Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 2nd Year Physics Study Material 16th Lesson Communication Systems Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 2nd Year Physics Study Material 16th Lesson Communication Systems
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the basic blocks of a communication system? [TS June ’15]
Answer:
The basic blocks of a communication system are
- Transmitter
- Communication channel
- Receiver.
Question 2.
What is “world wide web” (www)? [IMP]
Answer:
It is an encyclopedia of knowledge accessible to everyone round the clock throughout year with the help of computer connectivity.
Question 3.
Mention the frequency range of speech signals.
Answer:
Frequency range of speech signals is 300 Hz to 3100 Hz.
Question 4.
What is sky wave propagation? (IMP)[AP May ’16; June ’15]
Answer:
In the frequency range from a few MHz upto about 30 MHz, long distance communication can be achieved by the ionospheric reflection of radio waves back towards the earth. This mode of propagation is called sky wave pro-pagation and it is used by short wave broadcast services.
Question 5.
Mention the various parts of the ionosphere? [TS May ’16]
Answer:
Parts of ionosphere are
- D – Layer at a height of 65 to 75 km from ground.
- E – Layer at a height of nearly 100 km.
- F1 – Layer at a height of 170 to 190 km.
- F2 – Layer at a height of 250 to 400 km.
Note : F1 and F2 will merge during night.
![]()
Question 6.
Define modulation. Why is it necessary? [AP Mar. 18, 17, 16, 14; May 17, 14; TS Mar. 19, 16, 15, May 18, 17]
Answer:
Modulation :
The process of combining audio frequency signal with high frequency signal is called modulation. Modulation is necessary for the following reasons.
- to reduce the size of antenna.
- to increase the effective power radiated by antenna.
- to avoid mixing up of signals from different transmitters.
Question 7.
Mention the basic methods of modulation [AP Mar. 19. 16; TS Mar.’ 18, ’17, ’15]
Answer:
The basic methods of modulation are :
a) Amplitude modulation
b) Frequency modulation and
c) Phase modulation.
Question 8.
Which type of communication is employed in mobile phones? [AP May ’18, Mar. ’15]
Answer:
Space wave communication is employed in mobile phones.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Draw the block diagram of a generalized communication system and explain it briefly.
Answer:
The block diagram of a generalized communication system are as shown. It consists of the following three parts.
- Transmitter
- Communication channel and
- Receiver.
In this system, the transmitter and receiver are located at two different places and the channel is the physical medium that connects them depending upon the type of communication system. A channel may be in the form of wires (or) cables connecting the transmitter and the receiver, or it may be wireless.
Using the transmitter, the original message is converted into a form so that it can be transmitted over the communication channel. Hence it is called as a-message signal.
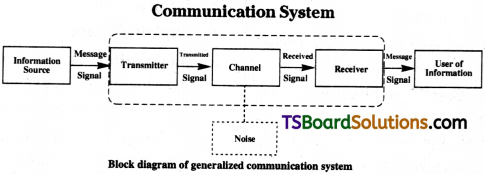
The uses of these three parts are :
1) Transmitter :
Purpose of transmitter is to convert the message signal produced by source into a form suitable for transmission through channel.
2) Channel :
Channel is used for transmission of signals. It may consist a medium like coaxial cable, optical fibre, (or) even space is used as channel in wireless communication where E.M waves are used.
3) Receiver :
Receiver will convert the signals received through channel into a recognisable form of the original message signal.
![]()
Question 2.
What is a ground wave? When is it used for communication?
Answer:
Ground wave :
In A.M. broadcasting ground based vertical metallic towers called antennas are used for transmission. For such antennas ground has strong influence on transmission. Near transmitting antennas energy of E.M wave is high. They have strong influence on propagation of signals along the ground surface. A strong E.M. wave near antenna will induce current on surface of ground over which it passes. So E.M waves slides along surface of ground.
For ground wave propagation attenuation on surface of earth is high. The magnitude of attenuation is proportional to frequency. Due to very high energy absorption of ground.
The ground wave propagation is limited to few kilometers from transmitting antenna.
Question 3.
What are sky waves? Explain sky wave propagation, briefly.
Answer:
Sky waves :
The electromagnetic waves which suffers reflection of ionosphere and reaches earth are called sky waves.
Sky wave propagation :
Electromagnetic waves with in the range of 30 to 40 MHz are reflected by ionosphere. The degree of ioni-sation varies with height above ground. Due to ionospheric reflection long range com-munication is possible with sky waves. Because these reflected waves reach earth at a longer distance. Short wave broadcast for long distance is possible with sky waves. Generally E.M waves with in the frequency range of 3 to 30 MHz are highly suitable for sky wave propagation. E.M waves of higher frequencies i.e., frequency > 30 MHz will penetrate ionosphere. Hence sky wave propagation is not possible with high frequency electro magnetic waves.
Question 4.
What is space wave communication? Explain.
Answer:
Space wave :
A space wave will travel from transmitting antenna to receiver in the form of straight lines. Space waves will obey line of sight properties.
Space wave propagation :
This type of propagation of E.M waves is called space wave propagation.
Space wave propagation is mainly used in television transmission. Due to curvature of earth range of space wave propagation is limited to certain distance only. Range depends on height of the antenna. Let height of transmitting antenna is ‘hT’ and radius of earth is ‘R’ the distance upto which signals will reach with LOS (hne-of-sight) properties is dr = \(\sqrt{2Rh_T}\). If receiving antenna is at a height hR then also distance dr upto which signals can be reached with LOS properties will increase. In this case dr = \(\sqrt{2Rh_T}+\sqrt{2Rh_R}\).
Question 5.
What do you understand by modulation? Explain the need for modulation.
Answer:
Modulation :
The process of super imposing a low frequency signal onto a high frequency carrier wave is known as modulation.
Modulation is necessary for long range transmission of signals.
Modulation is a very essential part of communication. Transmission of low frequency of voice signals (frequency range 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz) to longer distances is not possible because energy associated with low frequency signals is less.
So our voice signals after converting into electrical signals must be superposed on to a high frequency signal called carrier wave. Generally frequency of carrier wave is high. This will help for efficient transmis¬sion and reception. Modulation is necessary for the following reasons,
- To reduce the size of antenna for E.M. waves to be transmitted as antenna is necessary.
- To increase effective power radiation by transmitter.
- To avoid mixing up of signals from different transmitters.
To obtain the above advantages we are using modulation techniques where a low frequency signal is superposed on a high requency carrier wave.
![]()
Question 6.
What should be the size of the antenna or aerial? How the power radiated is related to length of the antenna and wavelength?
Answer:
Antenna and its size :
It is a must for every transmitter to have an antenna. Without antenna, it is not possible to radiate electrical energy output of transmitter into space in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
Antenna size must be comparable to wavelength of the signal to be transmitted.
To transmit all information contained in a signal without any loss in quality the minimum size of antenna must be at least \(\frac{\lambda}{4}\).
For good transmission output power of transmitter must be high.
Relation between length of antenna ‘l’ and wavelength ‘ λ’ and power radiated is
Power radiated ∝ (\(\frac{1}{\lambda}\))²
Question 7.
Explain amplitude modulation.
Answer:
Amplitude modulation (A.M.) :
In amplitude modulation (A.M.) the amplitude of carrier wave is varied in accordance with the voice signal superimposing on it.
Theory :
Let time varying carrier wave is c(t) = Ac sin ωct
Time varying modulating wave is m(t) = Am sin ωmt
when these two waves are superposed modulated wave is given by
cm(t) = (Ac + Am sin ωt) sin ωct
Because modulating wave changes only amplitude of carrier wave but not its frequencies
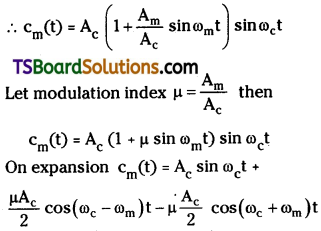
is the modulated wave. Where (ωc – ωm) and (ωc + ωm) are lower and upper side frequencies. Production of amplitude modulated wave.
Question 8.
How can an amplitude modulated wave be generated?
Answer:
The block diagram to produce amplitude modulated wave is as shown. Here modulating signal Am sin ωmt is mixed with a carrier signal Ac sin ωct in a square law device.
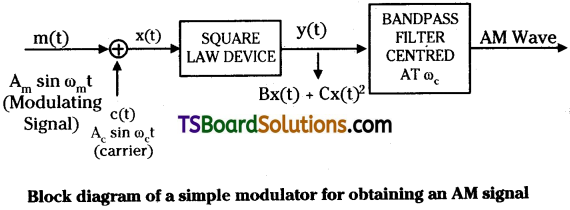
The output of square law device y(t) = B x (t) + Cx²t
Where B and C are constants.
∴ y(t) = BAm sin ωmt + BAc sin ωct + C (Am sin ωmt + Ac sin ωct)² …………… (1)
By using trigonometric relations (1)
sin²A = (1 – cos 2A) / 2
and (2) sin A sin B = \(\frac{1}{2}\) [cos (A – B) – cos (A + B)] equation (1) can be written as
y(t) = BAmsin ωmt + BAc sin ωct
+ C\(\frac{\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{m}}^2}{2}\) + A²c – \(\frac{c\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{m}}^2}{2}\) cos 2ωmt – cos 2ωmt
\(\frac{C\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{c}}^2}{2}\) cosωct + cAmAccos(ωc – ωm
CAmAc cos(ωc
This signal is passed through a b filter which rejects the D.C compc sinusoidal frequencies ωm , 2ωm a, ailows the frequencies ωc, ωc ωm + ωm at the out put side. This me signal is transmitted through ante
In this way amplitude modulat is produced.
![]()
Question 9.
How can an amplitude modulated wave be detected?
Answer:
The block diagram of amplitude modulated wave detector is as shown.
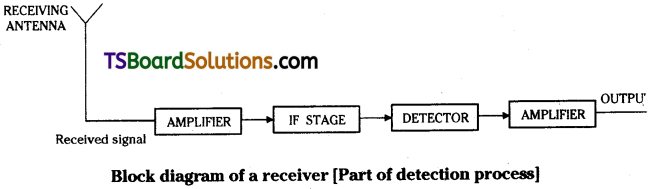
The receiving antenna will collect the amplitude modulated waves from space. These are passed through an amplifier to increase strength of signals.
These signals are passed through intermediate frequency stage (I.F. stage) to frequency of carrier.
For recovery of original massage signal m(t) with angular frequency ωm the modulated signal is passed detector which consists (1) a rectifier where lower half (- ve half) p modulated signals is eliminated. (2) Later it was sent through envelope detector to recive the original signal.
This signal is passed through a amplifier and finally signal with sufficient strength is going to a microphone to convert electrical signals into audio signals.