Students must practice these Maths 1A Important Questions TS Inter 1st Year Maths 1A Hyperbolic Functions Important Questions to help strengthen their preparations for exams.
TS Inter 1st Year Maths 1A Hyperbolic Functions Important Questions
Question 1.
Show that sin h(x + y) = sin x cos hy + cos hx sin hy. [Mar ’98]
Answer:
R.H.S = sin x cos hy + cos hx sin hy
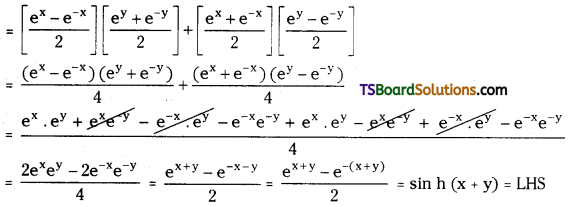
∴ sin h(x + y) = sin hx cos hy – cos hx. sinhy
Question 2.
Show that cos h(x + y) = cos hx cos hy + sin hx sin hy. [Mar. ’98, ’92]
Answer:
R.H.S = cos hx cos hy + sin hx sin hy
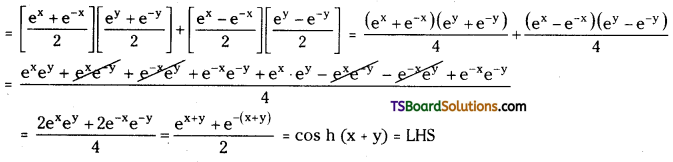
∴ cos h(x + y) = cos hx cos hy + sin hx sin hy.
Question 3.
Prove that sinh 2x = \(\frac{2 \tan h x}{1-\tan h^2 x}\). [May ’00]
Answer:
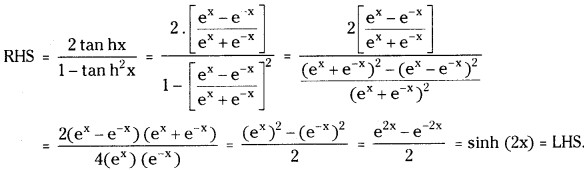
Question 4.
Show that cosh 2x – 1 = 2sinh2x. [Mar. ’08]
Answer:
L.H.S = cosh 2x – 1 = \(\frac{\mathrm{e}^{2 x}+\mathrm{e}^{-2 x}}{2}\) – 1
= \(\frac{\mathrm{e}^{2 x}+\mathrm{e}^{-2 \mathrm{x}}-2}{2}=\frac{\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}}-\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{x}}\right)^2}{2}\)
= \(2\left[\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}}-\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{x}}}{2}\right]^2\) = 2sinh2x = RHS
![]()
Question 5.
Show that sinh-1x = loge(x + \(\sqrt{x^2+1}\)) [May ’03, ’97, ’95, ’91; Mar. ’95]
Answer:
Let sinh-1x = y
sinh y = x ⇒ \(\frac{e^y-e^{-y}}{2}\) = x
⇒ ey – e-y = 2x
⇒ ey – \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{y}}}\) = 2x
⇒ (ey)2 – 1 = 2xey
⇒ (ey)2 – 2xey – 1 = 0
This is a quadratic equation in ey then
x = \(\frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-4 a c}}{2 a}\)
⇒ e = \(\frac{-(-2 x) \pm \sqrt{(-2 x)^2-4(1)(-1)}}{2.1}=\frac{2 x \pm \sqrt{4 x^2+4}}{2}\)
= x ± \(\sqrt{x^2+1}\)
Since ey > 0 then, ey = x + \(\sqrt{x^2+1}\)
y = loge(x + \(\sqrt{x^2+1}\)
∴ sinh-1x = loge(x + \(\sqrt{x^2+1}\))
Question 6.
Show that cosh-1x = loge(x + \(\sqrt{x^2-1}\)) [Mar. ’03; May. ’96]
Answer:
Let cosh-1x = y
cosh y = x ⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{y}}+\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{y}}}{2}\) = x
⇒ ey + e-y = 2x
⇒ ey + \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{y}}}\) = 2x
⇒ (ey)2 + 1 = 2xey
⇒ (ey)2 – 2xey + 1 = 0
This is a quadratic equation in ey then
x = \(\frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-4 a c}}{2 a}\) ey
= \(\frac{-(-2 \mathrm{x}) \pm \sqrt{(-2 \mathrm{x})^2-4(1)(1)}}{2.1}=\frac{2 \mathrm{x} \pm \sqrt{4 \mathrm{x}^2-4}}{2}\)
= x ± \(\sqrt{x^2-1}\)
Since ey > 0 then ey = x + \(\sqrt{x^2-1}\)
y = loge (x + \(\sqrt{x^2-1}\))
∴ cosh-1x = loge(x + \(\sqrt{x^2-1}\))
Question 7.
Show that tanh-1x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge\(\left(\frac{1+x}{1-x}\right)\). [May ’97, ’93]
Answer:
Let tanh-1x = y
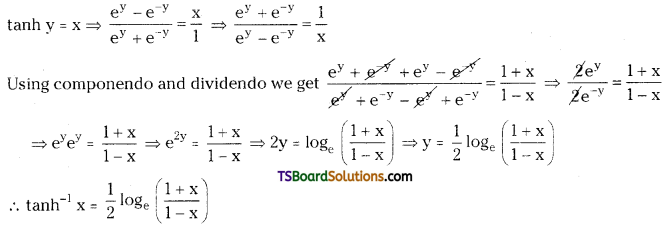
Question 8.
If cosh x = \(\frac{5}{2}\), find the values of (i) cosh (2x) (ii) sinh (2x). [Mar. ’19, ’17 (TS), 16′ (AP), ’11, ’10, ’01; May ’15(TS), ’11, ’06]
Answer:
Given cosh x = \(\frac{5}{2}\)
(i) cosh (2x) = 2 cosh2x – 1 = 2\(\left(\frac{5}{2}\right)^2\) – 1
= 2\(\left(\frac{25}{4}\right)\) – 1 = \(\frac{25-2}{2}=\frac{23}{2}\)
∴ cosh (2x) = \(\frac{23}{2}\)
(ii) We know that cosh2(2x) – sinh2(2x) = 1
\(\left(\frac{23}{2}\right)^2\) – sinh2(2x) = 1
⇒ \(\frac{529}{4}\) – sinh2 (2x) = 1
⇒ sinh2(2x) = \(\frac{529}{4}\) – 1
= \(\frac{525}{4}\) sinh (2x) = \(\pm \sqrt{\frac{525}{4}}=\pm \frac{5 \sqrt{21}}{2}\)
Question 9.
If cos hx = \(\frac{3}{2}\), then prove that tanh2\(\frac{x}{2}\) = tan2 \(\frac{θ}{2}\). [May ’13; Mar. ’13]
Answer:
Given cosh x = sec θ
LHS = tanh2(\(\frac{x}{2}\)) = \(\frac{\cosh x-1}{\cosh x+1}=\frac{\sec \theta-1}{\sec \theta+1}=\frac{1-\cos \theta}{1+\cos \theta}\) = tan2(\(\frac{θ}{2}\)) = RHS
Question 10.
If sinh x = \(\frac{3}{4}\), find cosh (2x) and sinh (2x) [Mar. ’14; ’12; May ’14, ’09]
Answer:
Given sinh x = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
(i) cosh (2x) = 1 + 2 sinh2x = 1 + 2\(\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)^2\)
= 1 + 2\(\left(\frac{9}{16}\right)=\frac{8+9}{8}=\frac{17}{8}\)
∴ cosh (2x) = \(\frac{17}{8}\)
(ii) We know that cosh2(2x) – sinh2(2x) = 1
\(\left(\frac{17}{8}\right)^2\) – sinh(2x) = 1 ⇒ \(\frac{289}{64}\) – sinh2(2x) = 1
sinh2(2x) = \(\frac{289}{64}-1=\frac{289-64}{64}=\frac{225}{64}\)
∴ sinh2(2x) =±\(\frac{15}{8}\)
Question 11.
If sinh x = 3, then show that x = loge(3 + \(\sqrt{10}\)) [May ’10; B.P]
Answer:
Given sin hx = 3 ⇒ x = sinh-1(3) = loge(3 + \(\sqrt{3^2+1}\)) [∵ sinh-1x = loge(x + \(\sqrt{\mathrm{x}^2+1}\))]
∴ x = loge(3 + \(\sqrt{10}\))
Question 12.
Show that tanh-1(\(\frac{1}{2}\)) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge 3. [Mar. ’19, ’17, ’15(AP), ’08, ’05, ’02 May ’15(AP), ’07, ’05]
Answer:
L.H.S = tanh-1(\(\frac{1}{2}\))
We know that tanh-1(x) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge\(\left(\frac{1+\mathrm{x}}{1-\mathrm{x}}\right)\)
Put x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
⇒ tanh-1(\(\frac{1}{2}\)) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge\(\left(\frac{1+\frac{1}{2}}{1-\frac{1}{2}}\right)\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge\(\left(\frac{2+1}{2-1}\right)\)
∴ tanh-1(\(\frac{1}{2}\)) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge (3)
![]()
Question 13.
Prove that (cosh x – sinh x)n = cosh (nx) – sinh (nx). [Mar. ’15(TS); Mar. ’07, ’06]
Answer:
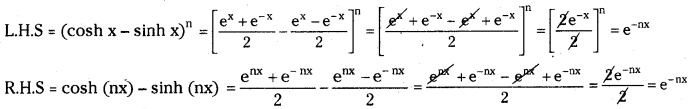
∴ L.H.S = R.H.S
∴ (cosh x – sinh x)n = cosh (nx) – sinh (nx).
Question 14.
Find the domain and range of the function y = tanh x. [May . ’04]
Answer:
Domain = R
Range = (-1, 1)
Question 15.
Show that f(x) = cosh x is an even function. [Mar. ’04]
Answer:
Given f(x) = cosh x = \(\frac{e^x+e^{-x}}{2}\)
Now, f(x) = \(\frac{\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{x}}+\mathrm{e}^{-(-\mathrm{x})}}{2}=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{x}}+\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}}}{2}\) = f(x)
∴ f(x) is an even function.
Some More Maths 1A Hyperbolic Functions Important Questions
Question 1.
Show that sinh (x – y) = sinh x cosh y – cosh x sinh y
Answer:
RHS = sinh x cosh y – cosh x sinh y
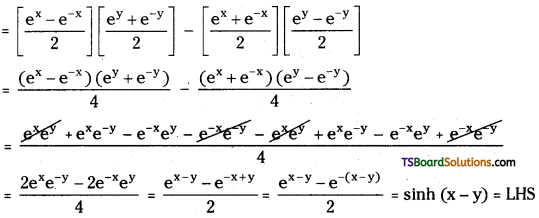
∴ sinh (x – y) = sinh x cosh y – cosh x sinh y
Question 2.
Show that cosh(x – y) = cosh x cosh y – sinh x sinh y
Answer:
RHS = cosh x cosh y – sinh x sinh y = \(\left[\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}}+\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{x}}}{2}\right]\left[\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{y}}+\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{y}}}{2}\right]-\left[\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}}-\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{x}}}{2}\right]\left[\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{y}}-\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{y}}}{2}\right]\)
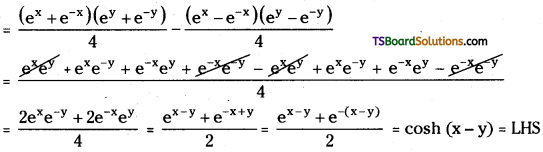
∴ cosh(x – y) = cosh x cosh y – sinh x sinh y
Question 3.
If cosh x = \(\frac{3}{2}\), then find the values of
(i) cosh 2x
(ii) sinh 2x
Answer:
Given cosh x = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
i) cosh 2x = 2cosh2x – 1 = 2\(\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)^2\) – 1 = 2.\(\frac{9}{4}\) – 1 = \(\frac{9}{2}\) – 1 = \(\frac{7}{2}\)
∴ cosh 2x = \(\frac{7}{2}\)
ii) We know that cosh22x – sinh22y = 1
\(\left(\frac{7}{2}\right)^2\) – sinh22x = 1 = \(\frac{49}{4}\) = sinh22x = \(\frac{49}{4}\) – 1 = \(\frac{45}{4}\)
⇒ sinh 2x = \(\frac{3 \sqrt{5}}{2}\)
Question 4.
If sin hx = 5, then show that x = loge(5 + \(\sqrt{26}\))
Answer:
Given sin hx = 5 ⇒ x = sinh-1x ⇒ sinh-1(5)
We know that sinh-1x = loge(x + \(\sqrt{\mathrm{x}^2+1}\))
⇒ sinh-1(5) = loge(5 + \(\sqrt{5^2+1}\))
⇒ x = loge(5 + \(\sqrt{25+1}\)) = log (5 + \(\sqrt{26}\))
∴ x = loge(5 + \(\sqrt{26}\))
![]()
Question 5.
If tan hx = \(\frac{1}{4}\), then prove that x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge\(\left(\frac{5}{3}\right)\)
Answer:
Given tan hx = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
⇒ x = tan h-1\(\left(\frac{1}{4}\right)\)
We know that tan h-1x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge\(\left(\frac{1+\mathrm{x}}{1-\mathrm{x}}\right)\) ⇒ tan h-1\(\left(\frac{1}{4}\right)\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge\(\left(\frac{1+\frac{1}{4}}{1-\frac{1}{4}}\right)\)
⇒ x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge\(\left(\frac{4+1}{4-1}\right)\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge\(\left(\frac{5}{3}\right)\)
∴ x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge\(\left(\frac{5}{3}\right)\)
Question 6.
Prove that (cosh x + sinh x)n = cosh(nx) + sinh (nx)
Answer:
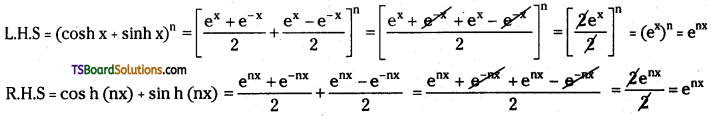
∴ L.H.S = R.H.S
∴ (cosh x + sinh x)n = cosh(nx) + sinh (nx)
Question 7.
Prove that cosh2x – sinh2x = 1
Answer:
L.H.S = cosh2x – sinh2x
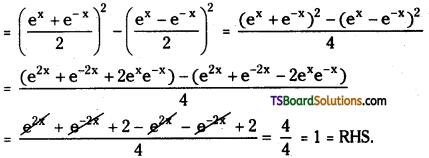
Question 8.
For any x ∈ R show that cosh 2x = 2cosh2x – 1.
Answer:
LHS = cosh 2x = \(\frac{\mathrm{e}^{2 \mathrm{x}}+\mathrm{e}^{-2 \mathrm{x}}}{2}\)
RHS = 2cosh2x – 1
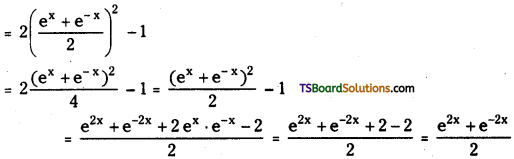
∴ LHS = RHS
∴ cosh 2x = 2cosh2x – 1
Question 9.
Prove that sinh (3x) = 3sin hx + 4 sinh3x
Answer:
RHS = 3sin hx + 4 sinh3x
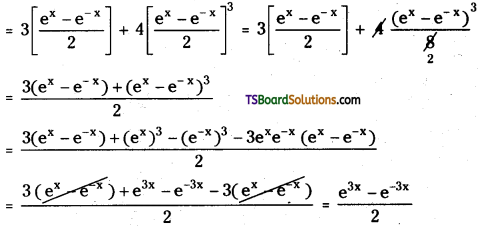
= sinh (3x) = LHS
∴ sinh (3x) = 3sin hx + 4 sinh3x
Question 10.
Prove that cos h(3x) = 4cos h3x – 3 cos hx
Answer:
RHS = 4cos h3x – 3 cos hx
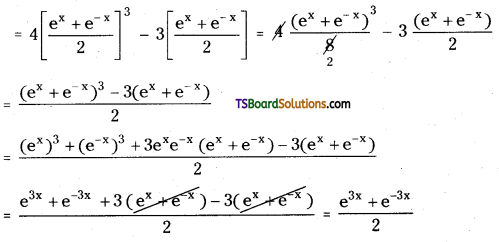
= cos h(3x) = LHS
∴ cos h(3x) = 4cos h3x – 3 cos hx
![]()
Question 11.
Prove that tanh 3x = \(\frac{3 \tanh x+\tanh ^3 x}{1+3 \tanh ^2 x}\)
Answer:
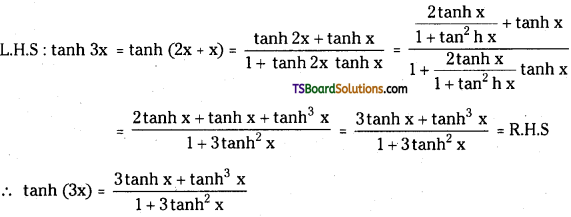
Question 12.
Prove that tanh(x – y) = \(\frac{\tanh x-\tanh y}{1-\tanh \times \tanh y}\)
Answer:
LHS = tanh(x – y)
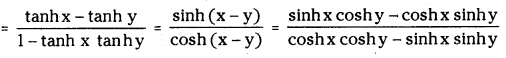
Dividing numerator and denominator by cos hx cos hy we get = \(\frac{\tanh x-\tanh y}{1-\tanh \times \tanh y}\) = RHS
∴ tanh(x – y) = \(\frac{\tanh x-\tanh y}{1-\tanh \times \tanh y}\)
Question 13.
Prove that coth(x – y) = \(\frac{{coth} x \cdot {coth} y-1}{{coth} y-{coth} x}\)
Answer:
LHS = coth(x – y)
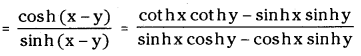
Dividing by sinh x sinh y we get = \(\frac{{coth} x {coth} y-1}{{coth} y-{coth} x}\) = RHS
∴ coth(x – y) = \(\frac{{coth} x \cdot {coth} y-1}{{coth} y-{coth} x}\)