringing about certairi atmospheric changes which are likely cause uncertain and irreversible hazards like green house effects and ozone deplection to future generations. Air bom, water borne and sound related health issues have been increasing.
- Bio-diversity is important to maintain the balance of the eco-system. Environment degradation leads to loss of bio-diversity.
- Ozone layer protects the earth from harmful ultraviolet rays. Environmental degrada-tion depletes the ozone layer. Harmful radiations are sent back to the earth.
- Tourists visit a country to see and enjoy the nature, animals birds and lush green landscape. Environmental degradation discourages tourist traffic into a country.
- Government is constrained to spend huge amounts to protect environment from degradation and this is an avoidable burden.
- Environmental degradation can be prevented and taken care of the mother earth. People should be educated on the need to preserve and protect environment from degradation.
Question 3.
Explain the causes and consequences of various pollutions.
Answer:
Answer:
Pollution :
Environmental pollution refers to the presence of mater (gas, liquid, solid) or energy (heat, noise, radiation) whose nature, location of quality directly or indirectly alters characteristics or processes of any part of environment, and causes (of has the potential to cause) damage to the condition, health, safety or welfare of animals, humans, plants or property. In short it is a term that refers to all the ways by which people pollute their surroundings.
1. Air Pollution :
Air pollution is a mixture of solid particles and gases in the air. The sources of air pollution are :
- agricultural activities
- Combustion
- manufacturing processes
- solvent usage; and
- nuclear energy programmes.
Air pollution affects the respiratory system of humans, animals and birds. It causes diseases like T.B. and asthma. Air pollution affects food items, vegetables and fruits. Plants, crops and grazing lands are covered with layers of dust and land productivity decreases. Its effects are felt on monuments, buildings and art forms as particles of acid are spread out.
It damages the green house and there by the temperature on the earth increases, icy glaciers and polar regions melt down. Life of the living organisms become vulnerable. Acid rains are also due to air pollution and they damage the earth’s surface, buildings, trees, plants and wild life.
2. Water Pollution :
The process of altering the properties of water which makes it useless or harmful is called water pollution. It is defined as the addition of excess materials to water, which are harmful to living organisms. It is a change in the quality of water due to which it is unusable or dangerous. Fresh water contains dissolved materials like phosphates, oxygen, hydrogen, organic compounds, silt and micro organisms. Lack of balance between them is due to pollution. Main water pollutants are :
- sewage and other oxygen demanding wastes infectious agents
- exotic organic chemicals and
- inorganic mineral and compounds.
- radioactive waste
- plastic pollution .
- chemical fertilisers and pesticides.
Water-born diseases like cholera, typhoid and dysentry affect human health, especially, in the rural areas where safe drinking water is a problem. Water pollution decreases the agricultural productivity and degrades the natural fertility of the soil. Cost of production of some industries increases as they have to spend huge amounts to purify water they need. Water pollution kills the fish and thus damages the aquatic food reserves.
3. Noise Pollution :
Noise pollution refers to the physiological or psychological harm created by sound. Traffic, railways, industries, construction works, public gatherings, use of loud speaker, crackers, drums etc. are the sources of noise pollution. Loud or disagreeable sound is noise. Noise is a pollution component and it deteriorates the environment. Noise pollution affects human beings, animals and birds also. It damages the ear and causes temporary or permanent hearing loss, Prolonged exposure to noise pollution causes deafness.
Some times noise pollution creates physiological disorders. It creates irritation and affects the brain and nervous system. Mental fatigue, lack of concentration and inability to think and act properly are the other effects. The efficiency of labour and their occupational performances decrease due to continuous exposure to noise.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the objectives of environmental sustainability? Explain the im-portance of sustainable development.
Answer:
Sustainable Development: Economic development without destruction of the envi-ronment is called sustainable development. Such a development integrates environment in the process. It can be defined as “development meeting the needs of the present without compro-mising the ability of the future generations to meet their own needs”. Mere growth is not enough to enhance the human well-being; it is accepted that a balance between the use of resources and their regeneration sustains the process of development.
Objectives of Sustainable Development :
1. Increase of Growth or Income :
Sustainable development aims to increase the standard of living of all the sections of the society. Health, education, participation in public life, clean environment and promotion of equity for the future generations are included in improving standards of livings.
2. Continuity of Development :
Physical, human and natural capital are to be preserved and carefully used under sustainable development. It emphasizes both present and future de-velopment.
3. Controlling Degradation :
Development should not lead to environmental degradation affecting the quality of life. Development should not reduce productivity in the long run. It implies control of pollution. Quality of land, water, air and soil should be maintained for sustainable development, Current decisions on economic development should not impair the prospects of living standards of future”generations.
4. Protection of Bio-Diversity :
Sustainable development assigns priority to preserve the bio-diversity. All production activities are related to bio-diversity Genetic diversity, species diversity and eco-diyersity are to be maintained for sustained development.
Importance of Sustainable Development: Sustainable development practices protect wild life, forests, water bodies and biodiversity needed for life to continue on earth. The importance of sustainable development is as follows :
1. Change of Attitudes :
Sustainable development changes the attitudes of the people. Instead of abusing nature we must preserve and protect it. It promotes the attitude to use natural resources to satisfy our needs but not greed.
2. Eco-Friendly Innovations :
It encourages only eco-friendly methods and innovations for economic development.
3. Limits Economic Activities :
It limits the economic activities within the absorbing capacity of the environment.
4. Future Development :
It ensures economic well-being of the future generations by protecting the environment.
5. Scope for Increased Action by the Government :
Sustained development assigns greater role to the governance. The activities of the government under sustained development include:
a) community involvement,
b) decentralization,
c) positive incentives,
d) creation of new policy and administrative mechanism; and
e) encouragement to environmental workers and NGOs.
6. New Look to Growth :
Sustainable development gives a new meaning to economic growth in terms of quality of life.
7. Conservation of Resources :
Sustainable development harps upon the need to conserve resources for continuity and equality in development. It encourages regeneration of resources.
8. Preserves Bio-Diversity :
Sustainable development recognizes the importance of bio-diversity. Human survival depends oh the preservation and maintenance of bio-diversity. It encourages policies to control:
a) environmental degradation.
b) pollution.
c) over exploitation fo natural resources.
d) decline in the flora and fauna; and
e) global environmental disparities.
9. Balances Economic, Social and Environmental Dimensions of Development :
The three components of sustainable development are interlinked as shown below:
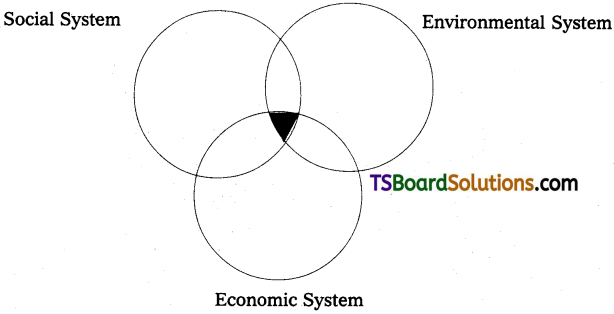
10. Realization of the Importance of Nature :
Sustainable development helps the stake holders to realize the importance of nature. This earth is meant for all the living organisms, but not to human beings only. All of us should preserve it and hand it over to future generations.
Sustainable development reminds the humanity of the need to work with others to help, sustain and heal the earth. It stresses the need to protect and preserve environment with all its resources.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are natural resources?
Answer:
Natural Resources :
Resources are the means to satisfy human needs at a given time and place. Nature is a reservoir of different resources. These resources are used in production process to satisfy the consumption needs. Natural resources are defined as organic and inorganic matter provided outside the economic system which are manipulated by humans to furnish the raw materials needed to satisfy human wants.
Features of Natural Resources :
- They are free gift of nature and persons only extract them.
- The stock of the natural resources is fixed at a given point of time.
- Some natural resources are hidden in nature and they come out only when persons explore them with technology.
- The stock is fixed by nature in many cases.
- The changes in the stock of natural resources are subject to natural and biological changes over a period of time.
- With the development of technology and scientific knowledge new resources emerge from nature over a period of time.
![]()
Question 2.
What is the sustainable development?
Answer:
Economic development without destruction of the environment is called sustainable de-velopment. Such a development integrates environment in the process. It can be defined as development meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of the future generations to meet their own needs. Mere growth is not enough to enhance the human well being it is accepted that a balance between the use of resources and their regeneration sustains the process of development. Hence, development strategies today emphasis the development of the environment economy and the society together. Development goes on taking place if it is sustainable.
The concept of sustainable development was first used in 1980 by the world conservation strategy presented by the international Union for Conservation for Nature. The term “sustain-able development” was brought into common use by the Brundtland report.
Daly (1990) gave three rules for sustainable development which include :
- Those resources which are renewable are not used at a rate which surpasses the rate of their regeneration.
- Those resources which are not renewable are not used at a rate which surpasses the rate at which a substituting resource become available.
- The rate of which polluting materials are disposed off does not surpass the carrying capacity Of the environment.
Question 3.
Why should we protect the environment?
Answer:
Need for Environment production :
The need for environmental protection can be explained here under:
1) Most of the developing countries including India depend on agriculture. Agricultural development and food security depend on environment. Good rains, climate, soil and quality seeds are made available by the environment. Over utilization of chemical fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides damage the environment andn in the long run, land loses its original fertility.
2) Forests and vegetation provide rains and balanced weathers. Forests regain water to maintain the ground water levels favourably. More trees should be planted to balance the depleted forests.
3) Environmental protection helps economic activities like mining, dairy, fisheries along with industries. A country can eliminate poverty by producing more goods in the long run by maintaining environmental balance.
4) Environmental protection contributes to social development by increasing health and wealth of a nation.
5) Environmental protection promotes human happiness. Environmental imbalances lead-ing to floods, earth quakes, famines, cyclones destroy the economy and society.
6) Over-use of natural resources by the present generation damages the interests and well being of the future generations. Environmental protection through sustainable development takes care of the future generations and their economic welfare.
7) Environmental protection ensures pollution – free living. Health and happiness of the humanity improve a lot in a no-pollufion situation.
8) Environmental protection helps to maintain bio-diversity and ecological balance. It also helps to maintain the ozone layer, glaciers and other endowments of nature in proper order.
![]()
Question 4.
Discuss the types of pollutions.
Answer:
Pollution :
Environmental pollution refers to the presence of mater (gas, liquid, solid) or energy (heat, noise, radiation) whose nature, location of quality directly or indirectly alters characteristics or processes of any part of environment, and causes (of has the potential to cause) damage to the condition, health, safety or welfare of animals, humans, plants or property. In short it is a term that refers to all the ways by which people pollute their surroundings.
1. Air Pollution :
Air pollution is a mixture of solid particles and gases in the air. The sources of air pollution are :
- agricultural activities
- Combustion
- manufacturing processes
- solvent usage; and
- nuclear energy programmes.
Air pollution affects the respiratory system of humans, animals and birds. It causes diseases like T.B. and asthma. Air pollution affects food items, vegetables and fruits. Plants, crops and grazing lands are covered with layers of dust and land productivity decreases. Its effects are felt on monuments, buildings and art forms as particles of acid are spread out.
It damages the green house and there by the temperature on the earth increases, icy glaciers and polar regions melt down. Life of the living organisms become vulnerable. Acid rains are also due to air pollution and they damage the earth’s surface, buildings, trees, plants and wild life.
2. Water Pollution :
The process of altering the properties of water which makes it useless or harmful is called water pollution. It is defined as the addition of excess materials to water, which are harmful to living organisms. It is a change in the quality of water due to which it is unusable or dangerous. Fresh water contains dissolved materials like phosphates, oxygen, hydrogen, organic compounds, silt and micro organisms. Lack of balance between them is due to pollution. Main water pollutants are :
- sewage and other oxygen demanding wastes infectious agents
- exotic organic chemicals and
- inorganic mineral and compounds.
- radioactive waste
- plastic pollution .
- chemical fertilisers and pesticides.
Water-born diseases like cholera, typhoid and dysentry affect human health, especially, in the rural areas where safe drinking water is a problem. Water pollution decreases the agricultural productivity and degrades the natural fertility of the soil. Cost of production of some industries increases as they have to spend huge amounts to purify water they need. Water pollution kills the fish and thus damages the aquatic food reserves.
3. Noise Pollution :
Noise pollution refers to the physiological or psychological harm created by sound. Traffic, railways, industries, construction works, public gatherings, use of loud speaker, crackers, drums etc. are the sources of noise pollution. Loud or disagreeable sound is noise. Noise is a pollution component and it deteriorates the environment. Noise pollution affects human beings, animals and birds also. It damages the ear and causes temporary or permanent hearing loss, Prolonged exposure to noise pollution causes deafness. Some times noise pollution creates physiological disorders. It creates irritation and affects the brain and nervous system. Mental fatigue, lack of concentration and inability to think and act properly are the other effects. The efficiency of labour and their occupational performances decrease due to continuous exposure to noise.
Question 5.
Bring out the relationship between environment and development.
Answer:
Economic development in the context of environmental degradation poses health related issues also to the poor. Environmental costs are not taken into account while calculating GNP. The basic reason for this lacuna is a historical absence of environmental consideration in the process of economic development. Long term national productivity is affected due to the damage to the environment. Rapid population growth and expanding economic activities are likely to damage the environment within which further economic activity would take place.
Environment provides the raw materials and proper climatic conditions for the economic activities. At the same time it absorbs the wastes discharged by the economic enterprises. Reckless and exploitative natue of the economic activity reduces the efficiency of environment to supply the needed resources. Over the years, the capacity of environment to absorb different wastes also decline. Economists like Kenneth E Bounding warned the world about the conse-quences of pressure in the interest of the future as well as the present generations. A balance between inputs to produce goods and the discharge of waste should be maintained. The quantitiy of wastes and emissions must be less, so that absorption by the environment can be feasible.
Environment performs three interlinked economic functions it supplies us both renewable and non-renewable resources it assimilates the waste and it provides’the life support services. These functions have positive values. Crisis arises when the environment fails to perform these three functions. Hence, economic functions of the. environment are to be viewed carefully. One should recognise that there are interlinkages between economic development and the environment.
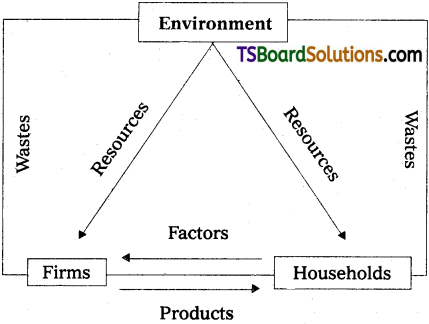
All the resources for economic development come from nature. Life on this earth survives only within environment. There is a necessity to conserve resources without decreasing the growth rates. Development projects involve ecological issues and depletion of the resources. So conservation programmes are to be planned while formulating social and economic objectives.
Economic development is to keep sustainability in view. Sustainable development aims to take care of future generations and environmental capital which includes pure air, safe drinking water, forest and mineral resources. Pollution of air, water, noise and vision is the direct dutcome of economic development. Environmental pollution is the externality of economic growth. Over production in a country creates air, water and noise pollution.
Economic policies concerned with agriculture and rural development should be environ-ment.friejidly. Farm practice, bio-diversity, limited use of chemical fertilizers, water harvesting and development of plantations be conceived in the interest of environmental protection and sustainable development.
Growing urbanization creates problems to the environment. Migration of rural people to urban centers has increased the slums. They create water, air and vision pollution. Sanitation becomes a major issue in the urban centers besides housing. Vehicular and industrial emissions pollute the environment. Urbanization as a result of rapid industrialization and growing economic activities damages the environment.
Grbwing consumerism in the process of development leads to over exploitation and misuse of natural resources. Depletion of ozone layer, global warming, acid rains and untimely floods are some of the problems due to production and excessive use of resources.
Environment provides the resources for economic development. At the same time it gets degraded through economic activities. A balance between these two is to be maintained by all the global partners.
![]()
Question 6.
Point out the reasons for environmental degradation.
Answer:
United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction characterizes environmental degradation as the decrease in the limit of the earth to meet social and environmental degradation.
Reasons for Environment Degradation :
1. Land Disturbance :
Weedy plant species assume control over nature and eliminate the local greenery. Invasive species destroy land and environmental assets. Over grazing also disturbs the fertile turf and earth becomes hard. Land degradation and soil erosion are serious problems which India is facing, as nearly 40 percent of land is subjected to soil erosion through water and wind.
2. Pollution :
Air, water, land and noise pollutions are harmful for the environment. They destroy the quality in air, water and land. Sound pollution damages the ears and threatens the animals and birds. Rapid population growth also puts strain on the natural resources due to which environment degrades.
3. Solid and Hazardous Wastes :
Many cities, particularly in developing countries, generate more solid wastes than they can collect or dispose of. Even where provision for collection is satisfactory, safe disposal of collected wastes often remains a problem. It badly affects human health and productivity. In addition to spreading disease, solid and hazardous wastes pollute ground water resources. E-waste is another important and growing hazardous waste. Electronic waste is one of the fastest growing waste streams worldwide.
4. Soil Degradation :
One of the chief forms of soil degradation is soil erosion, which is often a result of wind and water erosion. Soil erosion denudes the agricultural land of its top fertile layer and thus affects agricultural productivity adversely. It also harms productivity by depositing silt in dams, irrigation systems and river transport channels and by damaging fish-eries. Salinisation and water logging are other serious forms of soil degration. If salinity level is exceeded, the land becomes unfit for cultivation.
5. Rangeland Degradation :
In general, rangeland degradation is reduction in the status of natural Vegetation. The main causes of rangeland degradation in India are irrational land use management practices leading to denudation of vegetation from rangelands which exacerbated by intermittent droughts has resulted in many parts of desertification. Rangeland degradation affects water quality because streams, rivers and lakes are strongly influenced1 by land scape characteristics of their watershed.
6. Loss of Biodiversity :
Biodiversity comprises of genetic information, species and eco-systems. It is an essential requirement for the maintanance of global food supply. Production activities depend on biodiversity. Biological diversity provides the cultural identity. Hence, loss of biodiversity jeopardises all this.
7. Deforestation :
Deforestation is cutting down of trees to provide space for more homes and industries. Trees in the forest are destroyed for fuel and to take up agriculture. Big river valley projects are also responsible for the clearance of the forests. Deforestation increases global warming by sending carbon back into environment.
8. Natural Causes :
Earth quakes, tidal waves, storms, tsunamis and wild fires crush animals and plant groups. They have immediate as well as long term effectgs on nature.
9. Industrialization and Over Production :
Science and technology have expanded pro-ductive capacities of the nations at the global level; Raw materials and other natural resources are exploited extensively to produce more. Replacement is not planned. Industries through smoke, sound, effluents degrade the environment.
10. Faulty Mining Practices :
Large scale extraction of minerals are creating serious environmental problems, ruining the country’s land, water, forest and air. The disposable mining waste, mineral dust from mines are constantly polluting the air and also reducing agricultural productivity.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Types of Environment
Answer:
Environment is the combination of all physical and organic factors that act on living, being. These are three types of environment.
- Physical environment
- Biotic environment .
- Social or Cultural environment.
![]()
Question 2.
Ecosystem.
Answer:
This concept was given by A.G. Tansely in the year 1935. An ecosystem is a region with specific land scape such as forest grassland, desert, plant and animals.
Question 3.
Air pollution.
Answer:
Air is the combination of various individual gases like oxygen and hydrogen.
The recessive concentration of contaminated substance in the air which adversely affects the well’being of the individuals, living organs and properly of all forms is called as air pollution.
Question 4.
Water pollution.
Answer:
Water is very essential for the existence of all the living organisms. Water.pollution is defined as the addition of some substances of factor present in water which degrades its quality. So that it becomes health hazard or unfit for use. Increased human and economic activities make the water impure for consumption.
Question 5.
Physical Environment.
Answer:
It is also known as abiotic environment and natural environment. It includes non-living or physical things like land, water, air and atmosphere. Climatic factors like sun beams, rain water etc., are included in this.
Question 6.
Environmental degradation.
Answer:
Depletion of potentially renewable resources. It means the disintegration of the earth or the deterrioration of the natural assets in the environment. It has become one of the largest threats to the world.
Question 7.
Sustainable development.
Answer:
Concepts of sustainable development :
Economic development without the destruction of the environment is called sustainable development. It can be defined as development meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
![]()
Question 8.
Renewable and non-renewable resources.
Answer:
Natural resources which can be used permanently without depletion are called renewable resources. They are not exhaustible. Their stock is not fixed. These are also known as non-conventional resources. For example solar, wind, and tidal.
The natural resources which will exhaust by use are called nonrenewable resources. They cannot be regenerated. They are also called conventional resources example gold, silver, copper oil, gas, coal, etc.