Students must practice these Maths 1A Important Questions TS Inter 1st Year Maths 1A Matrices Important Questions Very Short Answer Type to help strengthen their preparations for exams.
TS Inter 1st Year Maths 1A Matrices Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll}
1 & 2 \\
3 & 4
\end{array}\right]\), B = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll}
3 & 8 \\
7 & 2
\end{array}\right]\) and 2X + A = B, then find X. [Mar. 15 (AP); Mar. 13, 11; May 12]
Answer:
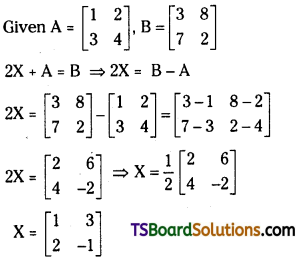
![]()
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
3 & 2 & -1 \\
2 & -2 & 0 \\
1 & 3 & 1
\end{array}\right]\), B = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
-3 & -1 & 0 \\
2 & 1 & 3 \\
4 & -1 & 2
\end{array}\right]\) and X = A + B then find X. [Mar. 17 (TS)]
Answer:
\(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
0 & 1 & -1 \\
4 & -1 & 3 \\
5 & 2 & 3
\end{array}\right]\)
Question 2.
If \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
x-3 & 2 y-8 \\
z+2 & 6
\end{array}\right]\) = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
5 & 2 \\
-2 & a-4
\end{array}\right]\), then find the values of x, y, z and a. [May 14, 06 Mar. 19(AP)]
Answer:
Given \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
x-3 & 2 y-8 \\
z+2 & 6
\end{array}\right]\) = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
5 & 2 \\
-2 & a-4
\end{array}\right]\)
From the equality of matrices,
x – 3 = 5
⇒ x = 8
2y – 8 = 2
2y = 10
y=5
z + 2 = – 2
z = – 4
a – 4 = 6
a = 10
∴ x = 8, y = 5, z = – 4, a = 10
If \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
x-1 & 2 & 5-y \\
0 & z-1 & 7 \\
1 & 0 & a-5
\end{array}\right]\) = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
1 & 2 & 3 \\
0 & 4 & 7 \\
1 & 0 & 0
\end{array}\right]\) then find the values of x, y, z and ‘a’.
Answer:
2, 2, 5, 5
If \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
x-1 & 2 & y-5 \\
z & 0 & 2 \\
1 & -1 & 1+a
\end{array}\right]\) = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
1-x & 2 & -y \\
2 & 0 & 2 \\
1 & -1 & 1
\end{array}\right]\) then find the values of x, y, z and ‘a’.
Answer:
1, \(\frac{5}{2}\), 2, 0
![]()
Question 3.
Find the trace of \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & 3 & -5 \\
2 & -1 & 5 \\
2 & 0 & 1
\end{array}\right]\).
Answer:
Let A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & 3 & -5 \\
2 & -1 & 5 \\
2 & 0 & 1
\end{array}\right]\)
∴ Tra A = 1 – 1 + 1 = 1
The elements of the principal diagonal = 1, – 1, 1
Fin the area of A if A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
1 & 2 & -1 / 2 \\
0 & -1 & 2 \\
-1 / 2 & 2 & 1
\end{array}\right]\)
Answer:
1
Question 4.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
1 & 2 & 3 \\
3 & 2 & 1
\end{array}\right]\) and B = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
3 & 2 & 1 \\
1 & 2 & 3
\end{array}\right]\), find 3B – 2A. [Mar, 19 (TS); Mar. 12]
Answer:
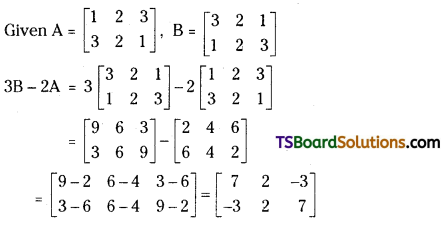
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
0 & 1 & 2 \\
2 & 3 & 4 \\
4 & 5 & -6
\end{array}\right]\) and B = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
-1 & 2 & 3 \\
0 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & -1
\end{array}\right]\) find B – A and 4A – 5B
Answer:
\(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
-1 & 1 & 1 \\
-2 & -2 & -4 \\
-4 & -5 & -5
\end{array}\right],\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
5 & -6 & -7 \\
8 & 7 & 16 \\
16 & 20 & -19
\end{array}\right]\)
![]()
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
0 & 1 & 2 \\
2 & 3 & 4 \\
4 & 5 & 6
\end{array}\right]\) and B = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
1 & -2 & 0 \\
0 & 1 & -1 \\
-1 & 0 & 3
\end{array}\right]\) find A – B and 4B – 3A
Answer:
\(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
-1 & 3 & 2 \\
2 & 2 & 5 \\
5 & 5 & 3
\end{array}\right],\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
4 & -11 & -6 \\
-6 & -5 & -16 \\
-16 & -15 & -6
\end{array}\right]\)
Question 5.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & -2 & 3 \\
2 & 3 & -1 \\
-3 & 1 & 2
\end{array}\right]\) and B = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
1 & 0 & 2 \\
0 & 1 & 2 \\
1 & 2 & 0
\end{array}\right]\) then examine whether A and B commute with respect to multiplication of matrices. [Nov, 98]
Answer:
Given A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & -2 & 3 \\
2 & 3 & -1 \\
-3 & 1 & 2
\end{array}\right]\), B = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
1 & 0 & 2 \\
0 & 1 & 2 \\
1 & 2 & 0
\end{array}\right]\)
Both A and B are square matrices of order 3.
Hence both AB and BA are defined and are matrices of order 3.
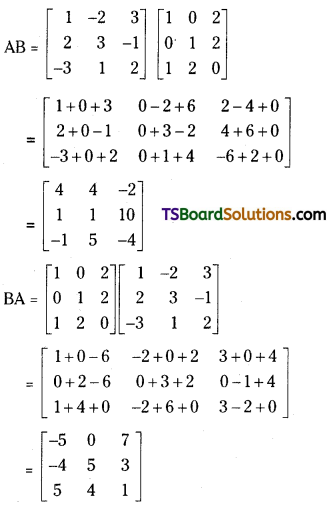
which shows that AB ≠ BA
Therefore A and B do not commute with respect to multiplication of matrices.
![]()
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & -2 & 3 \\
-4 & 2 & 5
\end{array}\right]\) and B = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll}
2 & 3 \\
4 & 5 \\
2 & 1
\end{array}\right]\) do AB and BA exist ? If they exist find them. Do A and B commute with respect to multiplication.
Answer:
\(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
0 & -4 \\
10 & 3
\end{array}\right]\), \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
-10 & 2 & 21 \\
-16 & 2 & 37 \\
-2 & -2 & 11
\end{array}\right]\) & AB ≠BA
Question 6.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
\mathbf{i} & 0 \\
0 & -\mathbf{i}
\end{array}\right]\), then show that A2 = – 1. [Mar. 16 (AP), 08]
Answer:
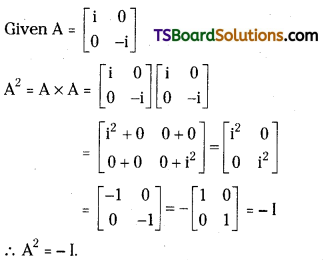
Find A2 where A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
4 & 2 \\
-1 & 1
\end{array}\right]\).
Answer:
\(\left[\begin{array}{rr}
14 & 10 \\
-5 & -1
\end{array}\right]\)
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll}
\mathbf{i} & \mathbf{0} \\
\mathbf{0} & \mathbf{i}
\end{array}\right]\), find A2.
Answer:
\(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-1 & 0 \\
0 & -1
\end{array}\right]\)
![]()
Question 7.
Find \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
\mathbf{0} & \mathbf{c} & -\mathbf{b} \\
-\mathbf{c} & \mathbf{0} & \mathbf{a} \\
\mathbf{b} & -\mathbf{a} & \mathbf{0}
\end{array}\right]\) \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
\mathbf{a}^2 & \mathbf{a b} & \mathbf{a c} \\
\mathbf{a b} & \mathbf{b}^2 & \mathbf{b c} \\
\mathbf{a c} & \mathbf{b c} & \mathbf{c}^2
\end{array}\right]\) [Mar. 96; May 91]
Answer:
Let A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
\mathbf{0} & \mathbf{c} & -\mathbf{b} \\
-\mathbf{c} & \mathbf{0} & \mathbf{a} \\
\mathbf{b} & -\mathbf{a} & \mathbf{0}
\end{array}\right]\), B = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
\mathbf{a}^2 & \mathbf{a b} & \mathbf{a c} \\
\mathbf{a b} & \mathbf{b}^2 & \mathbf{b c} \\
\mathbf{a c} & \mathbf{b c} & \mathbf{c}^2
\end{array}\right]\)
The order of matrix, A is 3 × 3
The order of matrix, B is 3 × 3
The no. of columns in A = The no. of rows in B.
∴ AB is defined.
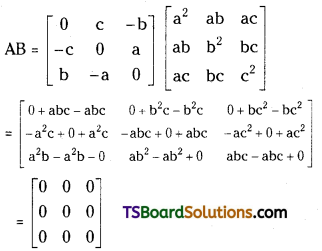
Question 8.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
2 & 4 \\
-1 & k
\end{array}\right]\) and A2 = 0, then find the value of k. [Mar. 17 (AP), 14, 05, May. 11, Mar. 08(TS)]
Answer:
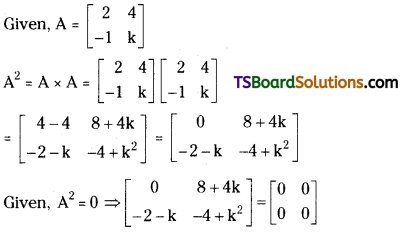
From equality of matrices, – 2 – k = 0 ⇒ k = – 2
![]()
Question 9.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
3 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 3 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 3
\end{array}\right]\) then find A4. [May 01]
Answer:
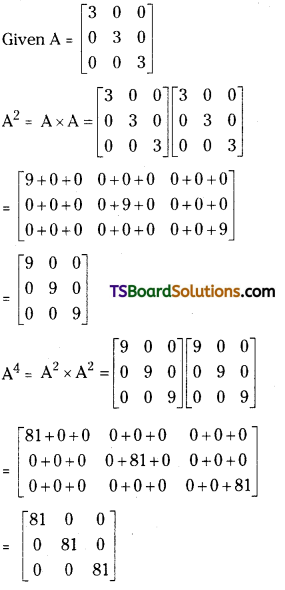
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
1 & 1 & 3 \\
5 & 2 & 6 \\
-2 & -1 & -3
\end{array}\right]\) then find A3.
Answer:
\(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
0 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0
\end{array}\right]\)
Question 10.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
1 & 4 & 7 \\
2 & 5 & 8
\end{array}\right]\) and B = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
-3 & 4 & 0 \\
4 & -2 & -1
\end{array}\right]\), then show that (A + B)’ = A’ + B’ [May. 09]
Answer:
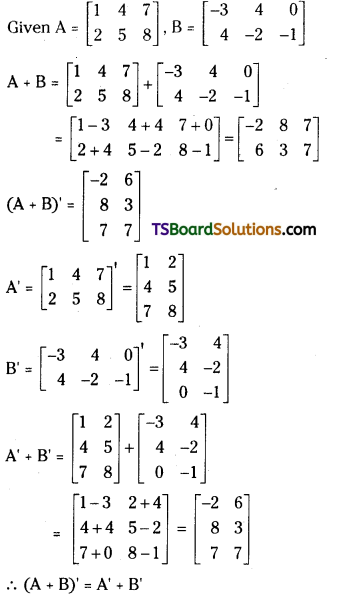
![]()
Question 11.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
-2 & 1 & 0 \\
3 & 4 & -5
\end{array}\right]\) and B = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
1 & 2 \\
4 & 3 \\
-1 & 5
\end{array}\right]\), then find A + B’. [May. 08]
Answer:
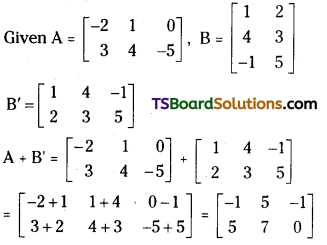
Question 12.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
2 & -1 & 2 \\
1 & 3 & -4
\end{array}\right]\) and B = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
1 & -2 \\
-3 & 0 \\
5 & 4
\end{array}\right]\), then verify that (AB)’ = B’A’ [Mar. 13]
Answer:
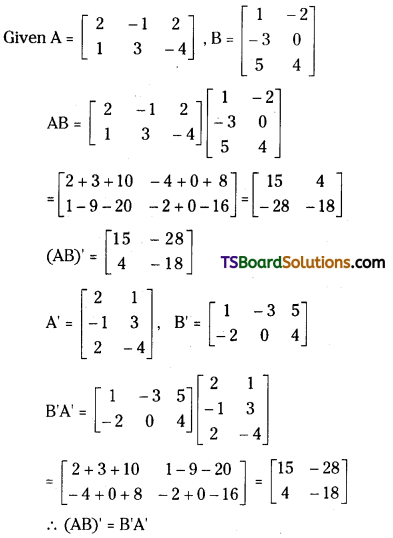
![]()
Question 13.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
2 & 0 & 1 \\
-1 & 1 & 5
\end{array}\right]\) and B = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
-1 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 1 & -2
\end{array}\right]\), then find (AB)’. [Mar. 19 (TS); May. 12]
Answer:
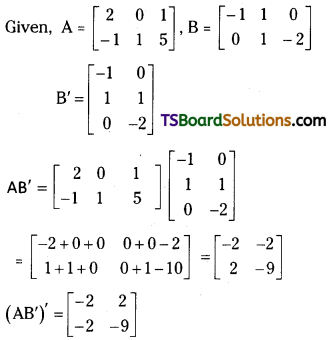
Question 14.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr}
-2 & 1 \\
5 & 0 \\
-1 & 4
\end{array}\right]\) and B = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
-2 & 3 & 1 \\
4 & 0 & 2
\end{array}\right]\) then find 2A + B’ and 3B’ – A. [Mar. 10]
Answer:
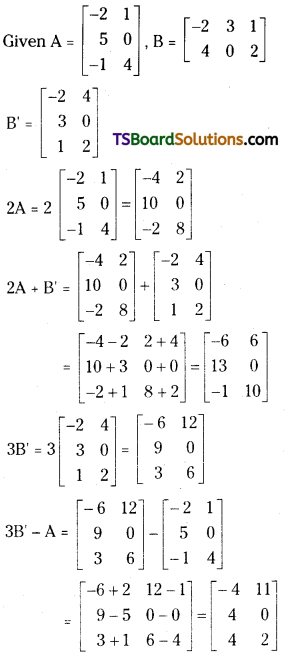
![]()
Question 15.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr}
2 & -4 \\
-5 & 3
\end{array}\right]\), then find A + A’ and AA’ [May 15 (AP); May 07, 02]
Answer:
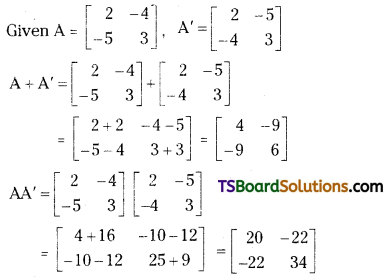
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-1 & 2 \\
0 & 1
\end{array}\right]\) then find AA’. Do A and A’ commute with respect to multiplication of matrices ? [Mar. 17(TS)]
Answer:
AA’ = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll}
5 & 2 \\
2 & 1
\end{array}\right]\), A’A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
1 & -2 \\
-2 & 5
\end{array}\right]\); AA’ ≠ A’A
Question 16.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
0 & 4 & -2 \\
-4 & 0 & 8 \\
2 & -8 & x
\end{array}\right]\) is a skew symmetric matrix, find the value of x. [Mar. 08]
Answer:
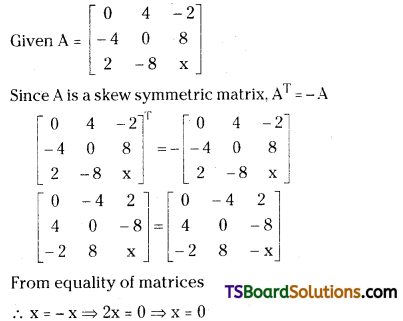
Question 17.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
-1 & 2 & 3 \\
2 & 5 & 6 \\
3 & x & 7
\end{array}\right]\) is a symmetric matrix, then find x. [Mar. 16 (AP), 05, 03, May. 15 (TS)]
Answer:

From equality of matrices, x = 6.
![]()
Question 18.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
0 & 2 & 1 \\
-2 & 0 & -2 \\
-1 & x & 0
\end{array}\right]\) is a skew symmetric matrix, then find x. [May. 14, 13, 11]
Answer:
A matrix A is said to be skew symmetric if,

From the equality of matrices, x = 2.
∴ x = 2
Question 19.
Is \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
0 & 1 & 4 \\
-1 & 0 & 7 \\
-4 & -7 & 0
\end{array}\right]\) symmetric or skew symmetric? [Mar. 09]
Answer:
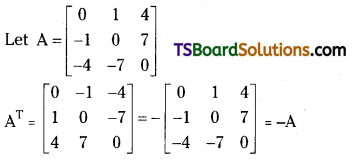
∴ A is a skew symmetric matrix since AT = – A.
Question 20.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
\cos \alpha & \sin \alpha \\
-\sin \alpha & \cos \alpha
\end{array}\right]\), show that AA’ = A’A = I. [Mar. 07]
Answer:
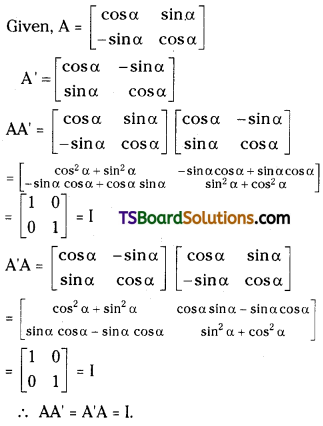
![]()
Question 21.
If ω is complex (non real) cube root of 1, then show that \(\left|\begin{array}{ccc}
1 & \omega & \omega^2 \\
\omega & \omega^2 & 1 \\
\omega^2 & 1 & \omega
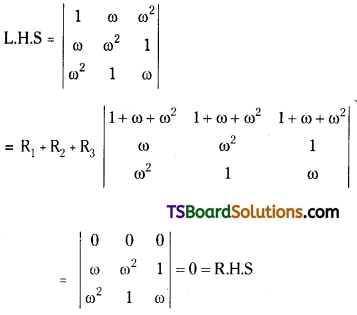
\end{array}\right|\) = 0 [Mar. 14, 11; May. 92]
Answer:
1, ω, ω2 are the cube roots of unity.
Then, 1 + ω + ω2 = 0, ω3 = 1.
Question 22.
Find the determinant of the matrix. [May. 95]
\(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
0 & 1 & 1 \\
1 & 0 & 1 \\
1 & 1 & 0
\end{array}\right]\)
Answer:
Let A = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
0 & 1 & 1 \\
1 & 0 & 1 \\
1 & 1 & 0
\end{array}\right]\)
det A = \(\left|\begin{array}{lll}
0 & 1 & 1 \\
1 & 0 & 1 \\
1 & 1 & 0
\end{array}\right|\) = 0(0 – 1) – 1 (0 – 1) + 1(1 – 0)
= 0(- 1) – 1 (- 1) + 1(1) = 0 + 1 + 1 = 2
Find the determinant of the matrix
\(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
\mathbf{a} & \mathbf{h} & \mathbf{g} \\
\mathbf{h} & \mathbf{b} & \mathbf{f} \\
\mathbf{g} & \mathbf{f} & \mathbf{c}
\end{array}\right]\).
Answer:
abc + 2fgh – af2 – bg2 – ch2
Find the determinant of the matrix
\(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
\mathbf{a} & \mathbf{b} & \mathbf{c} \\
\mathbf{b} & \mathbf{c} & \mathbf{a} \\
\mathbf{c} & \mathbf{a} & \mathbf{b}
\end{array}\right]\)
Answer:
3abc – a3 – b3 – c3
![]()
Question 23.
Find the determinant of the matrix \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
1^2 & 2^2 & 3^2 \\
2^2 & 3^2 & 4^2 \\
3^2 & 4^2 & 5^2
\end{array}\right]\). [Mar. 10]
Answer:
Let A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
1^2 & 2^2 & 3^2 \\
2^2 & 3^2 & 4^2 \\
3^2 & 4^2 & 5^2
\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
1 & 4 & 9 \\
4 & 9 & 16 \\
9 & 16 & 25
\end{array}\right]\)
det A = 1(225 – 256) – 4 (100 – 144) + 9 (64 – 81)
= – 31 + 176 – 153
= 176 – 184 = – 8.
Question 24.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & 0 & 0 \\
2 & 3 & 4 \\
5 & -6 & x
\end{array}\right]\) and det A = 45, then find x. [May 09, 03, 99, 96, Mar; 07, 03]
Answer:
Given A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr}
1 & 0 & 0 \\
2 & 3 & 4 \\
5 & -6 & \mathrm{x}
\end{array}\right]\) and det A = 45.
det A = 1 (3x + 24) – 0(2x – 20) + 0 (-12 – 15) = 3x + 24 – 0 + 0 = 3x + 24
Given, det A = 45 ⇒ 3x + 24 = 45 ⇒ 3x = 45 – 24 ⇒ 3x = 21 ⇒ x = 7.
Question 25.
Find the adjoint and inverse of the matrix \(\left[\begin{array}{rr}
2 & -3 \\
4 & 6
\end{array}\right]\). [Mar. 12]
Answer:
Let A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr}
2 & -3 \\
4 & 6
\end{array}\right]\)
Cofactor of 2 is A1 = + (6) = 6
Cofactor of 4 is A2 = – (- 3) = 3
Cofactor of – 3 is B1 = – (4) = – 4
Cofactor of 6 is B2 = + (2) = 2
∴ Cofactor matrix of A is B = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll}
\mathrm{A}_1 & \mathrm{~B}_1 \\
\mathrm{~A}_2 & \mathrm{~B}_2
\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
6 & -4 \\
3 & 2
\end{array}\right]\)
Adj A = B’ = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
6 & 3 \\
-4 & 2
\end{array}\right]\)
det A = ad – bc = 12 – (- 12) = 12 + 12 = 24 ≠ 0
∴ A is invertiable.
A-1 = \(\frac{{adj} A}{{det} A}=\frac{1}{24}\left[\begin{array}{rr}
6 & 3 \\
-4 & 2
\end{array}\right]\)
![]()
Find the adjoint and the Inverse of the matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
1 & 2 \\
3 & -5
\end{array}\right]\). [Mar. 18 (AP); May 06]
Answer:
\(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-5 & -2 \\
-3 & 1
\end{array}\right],\left[\begin{array}{cc}
\frac{5}{11} & \frac{2}{11} \\
\frac{3}{11} & \frac{-1}{11}
\end{array}\right]\)
Question 26.
Find the adjoint and inverse of the matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
\cos \alpha & -\sin \alpha \\
\sin \alpha & \cos \alpha
\end{array}\right]\) [Mar. 13, 09]
Answer:
Let A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}
\cos \alpha & -\sin \alpha \\
\sin \alpha & \cos \alpha
\end{array}\right]\)
Cofactor of cos α is A1 = + (cos α) = cos α
Cofactor of sin α is A2 = – (- sin α) = sin α
Cofactor of – sin α is B1 = – (sin α) = – sin α
Cofactor of cos α is B2 = + (cos α) = cos
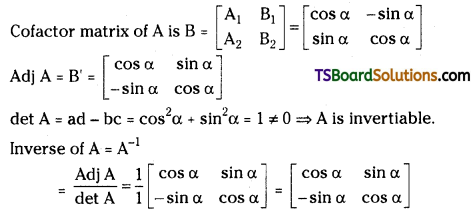
Question 27.
Find the rank of the matrix\(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
1 & 1 & 1 \\
1 & 1 & 1 \\
1 & 1 & 1
\end{array}\right]\). [Mar. 18 (TS); May 10; Mar. 08]
Answer:
Let A = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
1 & 1 & 1 \\
1 & 1 & 1 \\
1 & 1 & 1
\end{array}\right]\)
det A = 1(1 – 1) – 1(1 – 1) + 1 (1 – 1) = 0 – 0 + 0 = 0
Since det A = 0, Rank [A] ≠ 3
Now, \(\left[\begin{array}{ll}
1 & 1 \\
1 & 1
\end{array}\right]\) is a submatrix of A, whose determinant is 1 – 1 = 0 ∴ Rank [A] ≠ 2.
Now. [1] is a submatrix of A, whose determinant is 1 ≠ 0. ∴ Rank [A] = 1